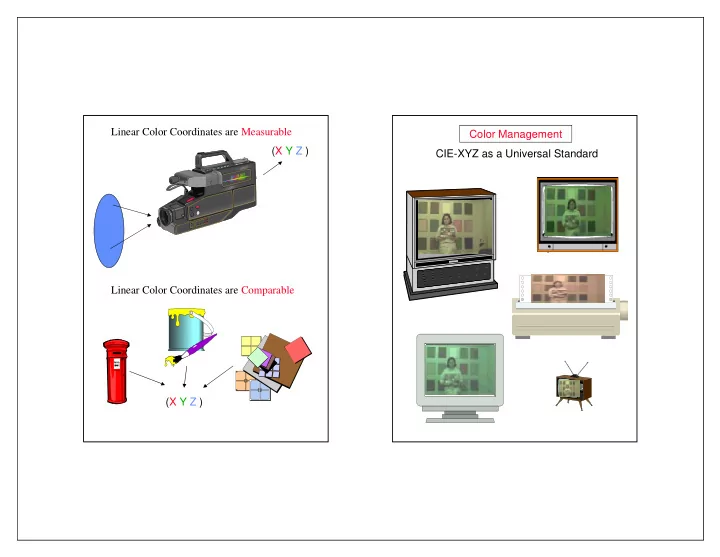

Linear Color Coordinates are Measurable Color Management (X Y Z ) CIE-XYZ as a Universal Standard Linear Color Coordinates are Comparable (X Y Z )
Chromaticity defined in Polar Coordinates Relationship between HSV and XYZ Given a reference white. Y vs V : Dominant Wavelength - wavelength of the spectral color Luminance (intensity) vs Brightness (Lightness) which added to the reference white, produces the given color. Complementary Wavelength - wavelength of the spectral color which added to the given color, produces the reference white. Excitation Purity - the ratio of the lengths between the given color and reference white and between the dominant wavelength light and reference white. Ranges between 0 .. 1. Luminance ∆ I2 I2 0.8 ∆ I1 I1 Dominant/complimentary Wavelength 0.6 I1 < I2, ∆ I1 = ∆ I2 purity Equal intensity steps: 0.4 reference white 0.2 Equal brightness steps: 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8
Munsell lines of constant Hue and Chroma. Weber’s Law 0.5 0.4 In general, ∆ I needed for just noticable difference (JND) over background I was found to satisfy: 0.3 y ∆ I = constant 0.2 I 0.1 ( I is intensity, ∆ I is change in intensity) Value =1/ 0 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 Weber’s Law: x MacAdam Ellipses of JND (Just Noticable difference) Perceived Brightness = log ( I ) 0.8 Perceived Brightness 0.6 y (Ellipses 0.4 scaled by 10) 0.2 Intensity 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 x
CIE- UVW Coordinates Munsell lines of constant hue and chroma plotted in CIE-uv coordinates: The transformation from XYZ space to perceptual space is Non Linear : 0.4 Linear approximation defined by CIE: 0.3 CIE Uniform Chromaticity Scale (UCS) : v 2 U = X 0.2 3 V = Y 0.1 Value =1/ W = -X + 3Y + Z 2 0 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 u U 0.66 0 0 X = 0 1 0 V Y W -0.5 1.5 0.5 Z CIE-uv Chromaticity Coordinates: 4x u = -2x + 12y + 3 6y v = -2x + 12y + 3
Munsell lines of constant hue and chroma Perceptual Color Spaces plotted in CIE- L * u * v * Coordinates: The transformation from XYZ space to perceptual 100 Value =5/ space is Non Linear : 50 CIE- L * a * b * Coordinates 0 v * a * = 500 [ (X/X 0 ) 1/3 - (Y/Y 0 ) 1/3 ] -50 b * = 200 [ (X/X 0 ) 1/3 - (Z/Z 0 ) 1/3 ] 116(Y/Y 0 ) 1/3 - 16 for Y/Y 0 > 0.01 -100 L * = 903(Y/Y 0 ) otherwise -150 -150 -100 -50 0 50 100 150 200 X 0 Y 0 Z 0 = coordinates of reference white u * MacAdam Ellipses of JND plotted in CIE- L * u * v * Coordinates CIE- L * u * v * Coordinates: u * = 13 L * (u’-u 0 ’) 100 v * = 13 L * (1.5v’-v 0 ’) 50 116(Y/Y 0 ) 1/3 - 16 for Y/Y 0 > 0.01 L * = 0 v * 903(Y/Y 0 ) otherwise -50 u 0 v 0 Y 0 = coordinates of reference white u‘ = u -100 v‘ = 1.5 v -150 -150 -100 -50 0 50 100 150 200 u *
