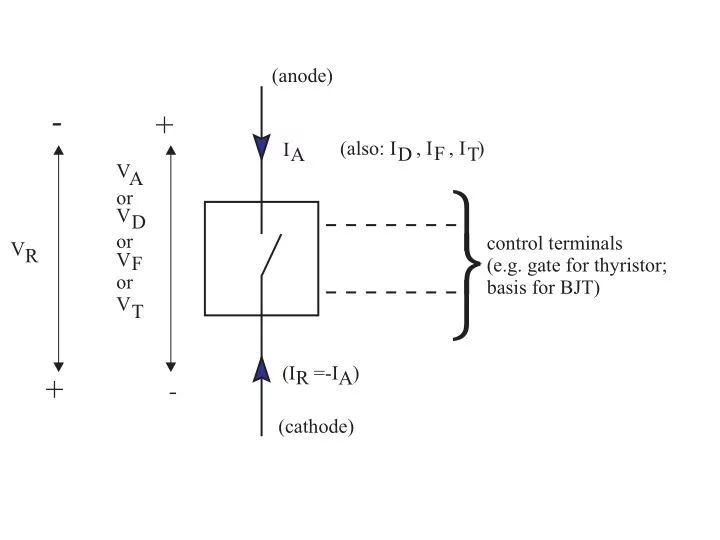

(anode) - + (also: ID , IF , IT) IA VA or VD or control terminals VR VF (e.g. gate for thyristor; or basis for BJT) VT (IR =-IA) + - (cathode)
IA conducting I F range forward current (1V) (100A) forward voltage drop A A anode reverse leakage + current I A (IF ) VA (1 A) � p VBR n (VF ) VF VA VFo - treshold voltage cathode K K reverse blocking (b) (a) reverse breakdown (1000V) (c)
IA conducting area forward breakover A A reverse leakage IA voltage + current VA (ID) p IH (I T) n VBR (VD ) G p VA IG3>IG2>IG1>IG=0 n (VT) G - K K forward blocking reverse blocking range range reverse (or avalanche) (a) (b) breakdown (c)
a VG a limit the conducting range b of the G-K diode c maximal value for the control power (PGmax) d recommended load line c of the control circuit VGT , IGT : gate voltage and b gate current above which d every thyristor should start to conduct VGT VGD , IGD : gate voltage and gate current below which no VGD thyristor should start to conduct IG IGD IGT
VDRM (kV) asymmetrical thyristor 4 symmetrical thyristor 2 0 (µs) toff 104 0 100 1000
+I T2 +iG + _ 300v + 300v _1v 1v _ V G _iG V _ T1 _I (a) (b)
A Anode curent Anode voltage IA G Vd K or voltage peak A tail current G K 0 or time A IGR G K (b) (a)
n + p n + p p p or = n n - n - + > n n + n + p + p + p + p + n + n + diode IGCT (b) (a) thyristor
saturation IC C C IC + N parameter IB P VCE B B IB N _ E E (a) (b) VCE npn (c) C VCE iC1 <iC2<iC3 B Darlington usable range E (e) IB (d)
logIC pulse control ICmax Pmax second breakdown limit VCEmax logVCE
I DS I DS 10 100 A A V = 15V 90 9 GS Drain Gate Source IDS Al 8 80 70 7 + SiO2 6 60 VDS 10V N+-Polysilicium _ + 5 50 N+ N P Gate V = 10V _ GS 4 40 VGS 5V 3 30 N+ _ Source 20 2 1 10 Drain 5V 4V 0 0 0 200 400 600 800 1000 V 0 2 4 6 8 10 V (a) (b) V DS V DS (c)
logIDS pulse control IDmax Pmax VDSmax logVDS
I CE I CE 150 20 C V = 10V 7V CE A ICE Emitter 9V Gate A Al V = 18V 8V CE 15 100 + SiO2 V = 15V G CE VCE 10 N+-Polysilicium + N+ P _ _ N 50 V = 12V CE 6V VGE 5 P+ _ V = 10V CE V = 6V CE 5V 0 E 0 200 400 600 800 1000 V Collector 0 V 0 2 4 6 8 10 V CE V CE (c) (a) (b) (d)
+ VBB + VBB R R IDS IDS VDS VDS VGS VGS MOSFET IGBT 15V 15V VGS VGS 0 0 ICE Itail IDS 0 0 1 s � + VBB + VBB VDS V CE 0 0
+ n source gate gate + + p p p n Drift layer + n 4H-SiC substrate
drain source dielectric gate AlGaN barrier III N ohmic GaN buffer Transition layer Si substrate
SOURCE PASSIVATION LAYER D + N N + + + + + + + P P P P P P P GATE - N C + N (b) DRAIN S (a)
PASSIVATION CATHODE LAYER + N GATE A + + + P P P + + P P N + + + N N P G K ANODE
ANODE OXIDE OXIDE GATE POLYSILICON POLYSILICON + + } } } N N + ON - FET P CHANNEL (ANODE) J1 P - (ON - FET N(PNP - BASE, P - (ON - FET SOURCE) OFF - FET DRAIN) SOURCE) (OFF - FET CHANNELS) A P - G (NPN BASE, ON - FET DRAIN) P BUFFER + N SUBSTRATE K CATHODE
U (kV) max IGCT 10kV 5kV 2,5kV 1kV Thyristor IGBT (BJT) (grid commutation) MOS- 1kA 10kA 100A FET I (A) max 100Hz 1kHz GTO 10kHz Traction applications 100kHz 100kHz (IGBT and IGCT) f (Hz) max
a) Classification of semiconductors unipolar bipolar majority charge carriers majority and minority Conduction charge carriers Schottky-Diode Diode, thyristor, BJT, Types MOSFET, JFET, SIT IGBT, GTO, IGCT, SITh, MCT none Conduction modulation injection of charge carriers high (exc.: Schottky) Forward voltage drop low short Switching time medium to long high Switching frequency low to medium voltage Control by current (voltage for IGBT) low Control power high (low for IGBT) low Driver cost high (low for IGBT) high cost/chip area low (high for SITh) Typical values b) Imax toff Pmax Vmax Frequency Type [A] [kVA] [V] [ s] [kHz] � 1400 300 15 to 25 500 0.5 to 5 BJT/darlington 600 500 5 to 10 150 0.5 to 5 1000 80 1 to 3 40 2 to 50 (with fine structure) IGBT 3000 1000 0.5 tt 3 3000 to 150 1000 2000 0.5 to 3 2000 to 150 MOSFET 1000 20 0.1 to 0.3 50 to 3000 60 150 0.1 to 0.3 20 to 3000 SIT 1400 300 0.1 to 0.3 200 30 to 300 GTO 4500 3000 10 to 25 10000 0.2 to 1 IGCT 6000 3000 2 to 5 10000 0.5 to 2 SITh 2000 600 2 to 4 300 1 to 10
