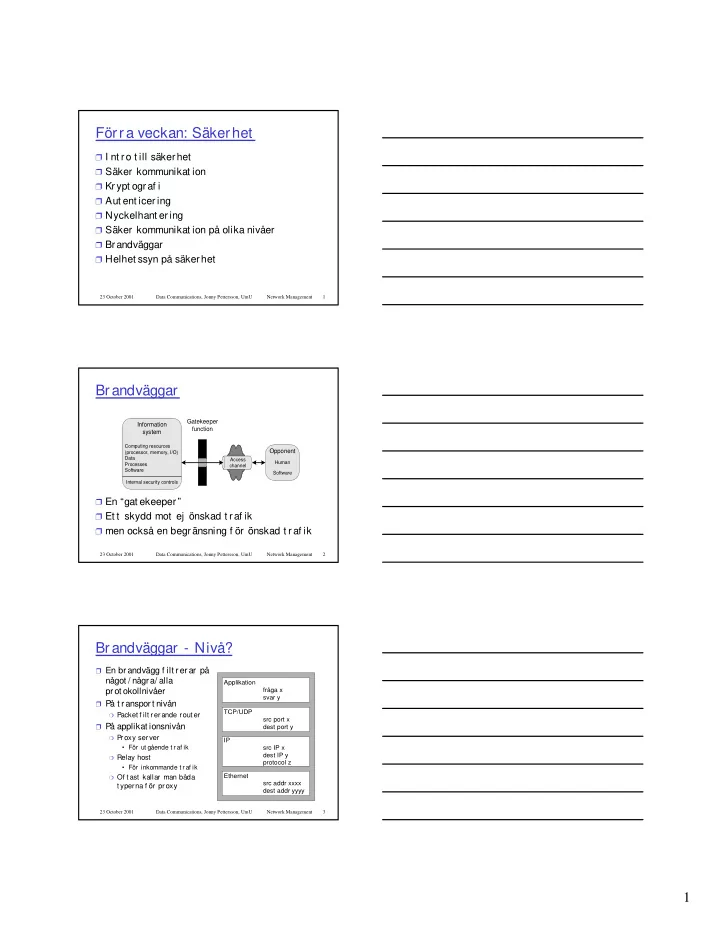

Förra veckan: Säkerhet ❒ I nt ro t ill säkerhet ❒ Säker kommunikat ion ❒ Krypt ograf i ❒ Aut ent icer ing ❒ Nyckelhant ering ❒ Säker kommunikat ion på olika nivåer ❒ Brandväggar ❒ Helhet ssyn på säkerhet 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 1 Brandväggar Gatekeeper Information function system Computing resources Opponent (processor, memory, I/O) Data Access Human Processes channel Software Software Internal security controls ❒ En “gat ekeeper” ❒ Et t skydd mot ej önskad t raf ik ❒ men också en begränsning f ör önskad t raf ik 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 2 Brandväggar - Nivå? ❒ En br andvägg f ilt r er ar på något / några/ alla Applikation pr ot okollnivåer fråga x svar y ❒ P å t r anspor t nivån TCP/UDP ❍ Packet f ilt rerande rout er src port x ❒ P å applikat ionsnivån dest port y ❍ Proxy server IP • För ut gående t r af ik src IP x dest IP y ❍ Relay host protocol z • För inkommande t r af ik Ethernet ❍ Of t ast kallar man båda src addr xxxx t yperna f ör proxy dest addr yyyy 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 3 1
Brandväggar - Konf igurering ❒ P roxyn sit t er ant ingen i brandväggen eller i en DMZ (DeMilit arized Zone) Yttre nät Skyddat nät Brandvägg DMZ 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 4 Brandväggar - Konf igurering (6) Webb Application Packet- servers servers filtering router Internet Data Backend system Second firewall Third firewall First firewall layer with load layer layer balancing (e) A secure firewall system according to Wineasy 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 5 Net wor k Management Goals: ❒ int r oduct ion t o net wor k management ❍ mot ivat ion ❍ maj or component s ❒ I nt er net net wor k management f ramewor k ❍ SMI : dat a def init ion language ❍ MI B: management inf or mat ion base ❍ SNMP : prot ocol f or net wor k management ❍ secur it y and administ r at ion ❒ present at ion services: ASN.1 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 6 2
What is net work management ? ❒ aut onomous syst ems (aka “net wor k”): 100s or 1000s of int er act ing hw/ sw component s ❒ f ive areas of net wor k management ❍ perf ormance management ❍ f ault management ❍ conf igur at ion management ❍ account ing management ❍ securit y management "Net work management includes t he deployment , int egrat ion and coordinat ion of t he hardwar e, sof t war e, and human element s t o monit or, t est , poll, conf igur e, analyze, evaluat e, and cont rol t he net work and element resources t o meet t he real-t ime, operat ional perf ormance, and Qualit y of Service requir ement s at a reasonable cost ." 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 7 I nf rast ruct ure f or net work management def init ions: managing ent it y agent dat a managed devices cont ain managing dat a managed device ent it y managed obj ect s whose dat a is gat hered int o a agent dat a Management I nf ormat ion net wor k Base (MI B) management managed device pr ot ocol dat a agent agent dat a managed device managed device 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 8 Net wor k Management st andar ds OSI CMI P SNMP: Simple Net wor k Management P r ot ocol ❒ Common Management I nf ormat ion P rot ocol ❒ I nt er net r oot s (SGMP ) ❒ designed 1980’s: t he ❒ st ar t ed simple unif ying net ❒ deployed, adopt ed r apidly management st andar d ❒ gr owt h: size, complexit y ❒ t oo slowly ❒ current ly: SNMP V3 st andar dized ❒ de f act o net wor k management st andar d 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 9 3