Measuring Color Differences Image Retrieval - Image Database ∆ e 2 = ∆ L * 2 + ∆ a * 2 + ∆ b * 2 ∆ e 2 = ∆ L * 2 + ∆ u * 2 + ∆ v * 2 ∆ e = 3 visually indistiguishable ∆ e = 5 acceptable error (most printers) ∆ e = 10 bad ∆ e = 15 unacceptable Luminance ∆ I2 I2 ∆ I1 I1 Distances should be measured in Perceptual Color space. error for ∆ I1 : ∆ e = 37.36 error for ∆ I2 : ∆ e = 4.64
Opponent Colors Why Opponent process ? A: Efficient Encoding. Ewald Hering (1905) - Pure colors R G B Y. No such colors greenish-red, yellowish-blue Cone Spectral Sensitivity 1 S M L Boynton & Gordon (1965) - With R G B Y can categorize all visible hues. Relative sensitivity L and M cone 0.75 sensitivities are Jameson & Hurvich (1955, 1957) - 0.5 highly correlated. Hue Cancellation Experiments 0.25 Hue Cancellation Experiment 0 400 500 600 700 Wavelength (nm) cancelling light test light Cone responses to several Natural SPDs : - + M-cone absorption S-cone absorption 1 1 0.75 0.75 + - 0.5 0.5 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.5 0.75 1 0.25 0.5 0.75 1 L-cone absorption M-cone absorption
Opponent Color Space Decorrelation: R O 1 0.30 0.59 0.11 = G O 2 0.60 -0.47 -0.22 B O 3 0.21 0.52 -0.31 + Spectral sensitivity of three decorrelating signals: - + Blue-Yellow Red-Green 1 Black-White - 1.5 0 -0.5 400 500 600 700
Opponent Color Space + black-white + blue-yellow - + red-green - -
YIQ - Color Space NTSC = National Television Systems Committee Y = luminance I = red-green Q = blue-yellow R Y 0.177 0.813 0.011 = G I 0.540 -0.263 -0.174 B Q 0.246 -0.675 0.404 R G B are the CIE-RGB
Subtractive Color System - CMYK Original Y - Blur Printer Dyes: Cyan = removes red Magenta = removes green Yellow = removes blue blacK = removes all Ideal block dyes: cyan magenta yellow transmit I - Blur Q - Blur B G R B G R B G R
Multiplicative (Subtractive) Color System Opponent Color Wheel red = magenta + yellow B G R magenta B G R * yellow B G R = red R B G R Additive primaries Subtractive Primaries red = magenta + yellow green = cyan + yellow blue = magenta + cyan
Cyan - controls amount of red in print: low C = high R (also high G and B) high C = low R (high G and B) cyan B G R R G B R G B R G B High density Low density Medium density cyan cyan cyan
CMY + Black C + M + Y = K (black) • Using three inks for black is expensive • C+M+Y = dark brown not black • Black instead of C+M+Y is crisper with more contrast. Undercolor removal - (gray component replacement) = + 100 50 70 50 50 0 20 C M Y K C M Y
Color Spaces - Summary RGB space - Additive space used for CRT, Color Image representation CIE-XYZ Tristimulus Coordinates - Device Independent, Universal standard CIE-Lab - Perceptual Space, used for image quality, Image Metric (distance measure). YIQ - Opponent Space, used for color television broadcast. HSV - Perceptual Digitized Space, used for Human Interactive Painting. CMYK - Subtractive Space used for ink and dyes (printing). All these color spaces are 3D. There are conversions from one space to the other.
Recommend
More recommend