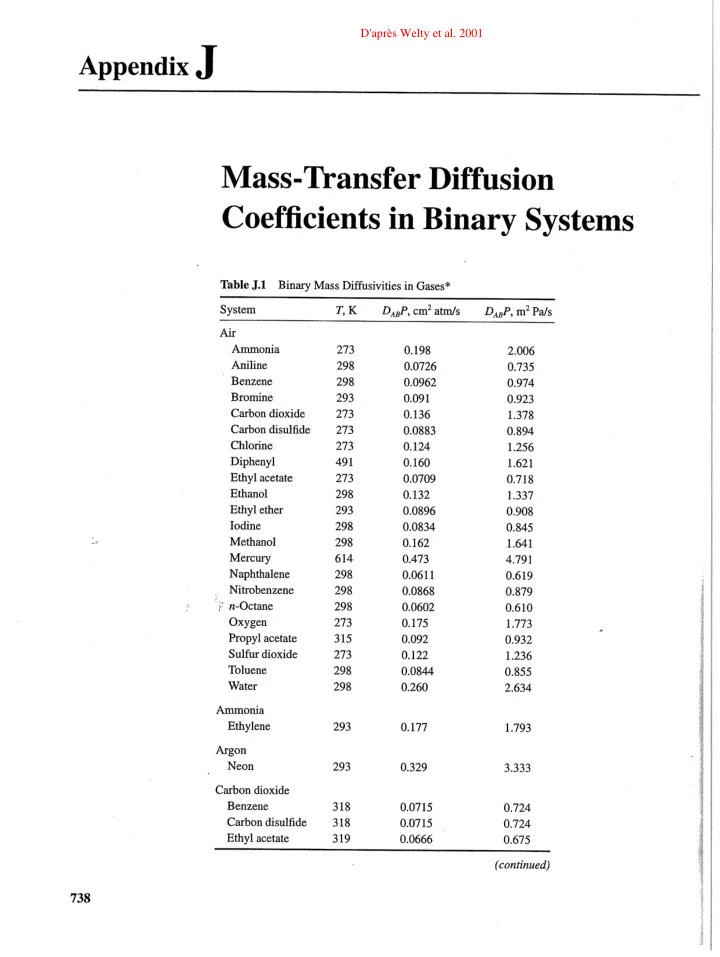

D'après Welty et al. 2001 Appendix J Mass- Transfer Diffusion Coefficients in Binary Systems Binar Mass Diffsivities in Gases* Table J.l System T,K D ABP, cm2 atms D ABP, m2 Pals Ai Amonia 273 0.198 2.006 Anline 298 0.0726 0.735 Benzene 298 0.0962 0.974 BromIne 293 0.091 0.923 Carbon dioxide 273 0.136 1.378 273 0.0883 Carbon disu1fide 0.894 Ch10rine 273 0.124 1.256 Dipheny1 491 0.160 1.621 Ethy1 acetate 273 0.0709 0.718 Ethanol 1.37 298 0.132 293 0.0896 0.908 Ethy1 ether Iodine 298 0.0834 0.845 Methanol 298 0.162 1.641 Mercur 614 0.473 4.791 Naphthalene 298 0.0611 0.619 Nitrobenzene 298 0.0868 0.879 ;' n-Octane 298 0.0602 0.610 Oxygen 273 1.773 0.1 75 315 0.092 0.932 Propy1 acetate Su1fu dioxide 273 0.122 1.236 To1uene 298 0.0844 0.855 Water 298 0.260 2.634 Ammonia Ethylene 293 0.177 1.793 Argon Neon 293 0.329 3.333 Carbon dioxide Benzene 318 0.0715 0.724 318 0.0715 0.724 Carbon disu1fide Ethy1 acetate 319 0.0666 0.675 ( continued) 738
739 Appendix J ( continued) Table J.l T,K System DABP, m2 Pals DABP, cm2 atms Carbon dioxide 0.0693 0.702 Ethanol 273 0.548 273 0.0541 Ethy1 ether 0.550 5.572 273 Hydrogen 0.153 1.550 Methane 273 1.06 298.6 0.105 Methanol 0.165 1.672 Nitrogen 298 1.85 0.117 Nitrous oxide 298 0.874 298 0.0863 Propane 0.164 1.661 Water 298 Carbon monoxide 1.530 0.151 Ethylene 273 0.651 6.595 Hydrogen 273 0.192 1.945 288 Nitrogen 1.874 273 0.185 Oxygen Helium 6.493 273 0.641 Argon 3.890 0.384 Benzene 298 5.00 0.494 Ethanol 298 16.613 293 1.64 Hydrogen 12.460 Neon 293 1.23 0.908 9.198 Water 298 Hydrogen Amonia 8.600 0.849 293 7.800 293 0.770 Argon 273 0.317 3.211 Benzene 4.447 0.439 Ethane 273 0.625 6.331 