
Metagenomics
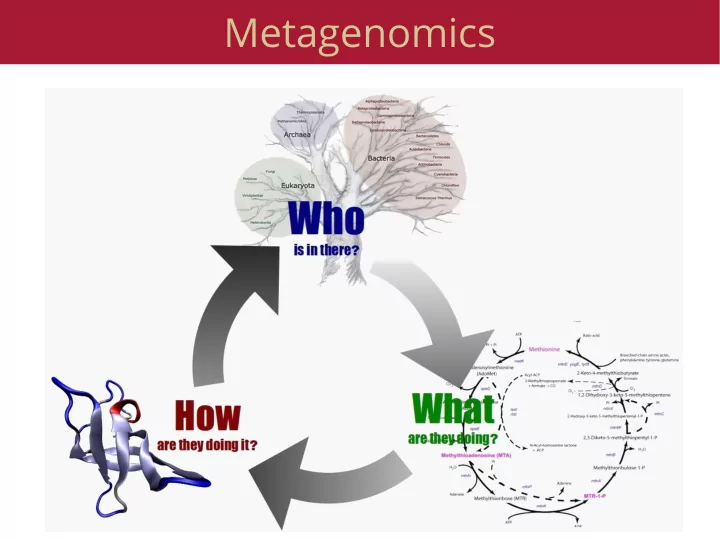
What is metagenomics ● Cloning genes from the environment, screening for function ● 16S sequencing ● Random community genomics ● Eukaryotic metagenomics
Screening from the environment ● Random fragments of DNA ● Clone into a vector – Low copy vectors – BACs – YACs
BACs Science Creative Quarterly
Screening from the environment ● Random fragments of DNA ● Clone into a vector – Low copy vectors – BACs – YACs ● Screen for a phenotype ● e.g. Diversa patents > 1,000 amylase genes Why did Diversa sequence whale-falls?
Screening from the environment ● Expression host? ● Pathway or single gene? ● Get what you select ● But remember … A selection is worth a thousand screens
16S sequencing ● Catalogs the bacteria that are present ● PCR amplify the 16S gene with standard primers ● Sequence the primers ● Compare to known databases
Ribosomes Ribosomes are made of proteins and RNA Prokaryotic ribosome: Large subunit: 50S 5S and 23S rRNA Small subunit: 30S 16S rRNA
30S Thermus aquaticus subunit Blue: protein Orange: rRNA
E. coli E. coli 16S rRNA 16S rRNA secondary secondary structure structure ● Highly conserved ● Base pairs = stems ● No pairing = loops
E. coli E. coli V7 V6 V5 16S rRNA 16S rRNA secondary secondary structure structure V8 V4 V9 V3 V1 Variable regions in Variable regions in the 16S rRNA. the 16S rRNA. V2 Vn – 9 regions forward/rev primers
16S Primers ● 27F – 1492R full length 1,465 base pairs ● 967F – 1046R V6 region 79 base pairs ● 1380F – 1510R V9 region 130 base pairs
Variable regions = Variable results! V1-V3 V1-V3 V3-V5 V3-V5 V6-V9 V6-V9
16S databases ● Greengenes – http://greengenes.lbl.gov/ – Gary Andersen, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory ● SILVA – ARB – http://www.arb-silva.de/ – Frank Oliver Gl öckner, MPI, Bremen, Germany ● VAMPS – http://vamps.mbl.edu/ – Mitch Sogin, Woods Hole, USA ● Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) – http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/ – James Cole, Michigan State University, USA
16S sequencing ● Cheap ● PCR bias ● Variable regions give ● Easy variable answers ● Portable ● Only tells you which organisms are present & abundance ● Does not explain much of the variance of the data What does 16S sequencing actually tell you?
What does 16S sequencing tell you?
What does 16S sequencing tell you?