Quest ions ❒ What should be monit ored? ❒ What f orm of cont rol can be exercised on t he monit ored ent it ies? ❒ What specif ic f ormat should exchanged inf ormat ion have? ❒ How should t he communicat ion prot ocol f or exchanging inf ormat ion look like? ❒ Which securit y model should be used? 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 10 SNMP overview: 4 key part s ❒ St ruct ure of Management I nf ormat ion (SMI ): ❍ dat a def init ion language f or MI B obj ect s ❒ Management inf ormat ion base (MI B): ❍ dist r ibut ed inf ormat ion st or e of net wor k management dat a ❒ SNMP prot ocol ❍ convey manager< -> managed obj ect inf o, commands ❒ securit y, administ rat ion capabilit ies ❍ maj or addit ion in SNMP v3 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 11 SMI : dat a def init ion language P ur pose: synt ax, semant ics of Basic Data Types management dat a well- INTEGER def ined, unambiguous Integer32 ❒ base dat a t ypes: Unsigned32 ❍ st r aight f or war d, bor ing OCTET STRING ❒ OBJ ECT-TYP E OBJECT IDENTIFIED ❍ dat a t ype, st at us, IPaddress semant ics of managed Counter32 obj ect Counter64 ❒ MODULE-I DENTI TY Guage32 ❍ groups relat ed obj ect s Tie Ticks int o MI B module Opaque 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 12 4
SNMP MI B MI B module specif ied via SMI MODULE-I DENTI TY (100 st andar dized MI Bs, mor e vendor -specif ic) MODULE OBJECT TYPE: OBJECT TYPE: OBJECT TYPE: obj ect s specif ied via SMI OBJ ECT-TYP E const r uct 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 13 MI B example: UDP module Obj ect I D Name Type Comment s 1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1 UDPI nDat agr ams Count er 32 t ot al # dat agr ams deliver ed at t his node 1.3.6.1.2.1.7.2 UDPNoPor t s Count er 32 # under liver able dat agr ams no app at por t l 1.3.6.1.2.1.7.3 UDI nErr or s Count er 32 # undeliver able dat agr ams all ot her r easons 1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4 UDPOut Dat agr ams Count er 32 # dat agr ams sent 1.3.6.1.2.1.7.5 udpTable SEQUENCE one ent r y f or each por t in use by app, gives por t # and I P addr ess 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 14 SNMP Naming quest ion: how t o name every possible st andard obj ect (prot ocol, dat a, more..) in every possible net work st andard?? answer: I SO Obj ect I dent if ier t ree: ❍ hier ar chical naming of all obj ect s ❍ each br anch point has name, number 1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1 udpI nDat agr ams I SO UDP I SO-ident . Or g. MI B2 US DoD I nt ernet management 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 15 5
OSI Obj ect I dent if ier Tr ee Check out www.alvest r and.no/ har ald/ obj ect id/ t op.ht ml 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 16 SNMP prot ocol Two ways t o convey MI B inf o, commands: managing managing ent it y ent it y r equest t r ap msg r esponse agent dat a agent dat a Managed device Managed device r equest / r esponse mode t r ap mode 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 17 SNMP pr ot ocol: message t ypes Message t ype Funct ion Get Request Mgr -t o-agent : “get me dat a” Get Next Request (inst ance,next in list , block) Get BulkRequest I nf ormRequest Mgr-t o-Mgr: here’s MI B value Set Request Mgr -t o-agent : set MI B value Agent -t o-mgr: value, r esponse t o Response Request Tr ap Agent -t o-mgr: inf orm manager of except ional event 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 18 6
SNMP secur it y and administ r at ion ❒ encrypt ion: DES-encrypt SNMP message ❒ aut hent icat ion: comput e, send MI C(m,k): comput e hash (MI C) over message (m) and secr et shared key (k) ❒ prot ect ion against playback: use nonce ❒ view-based access cont rol ❍ SNMP ent it y maint ains dat abase of access right s, policies f or various user s 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 19 The pr esent at ion pr oblem Q: does perf ect memory-t o-memory copy solve “t he communicat ion problem”? A: not always! struct { test.code test.code a a char code; test.x 00000001 int x; test.x 00000011 00000011 } test; 00000001 test.x = 256; test.code=‘a’ host 1 f ormat host 2 f ormat pr oblem: dif f erent dat a f ormat , st orage convent ions 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 20 Solving t he pr esent at ion pr oblem 1. Translat e local-host f or mat t o host -independent f or mat 2. Transmit dat a in host -independent f or mat 3. Translat e host -independent f ormat t o remot e-host f or mat 23 October 2001 Data Communications, Jonny Pettersson, UmU Network Management 21 7
Recommend
More recommend