Semiconductor Darlington BJT MOSFET IGBT Symbol B E S G S E G E + + + N N N P P P - - - N N N Structure + + + N N P C D C Blocking properties average low high (upper limits) Control circuit average small minimal complexity high low low & power Switching properties average short average Switch-on time long short average Switch-off time high low average Switching loss Conducting properties quite high high low Current low rather low high Power losses Pulse frequency =4kHz =250kHz 10kHz limit for 0.5 IDC
max power max max max switching max (3-phase) properties reverse forward frequency forward voltage current voltage [V] [A] [kHz] [V] - low current pulse for switching-on 0-5000 5000 0.4 20 MW 600-6000 Thyristor - switch-off requires killer circuit (Silicon Controlled - high overload allowed Rectifier, SCR) - low switching frequency 10 MW - low current pulse for switching-on 200 6000 1 Gate Turn-Off 800-6000 - high current pulse for switching-off Thyristor (500 Hz - lower maximum values than SCR (GTO) for high power) - improved switching compared to GTO - lower switching and conduction losses than IGCT 4500 3000 2 10 MW GTO en IGBT - 6000 2000 - snubber circuits not required - conduction requires continuous basis current Bipolar transistor 500 10 800 kW - reverse current pulse for switching-off 50 50 (BJT of HFBT) | (500Hz for (now replaced - high switching frequencies | and 1400 300 high power) by IGBT) darlington - quite low pulse for switching on and off Power-Mosfet 150 3000 40 kW - quite high switching fequencies 50 0 | | (5-10kW economical - rather high ON-state resistance limit, for higher 1000 20 - no reverse voltage allowed rather IGBT) 200 2000 100 quite low pulse for switching on and off Insulated-Gate 500 (lateral) | 2000 kW Bipolar Transistor | 500 1000 (IGBT) 3000 (vertical)
SIT MOSFET IGBT GTO SITh IGCT BJT typical (maximum) values 800 V 600 V 500 V 3000 V 4 kV 1500 V 4 kV for voltage and current 100 A 20 A 20 A 1000 A 2 kA 600 A 2 kA 5 kW typical converter power 100 kW 220kW 10 MW 20 MW 20 MW 1 MW (three-phase) (10 kW) UG UG UB UG UG UG UG typical gate signals IG IG IB IG IG IG IG t t t t 20 10 10 80 20 required power W W W W W 0,6 0,6 for the control 10 5 5 40 10 W W 0,2 0,2 20 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 100 200 0 20 40 0 10 20 0 1 kHz kHz 2 0 5 kHz 10 10 0 1 3 0 2 6 kHz kHz kHz kHz 2 kHz kHz kHz f f f f f f f 10 50 200 20 100 5 20 0.05 5 1 3 1 2 1 fp kHz 2.7 3.9 1.8 2.0 total control 39 52 21 60 60 90 63 195 30 60 Ps W power specific 0.02 0.04 0.1 0.13 0.35 1.0 0.05 0.08 0.007 0.008 0.03 0.05 0.035 0.1 control PST/PSR % power minimal complexity of the average - high average high average - high minimal control circuit (integrated)
IR reverse leakage current VR reverse blocking voltage repetitive also IRRM repetitive maximal reverse leakage current also VRRM (also for diodes) maximal reverse IRRMS (M) effective maximal reverse leakage current RRSM blocking voltage peak (surge) VRNM non-repetitive VD forward blocking voltage ID forward leakage current VDRM repetitive also IDRM repetitive maximal direct leakage current also (for thyristors) maximal direct (forward) VDSM I RMS (M) effective maximal direct leakage current blocking voltage D peak (surge) VDNM non-repetitive IL latching current IH holding current IT direct current VT PT conduction loss on-state voltage forward voltage drop (ITAV (M); ITRMS (M); ITSM; ITCM; ...) (for diodes: T F) � dv di dt dt max max (also for diodes) trr reverse recovery time toff of tq turn-off time ton = tgt gate controlled turn-on time (for thyristors) = ts (carrier storage time) + tf (fall time) = tgd (delay time + tr (rise time) ton = tgt gate controlled turn-on time toff of tgq gate controlled turn-off time (for GTOs) = tgd (delay time + tr (rise time) =tgs (carrier storage time) + tgf (fall time) PG control (gate) power VG gate voltage IG gate current IGT minimum gate triggered current VGT minimum gate triggered voltage IGD maximum gate non-triggered current VGD maximum gate non-triggered voltage
Recommend
More recommend