Methane 273 7.061 273 0.697 Oxygen 8.611 0.850 Water 293 Nitrogen 0.241 2.441 Ammonia 293 0.163 1.651 Ethylene 298 7.527 288 0.743 Hydrogen 0.709 273 0.070 Iodine 1.834 Oxygen 273 0.181 Oxygen Amonia 0.253 2.563 293 0.951 296 0.0939 Benzene 0.182 1.844 Ethylene 293 * R. C. Reid and T. K. Sherwood, The Propertes of Gases an Liquids, McGraw-Hil Book Company, New York, 1958, Chap. 8.
740 Appendix J Table J.2 Binar Mass Diffusivities in Liquids* Solute Concentration, Diffusivity Temperatue, in g mo1e/liter cm2/s X 105 inK or kg mo1e/m3 orm% X 109 Solute A Solvent B Chorine Water 289 0.12 1.26 Hydrogen Water 273 9 2.7 chloride 2 1.8 283 9 3.3 2.5 2.5 289 0.5 2.44 Amonia Water 278 3.5 1.24 288 1.0 1.77 Carbon dioxide Water 283 0 1.46 293 0 1.77 Sodium Water 291 0.05 1.26 chloride 0.2 1.21 1.0 1.24 3.0 1.36 5.4 1.54 Methanol Water 288 0 1.28 Water 285.5 1.0 0.82 Acetic acid 0.01 0.91 291 1.0 0.96 Ethanol Water 283 3.75 0.50 0.05 0.83 289 2.0 0.90 Water n-Butano1 288 0 0.77 Carbon dioxide Ethanol 290 0 3.2 Ch1oroform Ethanol 293 2.0 1.25 * R. E. TreybaI, Mass Transfer Operations, McGraw-Hil Book Company, New York, 1955, p. 25. Binar Diffsivities in Solids* Table J.3 Diffsivity, Diffsivity, cm2/s or Solute ft%r Solid K m2/s X 104 . Helium 293 Pyrex 4.49 X 10-11 1.74 X 10-10 773 2.00 X 10-8 7.76 X 10-8 Hydrogen Nickel 358 X 10-8 4.5 1.6 X 10-8 438 1.05 X 10-7 4.07 X 10-7 Bismuth Lead 293 1.0 X 10-16 4.27 X 10-16 Mercury Lead 293 9.7 X 10-15 2.50 X 10-15 Antimony Si1ver 293 3.51 X 10-21 1.6 X 10-20 A1umnum Copper 293 1.Q X 10-30 5.04 X 10-30 Cadmum Copper 293 2.71 X 10-15 1.05 X 10-14 * R. M. Barr, Difsion ln and Through Solids, The Macmilan Company, New York, 1941.
