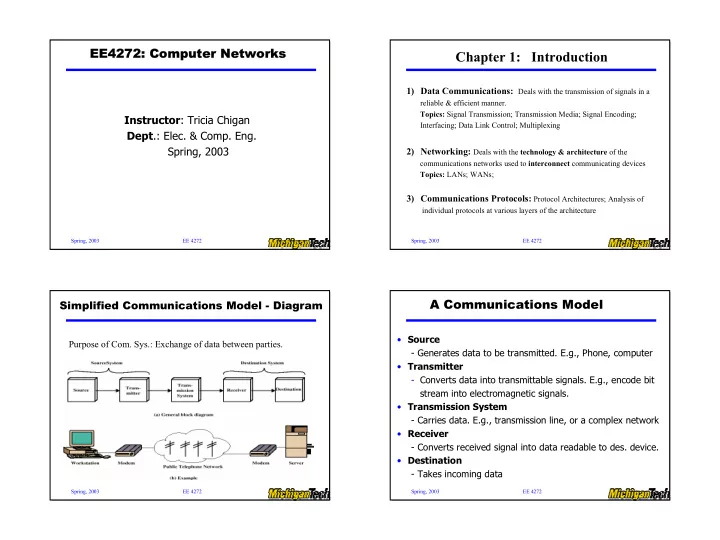

EE4272: Computer Networks EE4272: Computer Networks Chapter 1: Introduction 1) Data Communications: Deals with the transmission of signals in a reliable & efficient manner. Topics: Signal Transmission; Transmission Media; Signal Encoding; Instructor : Tricia Chigan Interfacing; Data Link Control; Multiplexing Dept .: Elec. & Comp. Eng. Spring, 2003 2) Networking: Deals with the technology & architecture of the communications networks used to interconnect communicating devices Topics: LANs; WANs; 3) Communications Protocols: Protocol Architectures; Analysis of individual protocols at various layers of the architecture Spring, 2003 EE 4272 Spring, 2003 EE 4272 A Communications Model Simplified Communications Model - Diagram • Source Purpose of Com. Sys.: Exchange of data between parties. - Generates data to be transmitted. E.g., Phone, computer • Transmitter - Converts data into transmittable signals. E.g., encode bit stream into electromagnetic signals. • Transmission System - Carries data. E.g., transmission line, or a complex network • Receiver - Converts received signal into data readable to des. device. • Destination - Takes incoming data Spring, 2003 EE 4272 Spring, 2003 EE 4272 1
Key Communications Tasks Simplified Data Communications Model • Transmission System Utilization: efficient/fair facility sharing • Signal Generation • Synchronization • Exchange Management • Error detection and correction • Addressing and routing • Recovery • Message formatting • Security • Network Management Reading assignment: read the details of P6-p7 Spring, 2003 EE 4272 Spring, 2003 EE 4272 Wide Area Networks Networking • Point-to-point communication not usually practical • Large geographical area - Devices are too far apart • Crossing public rights of way - Large set of devices would need impractical number of connections • Rely in part on common carrier circuits • Solution is a communications network • Alternative technologies: all about resource sharing � Circuit switching : Dedicated communications path established for the duration of the conversation. e.g. telephone network � Packet switching: Date are sent out in a sequence of packets; Each packet passes through the network along some path; Used for terminal-to-computer, or computer-to-computer comm. � Frame relay (up to 2 Mbps): reading assignment p10 � Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM): reading assignment p11 Spring, 2003 EE 4272 Spring, 2003 EE 4272 2
Local Area Networks Protocols • Smaller scope • Used for communications between entities in a system - Building or small campus • Entities: User applications; e-mail facilities; terminals • Usually owned by same organization as • Systems: Computer; Terminal; Remote sensor attached devices • Must speak the same language • Data rates much higher • Key Elements of a Protocol: • Usually broadcast systems (e.g. Ethernet Bus) - Syntax: Data formats; Signal levels • Now some switched systems (e.g. Gigabit - Semantics: Control information; Error handling Ethernet Switch ) and ATM are being introduced - Timing: Speed matching; Sequencing Spring, 2003 EE 4272 Spring, 2003 EE 4272 Protocol Architecture TCP/IP Protocol Architecture • Developed by the US Defense Advanced Research • Framework about how a set of protocols work Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched together to finish the communication task network (ARPANET) between source and destination • Used by the global Internet • Three Protocol Architectures: • No official model but a working one. - Three-Layer Model � Application layer: logic needed to support various user applications - TCP/IP Protocol Architecture � Host to host or transport layer: reliable end-to-end delivery mechanisms, e.g. TCP - OSI Model � Internet layer: provide routing function across multiple networks � Network access layer: concern the exchange of date between end system & the network to which it is attached � Physical layer: Physical interface between a data trans. device & a trans. medium or network Spring, 2003 EE 4272 Spring, 2003 EE 4272 3
TCP/IP Protocol Architecture Model OSI Model • Open Systems Interconnection : A framework for developing protocol standards. • Developed by the International Standardization Organization (ISO) • Seven layers • A theoretical system delivered too late! • TCP/IP is the de facto standard Spring, 2003 EE 4272 Spring, 2003 EE 4272 OSI Layers OSI v TCP/IP • Application: e.g. web browser, email, file transfer • Presentation: provides independence to the app. processes from differences in data representation (syntax). • Session: Provides control structure for comm. between applications; establish, manages, and terminates connections (sessions) between cooperating applications • Transport: end-to-end reliable delivery control • Network: routing/switching; establish/maintain/terminate connections • Data Link: reliable transfer of information across the physical links; send frames with necessary synch., error control, and flow control • Physical: concern with transmission of unstructured bit stream over physical medium; Spring, 2003 EE 4272 Spring, 2003 EE 4272 4
Standards Standards Organizations • Required to allow for interoperability between • Internet Society equipments • ISO • Advantages • ITU-T (formally CCITT) � Ensures a large market for equipment and software • ATM forum � Allows products from different vendors to communicate • IETF • Disadvantages Further Reading Resource � Freeze technology • Web sites for IETF, IEEE, ITU-T, ISO � May be multiple standards for the same thing • Internet Requests for Comment (RFCs) Spring, 2003 EE 4272 Spring, 2003 EE 4272 5
Recommend
More recommend