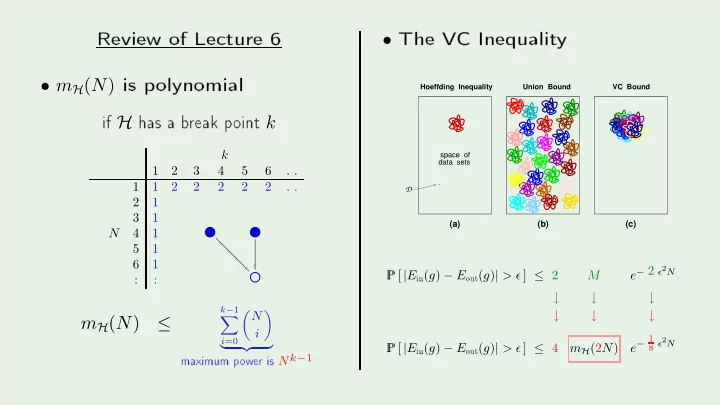

Review of Le ture 6 The V C Inequalit y is p olynomial • if H has a b reak p oint k • m H ( N ) Hoeffding Inequality Union Bound VC Bound space of k data sets 1 2 3 4 5 6 . . . 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 . . D 2 1 3 4 4 4 4 . . P P [ | E in ( g ) − E out ( g ) | > ǫ ] ≤ 2 3 1 4 7 8 8 8 . . top (a) (b) (c) 4 1 5 11 N . . . . . . . . 5 1 6 : . 6 1 7 : . e − 2 ǫ 2 N M : : : : . P P [ | E in ( g ) − E out ( g ) | > ǫ ] ≤ 4 bottom maximum p o w er is N k − 1 ↓ ↓ ↓ � N � k − 1 ↓ ↓ ↓ � m H ( N ) ≤ i e − 1 8 ǫ 2 N i =0 m H (2 N ) � �� �
Lea rning F rom Data Y aser S. Abu-Mostafa Califo rnia Institute of T e hnology Le ture 7 : The V C Dimension Sp onso red b y Calte h's Provost O� e, E&AS Division, and IST T uesda y , Ap ril 24, 2012 •
Outline The de�nition V C dimension of p er eptrons • Interp reting the V C dimension • Generalization b ounds • • Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 2/24 M � A L
De�nition of V C dimension The V C dimension of a hyp othesis set H , denoted b y d , is v ( H ) the la rgest value of N fo r whi h m H ( N ) = 2 N �the most p oints H an shatter� an shatter N p oints v ( H ) is a b reak p oint fo r H v ( H ) N ≤ d = ⇒ H Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 3/24 = ⇒ k k > d M � A L
The gro wth fun tion In terms of a b reak p oint k : k − 1 � N � � In terms of the V C dimension d : m H ( N ) ≤ v i v i =0 v maximum p o w er is N d d � N � � m H ( N ) ≤ i i =0 � �� � Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 4/24 M � A L
Examples is p ositive ra ys: v = 1 • H • is 2D p er eptrons : d v = 3 • H • is onvex sets : • • d v = ∞ • H up d Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 5/24 bottom M � A L
V C dimension and lea rning is �nite will generalize v ( H ) up Indep endent of the lea rning algo rithm = ⇒ g ∈ H d UNKNOWN TARGET FUNCTION PROBABILITY f: X Y DISTRIBUTION P X on Indep endent of the input distribution TRAINING EXAMPLES • ( , ), ... , ( , ) x y x y 1 1 N N FINAL Indep endent of the ta rget fun tion LEARNING • HYPOTHESIS ALGORITHM g ~ f ~ A HYPOTHESIS SET • H down Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 6/24 M � A L
V C dimension of p er eptrons F o r d = 2 , d v = 3 In general, v = d + 1 up W e will p rove t w o dire tions: d v ≤ d + 1 v ≥ d + 1 d d Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 7/24 down M � A L
Here is one dire tion A set of N = d + 1 p oints in R d shattered b y the p er eptron: T � x � T � x � T � x � 1 0 0 . . . 0 . . . . . . 1 . 0 . . 1 1 0 . . . 0 T 2 � x � X = = 1 0 1 0 3 . . . 1 0 . . . 0 1 is invertible d +1 Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 8/24 X M � A L
Can w e shatter this data set? F o r any y = an w e �nd a ve to r w satisfying . . . . . . ± 1 y 1 ± 1 y 2 = , sign (X w ) = y ± 1 y d +1 sign (X w )= y Easy! Just mak e whi h means Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 9/24 w = X − 1 y M � A L
W e an shatter these d + 1 p oints This implies what? [a℄ d v = d + 1 [b℄ d v ≥ d + 1 [ ℄ d v ≤ d + 1 � [d℄ No on lusion Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 10/24 M � A L
No w, to sho w that d v ≤ d + 1 W e need to sho w that: [a℄ There a re d + 1 p oints w e annot shatter [b℄ There a re d + 2 p oints w e annot shatter [ ℄ W e annot shatter any set of d + 1 p oints [d℄ W e annot shatter any set of d + 2 p oints � Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 11/24 M � A L
