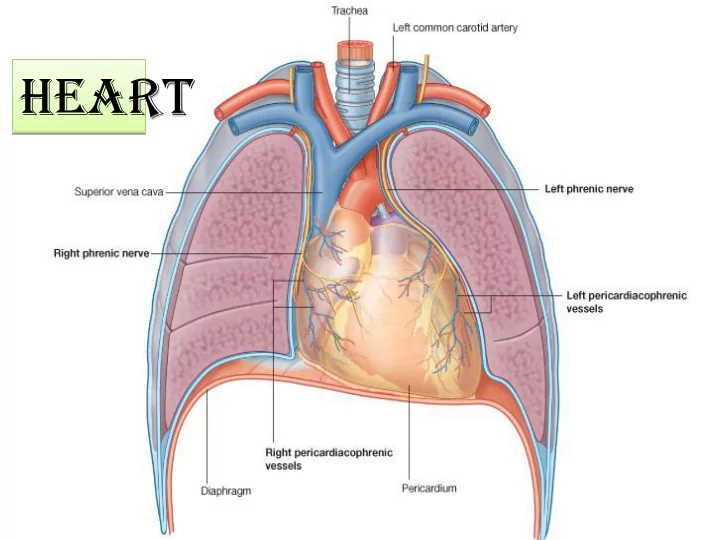

heart
MEDIASTINUM The mediastinum is a broad central partition that separates the two laterally placed pleural cavities . The mediastinum extends: from the sternum to the bodies of the vertebrae ; and from the superior thoracic aperture to the diaphragm
The mediastinum is subdivided into several smaller regions BY A transverse plane extending from the sternal angle to the intervertebral disc between vertebrae T 4 and T 5 separates the mediastinum into: 1-SUPERIOR MEDIASTINUM 2-INFERIOR MEDIASTINUM , which is further divided by the pericardial sac into: 1-THE ANTERIOR The area anterior to the pericardial sac and posterior to the body of the sternum . 2-MIDDLE The area in the middle, which includes the pericardial sac and its contents, is the middle mediastinum 3-POSTERIOR MEDIASTINUM The region posterior to the pericardial sac and the diaphragm and anterior to the bodies of the vertebrae is the posterior mediastinum.
The Pericardium The pericardium is a fibroserous sac surrounding the heart and the roots of the great vessels It consists of two components, 1-THE FIBROUS PERICARDIUM : is a tough connective tissue outer layer 2- THE SEROUS PERICARDIUM: is thin layer and consists of two parts: A-The parietal layer lines the inner surface of the fibrous; B- The visceral layer (epicardium) of serous pericardium adheres to the heart and forms its outer covering The narrow space created between the two Pericarditis layers of serous pericardium, containing a small Pericarditis is an inflammatory condition amount of fluid, is the pericardial cavity of the pericardium
Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped lies within the pericardium in the middlle mediastinum. MYOCARDIUM The walls of the heart are composed of : 1-EPICARDIUM : visceral serous ENDOCAR pericardium DIUM 2-MYOCARDIUM: cardiac muscle . 3-ENDOCARDIUM: layer of endothelium. EPICARDIUM
Surfaces of the Heart The heart has three surfaces: 1- Sternocostal (anterior) 2-Diaphragmatic (inferior) 3- A base (posterior ) The base of the heart , or the posterior surface, is formed mainly by the left atrium, The apex of the heart , formed by the left ventricle, is directed downward, forward, and to the left It lies at the level of the fifth left intercostal space, 3.5 in. (9 cm) from the midline.
Borders of the Heart These borders are important The to recognize when examining a right radiograph of the heart. The left border border, by the is left auricle; formed and below, by by the the left right ventricle atrium; the The lower apex is border is formed formed by the mainly by left the right ventricle ventricle but . also by the right atrium;
Grooves on its (heart) external surfaces Anterior view The anterior interventricular sulcus is on the anterior surface of the heart and The coronary sulcus circles the heart, separating the atria from the ventricles Posterior view The posterior interventricular sulcus is on the diaphragmatic surface of the heart
Chambers of the Heart The heart is divided by vertical septa into four chambers: 1-the right and left atria 2- the right and left ventricles.
