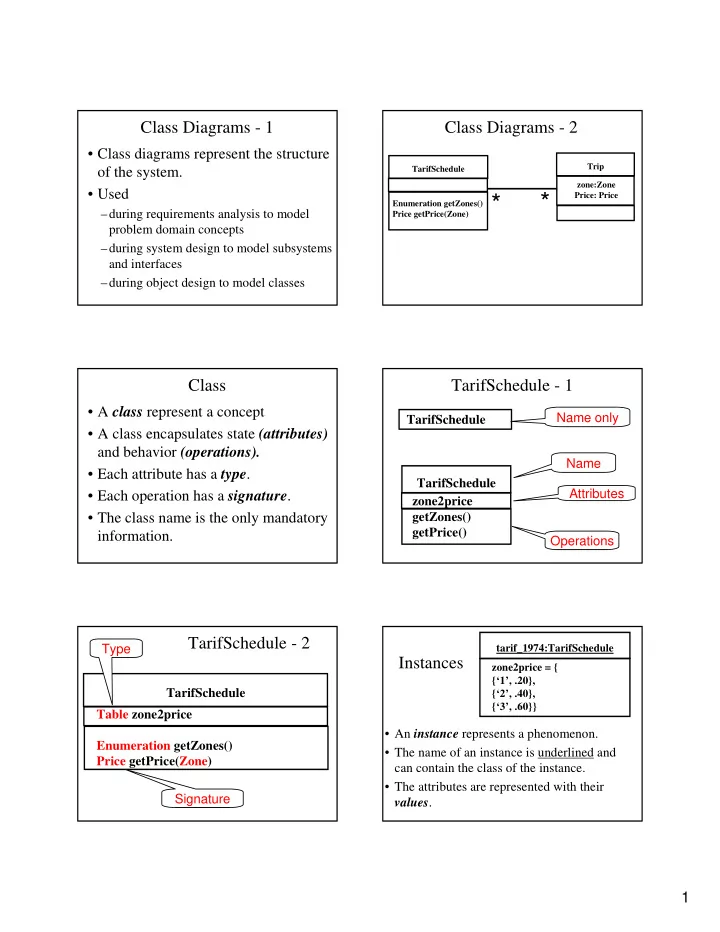

Class Diagrams - 1 Class Diagrams - 2 • Class diagrams represent the structure Trip TarifSchedule of the system. zone:Zone • Used * Price: Price * Enumeration getZones() –during requirements analysis to model Price getPrice(Zone) problem domain concepts –during system design to model subsystems and interfaces –during object design to model classes Class TarifSchedule - 1 • A class represent a concept Name only TarifSchedule • A class encapsulates state (attributes) and behavior (operations). Name • Each attribute has a type . TarifSchedule Attributes • Each operation has a signature . zone2price • The class name is the only mandatory getZones() getPrice() information. Operations TarifSchedule - 2 Type tarif_1974:TarifSchedule Instances zone2price = { {‘1’, .20}, TarifSchedule {‘2’, .40}, {‘3’, .60}} Table zone2price • An instance represents a phenomenon. Enumeration getZones() • The name of an instance is underlined and Price getPrice(Zone) can contain the class of the instance. • The attributes are represented with their Signature values . 1
Associations One-to-one association TarifSchedule City Country Trip Has-capital name:String zone:Zone name:String * Enumeration getZones() Price: Price * Price getPrice(Zone) • Associations denote relationships between classes. • The multiplicity of an association end denotes how many objects the source object can legitimately reference. One-to-many association From Problem Statement To Object Model • Problem Statement: A stock exchange lists Point Polygon many companies. Each company is uniquely * identified by a ticker symbol. A company x: Integer may be listed on more than one stock y: Integer draw() exchange. Company StockExchange Lists * * tickerSymbol To Java Code Converting many-to-many to many-to-one public class StockExchange { StockExchange * private ArrayList m_Company = new ArrayList(); Lists * tickerSymbol }; 1 public class Company Company { public int m_tickerSymbol; Qualifier private ArrayList m_StockExchange = new ArrayList(); }; 2
Aggregation - 1 Aggregation - 2 • An aggregation is a special case of • A solid diamond denotes composition , a association denoting a “consists of” hierarchy. strong form of aggregation where components • The aggregate is the parent class, the cannot exist without the aggregate. components are the children class. Exhaust system T icke tMach ine 1 0..2 Muffler Tailpipe 3 ZoneBut ton diameter diameter Inheritance Account Customer Bank * Amount • The children classes inherit the attributes * Has Balance() Name and operations of the parent class . Name Deposit() • Inheritance simplifies the model by Withdraw() CustomerId() eliminating redundancy. Checking Mortgage Savings But ton Account Account Account Withdraw() Withdraw() Withdraw() Cance lBut ton ZoneBut ton Packages - 1 Packages - 2 • A package is a UML mechanism for Dispatcher organizing elements into groups Interface (usually not an application domain concept) Incident Notification • Packages are the basic grouping Management construct with which you may • A complex system can be decomposed organize UML models to increase into subsystems, where each their readability. subsystem is modeled as a package 3
Recommend
More recommend