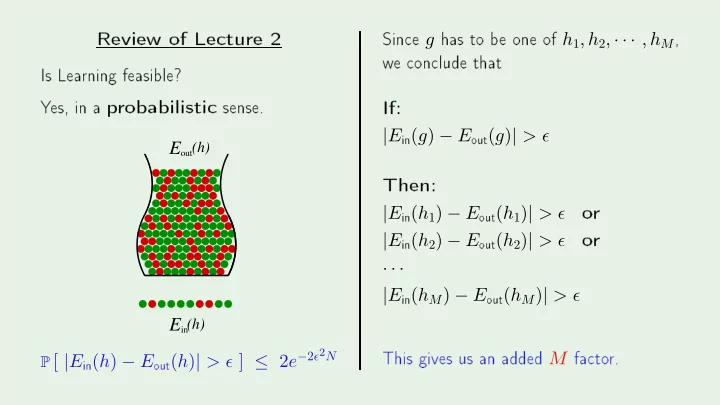

Review of Le ture 2 Sin e g has to b e one of h 1 , h 2 , · · · , h M , w e on lude that Is Lea rning feasible? Y es, in a p robabilisti sense. If: in ( g ) − E out ( g ) | > ǫ Hi Then: | E E (h) o r out in ( h 1 ) − E out ( h 1 ) | > ǫ o r in ( h 2 ) − E out ( h 2 ) | > ǫ | E in ( h M ) − E out ( h M ) | > ǫ | E · · · | E This gives us an added M fa to r. in ( h ) − E out ( h ) | > ǫ ] ≤ 2 e − 2 ǫ 2 N E in (h) Hi P [ | E
Lea rning F rom Data Y aser S. Abu-Mostafa Califo rnia Institute of T e hnology Le ture 3 : Linea r Mo dels I Sp onso red b y Calte h's Provost O� e, E&AS Division, and IST T uesda y , Ap ril 10, 2012 •
Outline Input rep resentation Linea r Classi� ation • Linea r Regression • Nonlinea r T ransfo rmation • • Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 2/23 M � A L
A real data set Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 3/23 M � A L
Input rep resentation `ra w' input x = ( x 0 ,x 1 , x 2 , · · · , x 256 ) linea r mo del: ( w 0 , w 1 , w 2 , · · · , w 256 ) F eatures: Extra t useful info rmation, e.g., intensit y and symmetry x = ( x 0 ,x 1 , x 2 ) linea r mo del: ( w 0 , w 1 , w 2 ) Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 4/23 M � A L
PSfrag repla ements 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 PSfrag repla ements PSfrag repla ements 0.7 0.8 0 0 0.9 2 2 1 4 4 6 0 6 8 8 0.1 10 10 0.2 12 12 0.3 14 14 0.4 16 16 0.5 18 18 0.6 0 0 2 0.7 2 4 4 0.8 6 6 0.9 8 8 1 10 10 0 12 12 0.1 14 14 Illustration of features 0.2 16 16 0.3 18 18 0 0 0.4 2 2 : intensit y : symmetry 0.5 4 4 0.6 6 6 0.7 8 8 0.8 10 10 x = ( x 0 ,x 1 , x 2 ) x 1 x 2 0.9 12 12 1 14 14 16 16 -8 18 18 -7 5 5 -6 10 10 -5 15 15 -4 5 5 -3 10 10 -2 15 15 5 -1 5 10 10 0 15 15 Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 5/23 M � A L
PSfrag repla ements What PLA do es out Evolution of E and E Final p er eptron b ounda ry in out 50% 0.05 10% 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 PSfrag repla ements A verage Intensit y 0.3 0.35 in 0.4 E 1% -8 -7 -6 Symmetry -5 -4 0 250 500 750 1000 -3 -2 -1 0 1 E Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 6/23 M � A L
The `p o k et' algo rithm out PLA: P o k et: 50% 50% PSfrag repla ements PSfrag repla ements 10% 10% out in in E 1% 1% 0 250 500 750 1000 0 250 500 750 1000 E E E Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 7/23 M � A L
PSfrag repla ements PSfrag repla ements Classi� ation b ounda ry - PLA versus P o k et PLA: P o k et: 0.05 0.05 0.1 0.1 0.15 0.15 0.2 0.2 0.25 0.25 A verage Intensit y 0.3 A verage Intensit y 0.3 0.35 0.35 0.4 0.4 -8 -8 -7 -7 -6 -6 Symmetry Symmetry -5 -5 -4 -4 -3 -3 -2 -2 -1 -1 0 0 1 1 Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 8/23 M � A L
Outline Input rep resentation Linea r Classi� ation • Linea r Regression regression ≡ real-valued output • Nonlinea r T ransfo rmation • • Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 9/23 M � A L
Credit again Classi� ation: Credit app roval (y es/no) Regression: Credit line (dolla r amount) age 23 y ea rs annual sala ry $30,000 Input: x = y ea rs in residen e 1 y ea r y ea rs in job 1 y ea r urrent debt $15,000 T x · · · · · · Linea r regression output: h ( x ) = d � Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 10/23 w i x i = w i =0 M � A L
The data set Credit o� ers de ide on redit lines: ( x 1 , y 1 ) , ( x 2 , y 2 ) , · · · , ( x N , y N ) is the redit line fo r ustomer x n . y n ∈ R Linea r regression tries to repli ate that. Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 11/23 M � A L