T ak e any d + 2 p oints F o r any d + 2 p oints, Mo re p oints than dimensions = w e must have x 1 , · · · , x d +1 , x d +2 ⇒ � x j = a i x i where not all the a i 's a re zeros i � = j Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 12/24 M � A L
So? � x j = Consider a i x i the follo wing di hotomy: i � = j 's with non-zero a i get sign ( a i ) and x j gets y i = x i No p er eptron an implement su h di hotomy! y j = − 1 Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 13/24 M � A L
Why? T x j = T x i � � x j = = ⇒ a i x i a i w T x i ) = T x i > 0 w If y i = sign ( w sign ( a i ) , then i � = j i � = j T x j = T x i > 0 This fo r es a i w � a i w T x j ) = +1 w Therefo re, sign ( w i � = j y j = Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 14/24 M � A L
Putting it together W e p roved and v ≤ d + 1 v ≥ d + 1 d d v = d + 1 d What is d + 1 in the p er eptron? It is the numb er of pa rameters w 0 , w 1 , · · · , w d Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 15/24 M � A L
Outline The de�nition V C dimension of p er eptrons • Interp reting the V C dimension • Generalization b ounds • • Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 16/24 M � A L
1. Degrees of freedom P a rameters reate degrees of freedom # of pa rameters: analog degrees of freedom : equivalent `bina ry' degrees of freedom v d Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 17/24 M � A L
PSfrag repla ements PSfrag repla ements 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0 0.8 0.2 1 0.4 -0.1 0.6 -0.08 0.8 -0.06 1 -0.04 -0.1 -0.02 -0.08 0 -0.06 0.02 -0.04 0.04 The usual susp e ts -0.02 0.06 0 0.08 P ositive ra ys ( d = 1 ): v 0.02 0.1 0.04 0.06 h ( x ) = − 1 h ( x ) = +1 a 0.08 x 1 x 2 x 3 . . . x N P ositive intervals ( d = 2 ): v 0.1 Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 18/24 h ( x ) = − 1 h ( x ) = +1 h ( x ) = − 1 x 1 x 2 x 3 . . . x N M � A L
Not just pa rameters P a rameters ma y not ontribute degrees of freedom: down y x measures the e�e tive numb er of pa rameters v down d Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 19/24 M � A L
2. Numb er of data p oints needed T w o small quantities in the V C inequalit y: P [ | E P in ( g ) − E out ( g ) | > ǫ ] ≤ 4 m H (2 N ) e − 1 8 ǫ 2 N If w e w ant ertain ǫ and δ , ho w do es N dep end on d ? v � �� � δ Let us lo ok at N d e − N Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 20/24 M � A L
N d e − N Fix N d e − N = small value Ho w do es N hange with d ? 10 10 N 30 e − N 5 10 Rule of thumb: 0 10 v −5 10 N ≥ 10 d 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 21/24 M � A L
Outline The de�nition V C dimension of p er eptrons • Interp reting the V C dimension • Generalization b ounds • • Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 22/24 M � A L
Rea rranging things Sta rt from the V C inequalit y: P [ | E P out − E in | > ǫ ] ≤ 4 m H (2 N ) e − 1 Get ǫ in terms of δ : 8 ǫ 2 N � �� � δ � N ln 4 m H (2 N ) 8 8 ǫ 2 N = δ = 4 m H (2 N ) e − 1 ⇒ ǫ = δ � �� � With p robabilit y ≥ 1 − δ , out − E in | ≤ Ω( N, H , δ ) Ω Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 23/24 | E M � A L
Generalization b ound With p robabilit y ≥ 1 − δ , out − E in | ≤ Ω( N, H , δ ) | E With p robabilit y ≥ 1 − δ , = ⇒ out in + Ω ≤ E E Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 7 24/24 M � A L
Recommend
More recommend