What is metagenomics ● Cloning genes from the environment, screening for function ● 16S sequencing ● Random community genomics ● Eukaryotic metagenomics
16S sequencing is not good for functions
How much of the data? Topography of [fungi and] Study = bacteria on the skin 5,000 taxa 14 skin sites 10 people 3 skin types 5,000 variables The remainder of the variance (85.1%) is explained by a few taxa each Findley et al, Nature 2013 Each dimension only adds marginal doi: 10.1038/nature12171 information They don't explain the meaning of j-q
How much of the data? Nine biomes paper Variance: 1,040,665 reads total (from 45 samples) 30 subsystems 9 biomes 30 variables Fewer of the variables explain more of the data Dinsdale et al., Nature 2008 The variables are distinctive doi:10.1038/nature06810 for each environment
Shotgun sequencing (HiSeq) Movies courtesy Will Trimble, Argonne National Labs http://www.mcs.anl.gov/~trimble/flowcell/
16S sequencing (MiSeq) Movies courtesy Will Trimble, Argonne National Labs http://www.mcs.anl.gov/~trimble/flowcell/
Shotgun + 16S (HiSeq) Movies courtesy Will Trimble, Argonne National Labs http://www.mcs.anl.gov/~trimble/flowcell/
There is no 16S for viruses Rohwer and Edwards, 2002. The phage proteomic tree. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.16.4529-4535.2002
Random community genomics 200 liters water 5-500 g fresh fecal matter Concentrate and purify viruses or bacteria Extract nucleic acids DNA/RNA LASL Epifmuorescent Microscopy Sequence
How do you sequence the environment? • Extract DNA – Soil extraction kit – Water extraction kit • Create library – LASLs – fosmids • Sequence fragments
Linker-Amplifjed Shotgun Libraries (LASLs) Soil Extraction Kit This method Hydroshear produces high coverage libraries of over 1 million clones Blunt-ending d n d A i d i t - o n e u t n l B h e s o r d y H i s r k e n L f o g n i r a c a F g me f i a i l p m A r s t n o f n o i t from as little as 1 ng DNA Addition of Linkers Amplification of David Mead - Fragments Breitbart (2002) PNAS
Early Attempts at a Metagenomics Platform • http://phage.sdsu.edu/~rob/cgi-bin/remoteblast.cgi • Submit BLAST to local and remote databases – Local (as fast as possible) – NCBI (one search every 3 seconds) • Many concurrent searches – One search versus 1,000 searches • Parse data into tables for Excel – Access to taxonomy etc
Human-associated viruses • More bacteria than somatic cells by at least an order of magnitude • More phages than bacteria by an order of magnitude • Sample the bacteria in the intestine by sampling their phage
Most Viral DNA Sequences in Adult Human Feces are Unknown Phages Eukaryotic Viruses 6% Known 40% Unknown Phages 60% 94% Breitbart (2003) J. Bacteriol.
Abundance of viruses in twins Reyes et al, Nature 2010
Abundance of viruses in twins Microbial samples in guts don't change very much Reyes et al, Nature 2010
Abundance of viruses in twins Phage samples in guts change a lot Reyes et al, Nature 2010
Abundance of viruses in twins Microbial Phage Reyes et al, Nature 2010
Most Human RNA Viruses are Known Other Plant Unknown Viruses 8% 9% Other 26% Pepper Mild Known Mottle 92% Virus 65% Zhang (2006) PLoS Biology