Table 24,4 Mo1ecular Volumes at Normal Boilng Point for Some Commonly Encountered Compounds Mo1ecular Molecular volume, in volume, Compound cm3/g mole cm3/g mole Compound 23,6 Nitrc oxide, NO 14.3 Hydrogen, H2 36.4 Nitrous oxide, N20 25.6 Oxygen, O2 25,8 31.2 Amonia, NH3 Nitrogen, N2 18,9 Ai Water, H20 29.9 32,9 Hydrogen sulfide, H2S 30,7 Carbon monoxide, CO 53,2 34,0 Carbon dioxide, CO2 Bromine, Br2 48.4 51.5 Carbonyl sulfide, COS Chlorie, C12 71.5 44.8 Iodne, 12 Sul dioxide, S02 Table 24,5 Atomic Volumes for Comp1ex Mo1ecular Volumes for Simple Substacest Atomic volume, Atomic volume, Element in cm3/g mole in cm3/g mole Element 7.4 Broinne 27,0 Oxygen, except as noted be10w Oxygen, in methy1 esters 9,1 Carbon 14,8 9.9 21.6 Oxygen, in methy1 ethers Chlorine 3,7 Oxygen, in higher ethers Hydrogen 11.0 37.0 and other esters lodine 12,0 Oxygen, in acids Nitrogen, double bond 15,6 Sulf 25,6 10,5 Nitrogen, in priar amnes 12,0 Nitrogen, in secondar amnes t G. Le Bas, The Molecular Volums of Liquid Chemical COfnouns, Longmas, Green & Company, Ltd., London, 1915, Solvent epB water 2,26* methano1 1.9 1 ethano1 1.5 benzene, ether, heptane, and other unassociated solvents 1.0
D'après Bird et al. 2007 Appendix E Tables for Prediction of Transport Properties §E.l Intermolecular force parameters and critical propertes §E.2 Functions for prediction of transport propertes of gases at low densities ..'.', . r: L 863
Table E.l 00 Lennard-Jones (6-12) Potential Parameters and Critical Propertes 0" ~ 1 Lennard-Jones parameters Critical propertiesg,1i 1 1 1 Molecular Weight e/K Ref. cr Tc Vc !hc X 106 Pc kc X 106 Substance M (À) (K) (atm) (cm3/ g-mole) (g/cm' s) (K) (cal/cm' s. K) Light elements: Hz 2.016 2.915 38.0 a 33.3 12.80 65.0 34.7 He 57.8 \ 4.003 2.576 10.2 a 5.26 2.26 25.4 Noble gases: Ne 20.180 2.789 35.7 a 44.5 26.9 41.7 79.2 .', -l,56. Ar 39.948 3.432 122.4 150.7 48.0 b 75.2 264. 71.0 Kr 83.80 3.675 170.0 209.4 54.3 92.2 b ~96. 49.4 Xe 131.29 4.009 234.7 289.8 58.0 118.8 490. b 40.2 Simple polyatomic gases: Air 28.964; 3.617 97.0 132.4; a 37.0; 86.7; 193. 90.8 Nz 28.013 3.667 99.8 126.2 33.5 90.1 b 180. 86.8 Oz 31.999 3.433 154.4 113. a 49.7 74.4 250. 105.3 CO j 28.010 3.590 110. a 34.5 .132.9 93.1 190. 86.5 COz 44.010 3.996 304.2 190. a 72.8 343. 94.1 122. NO 30.006 3.470 119. a 180. 64. 57. 258. 118.2 NzO 44.012 3.879 220. a 309.7 71.7 96.3 332. 131. SOz 64.065 4.026 363. 430.7 c 77.8 122. 411. 98.6 37.997 3.653 Fz 112. a - Clz 70.905 4.115 357. a 417. 76.1 124. 420. 97.0 1 159.808 4.268 Brz 520. a 584. 102. 144. 253.809 4.982 550. a 800. IZ Hydrocarbons: 191. CH4 16.04 3.780 154. 45.8 b 98.7 159. 158. CH==H 26.04 4.114 212. d 308.7 61.6 112.9 237. CHz=CHz 28.05 4.228 216. 282.4 50.0 124. 215. b 30.07 CZH6 4.388 232. 305.4 48.2 b 148. 210. 203. CH3C==H 40.06 4.742 261. d 394.8 CH3CH=CHz 42.08 4.766 275. 365.0 45.5 181. 233. b C3Hs 44.10 4.934 273. 369.8 41.9 200. 228. b n--4HlO 58.12 5.604 304. 425.2 37.5 255. b 239.
Recommend
More recommend