A-Right Atrium The right atrium consists of a main cavity and a small outpouching, the auricle Openings into the Right Atrium 1-The superior vena cava : It returns the blood to the heart from the upper half of the body. 2-The inferior vena cava It returns the blood to the heart from the lower half of the body. 3-The coronary sinus which drains most of the blood from the heart. 4- The right atrioventricular orifice is guarded by the tricuspid valve Fetal Remnants FOSSA OVALIS Located on the atrial septum, which separates the right atrium from the left atrium ; which was the site of the foramen ovale in the fetus
B-Right Ventricle The right ventricle communicates with 1- The right atrium through the atrioventricular orifice 2-The pulmonary trunk through the pulmonary orifice As the cavity approaches the pulmonary orifice it becomes funnel shaped, at which point it is referred to as the infundibulum. Its internal structure shows several internal projecting ridges formed of muscle bundles known as trabeculae carneae. An example of trabeculae carneae is the papillary muscles , It is attached by their bases to the ventricular wall while their apices are connected by fibrous chords ( the chordae tendineae ) to the cusps of the tricuspid valve
C-Left Atrium consists of a main cavity and a left auricle. the fibrous pericardium separates it from the esophagus Openings into the Left Atrium 1-The four pulmonary veins (two from each lung, 2-The left atrioventricular orifice is guarded by bicuspied valve or MITRAL VALVE
4-Left Ventricle The left ventricle communicates with 1- The left atrium through the atrioventricular orifice 2- The aorta through the aortic orifice The walls of the left ventricle are three times thicker than those of the right ventricle. There are well-developed trabeculae carneae The part of the ventricle below the aortic orifice is called The aortic vestibule
Semilunar valves The aortic valve guards the aortic orifice The pulmonary valve guards the pulmonary orifice and consists of three semilunar cusps. No chordae or papillary muscles are associated with these valves
The mitral valve guards the left atrioventricular orifice It consists of two cusps. The tricuspid valve guards the right atrioventricular orifice consists of three cusps formed The bases of the cusps are attached to the fibrous ring of the skeleton of the heart, whereas their free edges and ventricular surfaces are attached to the chordae tendineae. The chordae tendineae connect the cusps to the papillary muscles. When the ventricle contracts, the papillary Valves are opened and closed muscles contract and prevent the cusps from by the difference in blood being forced into the atrium. pressure
Arterial Supply of the Heart The arterial supply of the heart is provided by : 1-THE RIGHT CORONARY ARTERY 2-LEFT CORONARY ARTERIY which arise from the ascending aorta The right coronary artery: One of its branches (commonly) is THE POSTERIOR INTERVENTRICULAR (DESCENDING) ARTERY
The left coronary artery is usually larger than the right coronary artery supplies the major part of the heart divides into 1- ANTERIOR INTERVENTRICULAR BRANCH AND 2-A CIRCUMFLEX BRANCH.
Venous Drainage of the Heart Most !blood from the heart wall drains into the right atrium through THE CORONARY SINUS which lies in the posterior part of the atrioventricular groove tributaries of the coronary sinus. GREAT CARDIAC VEIN SMALL CARDIAC VEINS MIDDLE CARDIAC VEINS
THE CONDUCTING SYSTEM OF THE HEART consists of specialized cardiac muscle present in THE SINUATRIAL NODE THE ATRIOVENTRICULAR NODE THE ATRIOVENTRICULAR BUNDLE RIGHT AND LEFT TERMINAL BRANCHES THE SUBENDOCARDIAL PLEXUS OF PURKINJE FIBERS
Conducting System of the Heart The normal heart contracts rhythmically at about 70 to 90 beats per minute in the resting adult. The rhythmic contractile process originates Read only spontaneously in the conducting system and the impulse travels to different regions of the heart, so the atria contract first and together, to be followed later by the contractions of both ventricles together The slight delay in the passage Read only of the impulse from the atria to the ventricles allows time for the atria to empty their blood into the ventricles before the ventricles contract.
Nerve Supply of the Heart The heart is innervated by sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers of the autonomic nervous system via the cardiac plexuses The sympathetic supply arises from the cervical and upper thoracic portions of the sympathetic trunks The parasympathetic supply comes from the vagus nerves Activation of sympathetic nerves results in cardiac acceleration, increased force of contraction of the cardiac muscle, and dilatation of the coronary arteries. Activation of the parasympathetic nerves results in a reduction in the rate and force of contraction of the heart and a constriction of the coronary
Recommend
More recommend