Ho w to measure the erro r T x Ho w w ell do es h ( x ) = w app ro ximate f ( x ) ? In linea r regression, w e use squa red erro r ( h ( x ) − f ( x )) 2 in-sample erro r: E in ( h ) = 1 N � ( h ( x n ) − y n ) 2 N n =1 Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 12/23 M � A L
PSfrag repla ements PSfrag PSfrag repla ements repla ements 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0 0 0.4 0.5 0.5 1 1 0.5 0 0 0.6 0.2 0.2 0.7 Illustration of linea r regression 0.4 0.4 0.8 0.6 0.6 0.9 0.8 0.8 1 1 1 0 0 0 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.7 0.7 0.7 y 0.8 0.8 y y 0.8 0.9 0.9 0.9 1 1 1 x 1 x 1 x 2 x 2 Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 13/23 x M � A L
The exp ression fo r E in T x n − y n ) 2 in ( w ) = N 1 � ( w E N n =1 1 N � X w − y � 2 = T � x 1 � T � x 2 � where . . . . . . y 1 T � x N � y 2 X = y = , Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 14/23 y N M � A L
Minimizing E in in ( w ) = 1 T (X w − y ) = 0 N � X w − y � 2 in ( w ) = 2 E T X w = X T y ∇ E N X T X) − 1 X T where X † = (X X is the ` pseudo-inverse ' of X w = X † y Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 15/23 X † M � A L
The pseudo-inverse T X) − 1 X T X † = (X − 1 � � � � � � � �� � �� � � � �� � d +1 × N d +1 × d +1 d +1 × N � �� � N × d +1 � �� � Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 16/23 d +1 × N M � A L
The linea r regression algo rithm 1: Constru t the matrix X and the ve to r y from the data set as follo ws T � x � T ( x 1 , y 1 ) , · · · , ( x N , y N ) � x � . . . . . . y 1 T 1 � x � y 2 2 X = y = , . ta rget ve to r input data matrix T X) − 1 X T 2: Compute the pseudo-inverse X † = (X . y N N � �� � � �� � 3: Return w = X † y . Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 17/23 M � A L
Linea r regression fo r lassi� ation Linea r regression lea rns a real-valued fun tion y = f ( x ) ∈ R Bina ry-valued fun tions a re also real-valued! ± 1 ∈ R T x n ≈ y n = ± 1 Use linea r regression to get w where w T x n ) In this ase, sign ( w is lik ely to agree with y n = ± 1 Go o d initial w eights fo r lassi� ation Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 18/23 M � A L
PSfrag repla ements 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 0.55 -8 Linea r regression b ounda ry -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 Symmetry -2 -1 0 A verage Intensit y Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 18/23 M � A L
Outline Input rep resentation Linea r Classi� ation • Linea r Regression • Nonlinea r T ransfo rmation • • Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 19/23 M � A L
Linea r is limited Data: Hyp othesis: 1 1 PSfrag repla ements PSfrag repla ements 0 0 − 1 Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 20/23 − 1 − 1 0 1 − 1 0 1 M � A L
Another example Credit line is a�e ted b y `y ea rs in residen e' but not in a linea r w a y! Nonlinea r [[ x i < 1]] and [[ x i > 5]] a re b etter. Can w e do that with linea r mo dels? Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 21/23 M � A L
Linea r in what? Linea r regression implements d � w i x i Linea r lassi� ation implements i =0 sign � d � � w i x i Algo rithms w o rk b e ause of linea rit y in the w eights i =0 Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 22/23 M � A L
T ransfo rm the data nonlinea rly Φ − → ( x 2 1 , x 2 ( x 1 , x 2 ) 2 ) 1 1 PSfrag repla ements PSfrag repla ements 0 . 5 0 Creato r: Y aser Abu-Mostafa - LFD Le ture 3 23/23 0 − 1 0 . 5 1 0 − 1 0 1 M � A L
Recommend
More recommend