Pepper Mild Mottle Virus (PMMV) • ssRNA virus; ≈6 kb genome • Related to T obacco Mosaic Virus • Infects members of Capsicum family • Widely distributed – spread through seeds • Fruits are small, malformed, mottled • Rod-shaped virions Viral particles in fecal sample TOBACCO MOSAIC VIRUS http://www.rothamsted.bbsrc.ac .uk/ppi/links/pplinks/virusems/
PMMV is common in Human Feces Fecal samples Extract total RNA RT-PCR for PMMV S S S S S S S S S PMM 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 V San Diego : 78% people are positive Singapore : 67% people are positive 10-50 fold increase in feces compared to food 10 6 -10 9 PMMV copies per gram dry weight of feces
Which Foods Contain PMMV? Indian PEPPERS NOT FOUND IN FRESH Chili sauces Chili powder curry Pork noodle red chili Chicken rice Chinese food Hong Kong chili sauce Hong Kong green chili Vegetarian chili
PMMV is Present at High Concentrations in Raw Sewage and Treated Wastewater Rosario et al. AEM (2009)
Difgerent PMMV families Lib3 Contig[0064] Lib3 Contig[0064] Lib2 Contig[0070] Lib2 Contig[0070] AB084456.1 AB084456.1 I I AB062049.1 AB062049.1 AB062051.1 AB062051.1 AF103778 AF103778 AY632863.1 AY632863.1 AB119482.1 AB119482.1 AJ429088.1 AJ429088.1 AB062054.1 AB062054.1 CoatProtein CoatProtein AB069853.1 AB069853.1 II II AB062052.1 AB062052.1 • Diverse populations AB000709.2 AB000709.2 M87827.1 M87827.1 AJ429087.1 AJ429087.1 AF525080.1 AF525080.1 Lib2_2217 Lib2_2217 • Differences between individuals Lib3_Contig[0494] Lib3_Contig[0494] Lib3_Contig[1213] Lib3_Contig[1213] Lib2_Contig[0458] Lib2_Contig[0458] Lib2_Contig[1099] Lib2_Contig[1099] and over time Lib3_65 Lib3_65 Lib3_Contig[0273] Lib3_Contig[0273] Lib3_Contig[0078] Lib3_Contig[0078] Lib3_Contig[0863] Lib3_Contig[0863] AJ308228.1 AJ308228.1 III III AB062053.1 AB062053.1 Same AJ429089.1 AJ429089.1 X72587.1 X72587.1 Lib2_1377 Lib2_1377 Library 1 person 6 Lib2_2914 Lib2_2914 Lib1_2299 Lib1_2299 Lib3_928 Lib3_928 months Lib2_1656 Lib2_1656 Lib2_2549 Lib2_2549 Library 2 Lib3_462 Lib3_462 Lib2_492 Lib2_492 apart Lib3_Contig[0655] Lib3_Contig[0655] Lib2_133 Lib2_133 Lib1_Contig[0253] Lib1_Contig[0253] Library 3 Lib1_Contig[0123] Lib1_Contig[0123] Lib1_Contig[0279] Lib1_Contig[0279] Lib1_Contig[0107 Lib1_Contig[0107 IV IV ] ] Lib1_Contig[0052 Lib1_Contig[0052 ] ] Lib1_Contig[0004 Lib1_Contig[0004 ] ] Lib2_Contig[0995] Lib2_Contig[0995] Lib1_Contig[0009] Lib1_Contig[0009] Lib1_Contig[0166] Lib1_Contig[0166] Lib1_Contig[0657] Lib1_Contig[0657] Lib1_1449 Lib1_1449 Lib1_2211 Lib1_2211 Lib1_Contig[0029] Lib1_Contig[0029] Lib1_1733 Lib1_1733 Lib1_Contig[0076] Lib1_Contig[0076] Lib1_1168 Lib1_1168 Lib1_Contig[0261] Lib1_Contig[0261] Lib1_2361 Lib1_2361 Lib2 1468 Lib2 1468 Lib2 Contig[0031] Lib2 Contig[0031] V V Lib2 Contig[1202] Lib2 Contig[1202] Lib1_Contig[0005] Lib1_Contig[0005] Lib1_Contig[0558] Lib1_Contig[0558] AF103776.1 AF103776.1 AB062050.1 AB062050.1 0.1 0.1
Human-fecal borne PMMV can infect plants • Spread of infection to Hungarian Fecal sample wax pepper evident within 1 week Viral concentrate • Infected leaf was positive by RT-PCR for PMMV Plant leaf inoculation • Animals may serve as vectors for plant viruses Total RNA PMMV RT-PCR Control Infected leaf
Recommend
More recommend