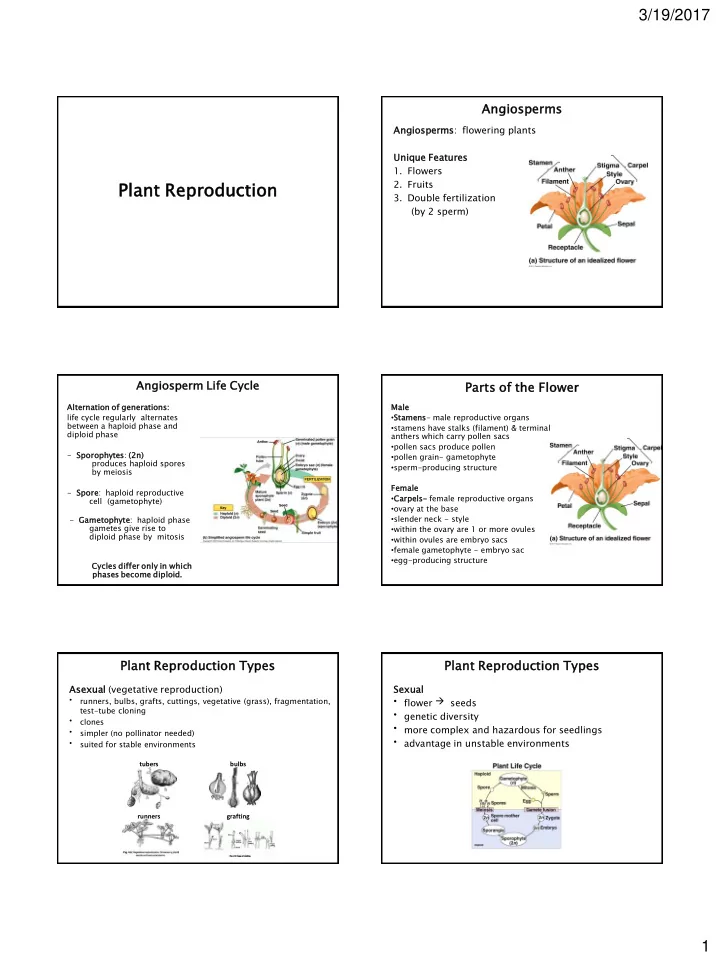

3/19/2017 Angios ospe perm rms Angio iosp sperm rms: flowering plants Uniqu ique e Featu tures res 1. Flowers Plant nt Reprodu oduction ction 2. Fruits 3. Double fertilization (by 2 sperm) Angiospe sperm rm Life Cycle Parts s of the Flowe wer Altern rnat ation on of generat ration ons: s: Male life cycle regularly alternates • Stamens- male reproductive organs between a haploid phase and • stamens have stalks (filament) & terminal diploid phase anthers which carry pollen sacs • pollen sacs produce pollen - Sporoph ophytes: (2n) • pollen grain- gametophyte produces haploid spores • sperm-producing structure by meiosis Femal ale - Spore: haploid reproductive • Carpels- female reproductive organs cell (gametophyte) • ovary at the base • slender neck - style - Gametop ophyte: haploid phase gametes give rise to • within the ovary are 1 or more ovules diploid phase by mitosis • within ovules are embryo sacs • female gametophyte - embryo sac • egg-producing structure Cycles s differ r only in which phase ses s become diploi oid. Plant t Reproducti ction on Types Plant t Reproducti ction on Types Asexu exual (vegetative reproduction) Sexu xual • flower seeds • runners, bulbs, grafts, cuttings, vegetative (grass), fragmentation, test-tube cloning • genetic diversity • clones • more complex and hazardous for seedlings • simpler (no pollinator needed) • advantage in unstable environments • suited for stable environments tubers bulbs runners grafting 1
3/19/2017 Pollinatio ation Mechanism sms Prevent Self Pollinati tion on Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma • Stamen mens s & carpels pels may mature re at differen erent t times s • Self lf pollin inatio tion • Arranged so that animal pollinator won’t transfer pollen • Cross ss Pollin inatio tion from m anth thers ers to stigma ma of same e flower er • Maximizes genetic variation • Self lf-in incompa patib tibilit ility: plant rejects own pollen or closely related plant Fertilizatio ation Developm opment t of the Sporoph ophyte te (plant embryo) Double e fertilization 2 sperm from pollen 1 sperm fertilize zes egg - diploi oid zygot ote 1 sperm fuses with 2 polar r nuclei to form 3n endosp sperm rm endospe osperm rm - food tissue in seed - coconut milk - grains Seeds and Plant Embryo Seeds Seed offers: Matu ture re seed (dorma mant) t) • protection for embryo Low metabolic rate • • stored nutrients for growth Growth & development • of embryo suspended coytle tledo dons- “seed leaves” Resumes growth when • - first leaves of new environmental conditions plant suitable for germination 2
3/19/2017 Seed Dispers rsal al Seed Germinatio ation • Plants produce enormous numbers of seeds to Seeds take up water (imbibit bitio ion) • compensate for low survival rate triggers metabolic changes to begin growth • • Vast amount of genetic variation for natural selection root develops shoot emerges leaves • to screen expand & turn green (photosynthesis) • Co- evolution: flowers and pollinators Very hazardous time for plants • r-strategy K-strategy vulnerability to predators, parasites, wind • Seed Developme pment into a Plant Fruit Fruit it is a mature re ovary ry seeds develop from ovules wall of ovary thickens to form fruit fruits protect dormant seeds & aid in their dispersal 3
Recommend
More recommend