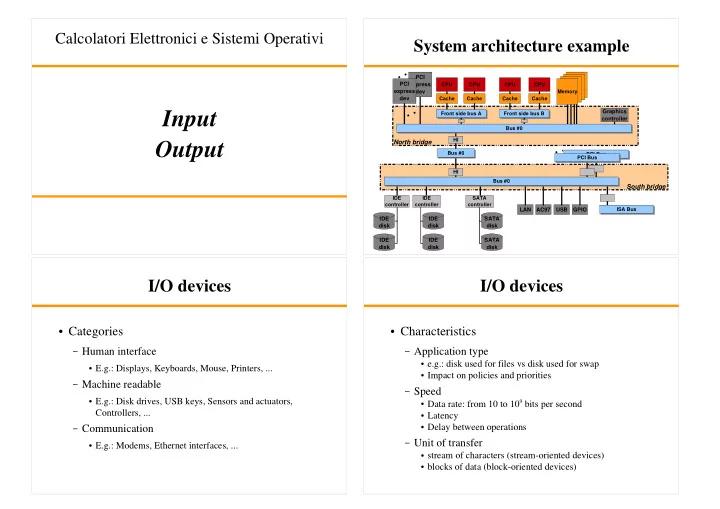

Calcolatori Elettronici e Sistemi Operativi System architecture example PCI PCI express CPU CPU CPU CPU express dev Memory dev Cache Cache Cache Cache Graphics Input Front side bus A Front side bus B controller Bus #0 HI North bridge Output Bus #0 PCI Bus PCI Bus HI Bus #0 South bridge IDE IDE SATA controller controller controller LAN AC97 USB GPIO ISA Bus IDE IDE SATA disk disk disk IDE IDE SATA disk disk disk I/O devices I/O devices � Categories � Characteristics – Human interface – Application type � e.g.: disk used for files vs disk used for swap � E.g.: Displays, Keyboards, Mouse, Printers, ... � Impact on policies and priorities – Machine readable – Speed � E.g.: Disk drives, USB keys, Sensors and actuators, � Data rate: from 10 to 10 9 bits per second Controllers, ... � Latency � Delay between operations – Communication – Unit of transfer � E.g.: Modems, Ethernet interfaces, ... � stream of characters (stream-oriented devices) � blocks of data (block-oriented devices)
I/O devices I/O devices � Characteristics � Characteristics – Access method – Data representation � Sequential / Random � Data encoding scheme � Redundancy – Transfer schedule – Error conditions � Synchronous / Asynchronous � Error types – I/O direction – e.g.: connection errors, wrong data, unreliable writing, ... � Read only / Write only / Read/write � Reporting – Sharing – interrupts, error codes, ... � Response � Dedicate / Shareable – retry, correct, fail, ... – Complexity of control � Consequences I/O devices I/O structure � Access User level code – Polling (programmed I/O) I/O subsystem – Interrupt-driven I/O Operating system – DMA Device Device Device driver driver driver � Address spaces Device Device Device controller controller controller Device controller (HW): � – CPU address space – Interprets commands from the HW/SW interface � Sends proper sequences of electrical signals to the device I/O device I/O device I/O device � Addresses used internally by CPU (virtual/logic addresses) – Interprets signals coming from the device � Modifies the value of its registers – Bus address space � Send IRQs � Addresses for I/O (physical addresses)
OS objectives OS objectives � Efficiency � Error handling � Abstraction (generality) � Low-level tuning – User code must see I/O class functions – Ethernet packet size � logical I/O functions ( read/write/see k) – Synchronous/Asynchronous transfers � communication functions ( socket handling ) � (e.g.: write-through or write-deferred with respect to � filesystem functions ( directory management, file permissions ) controller buffers) – Blocking/Non-blocking transfers – Kernel code maps user calls to HW specific features � Device drivers – ... � Sharing Efficiency OS I/O components � I/O is a major factor in system performance � I/O subsystem – Filesystems – Reduce the number of context switch – Networking – Reduce frequency of interrupts – Block devices � Use polling if busy-waiting can be minimized � Increase concurrency with DMA � SCSI, IDE, ... – Increase the efficiency of large transfers with DMA – Character devices – Reduce the number of buffer copies � Device driver ( HW dependent ) – Move processing primitives in hardware if possible
I/O subsystem features I/O subsystem components � Uniform interface – open, close, read, write, seek, ioctl, ... � Naming VFS Generic HW Network management � Protection Protocols (iomem, ioports) Filesystems – access through syscalls � Policy IRQ core – buffer sizes Caching/buffering – block sizes – high level error handling – scheduling Char devices Block devices Networking – data managing (e.g.: packet reordering) – spooling � SW caching – OS I/O buffers and caches I/O Scheduling I/O Buffering � Requests are classified by device � Manage speed mismatch � Apply scheduling algorithms � Fragment or riassembly data – Algorithms depend on devices characteristics � Multi-copy issue – Reordering – From device to memory (kernel) – Clustering – From memory to memory (user) User space – Save with memory mapping Device 1 REQ 1 REQ 3 REQ 7 buffer Kernel Copy space Data to user buffer transfer Device 2 REQ 4 REQ 5 REQ 6 REQ 8 Device 3 REQ 2 Device
Buffering strategies Caching � Cache: memory that holds a copy of data Single buffering Device � Main memory can be used to increase I/O speed User process – Example: � Files cached in main memory Double buffering Device – Physical I/O are deferred and clustered User process � Multiple writes can be merged in a single buffer copy � Reads are resolved in memory Circular buffering Device User process Spooling Device driver � I/O on non-shareable devices � HW access – e.g., printers – I/O through ports – Job are independent � no interference – Memory mapped I/O � IRQ handling – A list of jobs for each device that needs spooling � e.g., spooling directory � Low level error handling – System task ( spooler ) to read jobs and send to device � HW caching � Policy: – Controller buffers – FIFO – other
I/O request flow User-level code I/O req User process I/O completed yes Tranfer data Already I/O subsystem satisfiable? to process (device no independent) Send req to device driver Process req Manage data (send commands to Indicate I/O changes device controller) to I/O subsystem Device Receive IRQ driver IRQ Device controller Update buffers handler commands Start deferred work IRQ HW Interact Send IRQ (device controller) with device
Recommend
More recommend