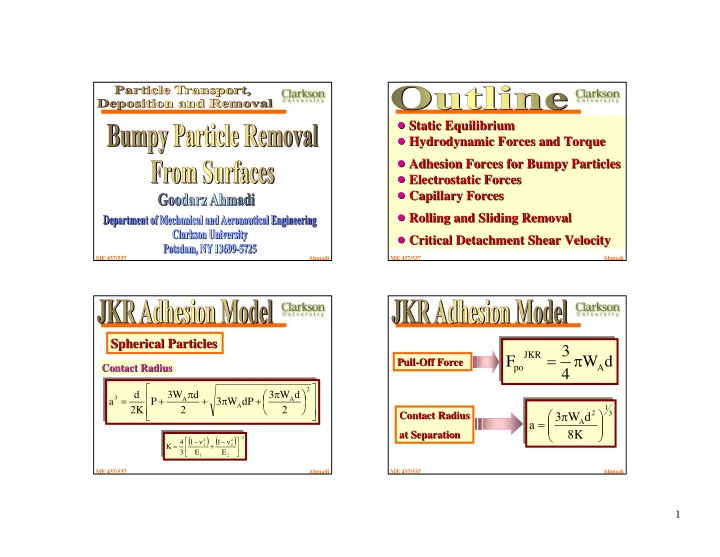

! Static Equilibrium ! Static Equilibrium ! Hydrodynamic Forces and Torque ! Hydrodynamic Forces and Torque ! Adhesion Forces for Bumpy Particles ! Adhesion Forces for Bumpy Particles ! Electrostatic Forces ! Electrostatic Forces ! Capillary Forces ! Capillary Forces ! Rolling and Sliding Removal ! Rolling and Sliding Removal ! Critical Detachment Shear Velocity ! Critical Detachment Shear Velocity ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi Spherical Particles Spherical Particles 3 = π JKR F W d Pull- -Off Force Off Force Pull Contact Radius Contact Radius po A 4 ⎡ ⎤ π ⎛ π 2 ⎞ d 3 W d 3 W d ⎢ ⎥ = + + π + ⎜ ⎟ 3 A A a P 3 W dP ⎢ A ⎝ ⎠ ⎥ 1 2 K 2 2 ⎛ π ⎞ ⎣ ⎦ 2 3 Contact Radius Contact Radius 3 W d = ⎜ ⎟ A a ⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ⎠ 8 K at Separation at Separation ( ) ( ) − ⎡ ⎤ 1 − ν − ν 2 2 4 1 1 = + ⎢ 1 2 ⎥ K ⎣ ⎦ 3 E E 1 2 ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi 1
Schematics of a Schematics of a β 2 3 Bumpy Particle Bumpy Particle = π β Adhesion Force Adhesion Force JKR f W Per contact Bump Per contact Bump po A 2 d d β = Total 3 Total n n N = π β JKR F N W u b Adhesion Adhesion ad c A 2 Force Force ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi 2 2 n e Capillary Force Capillary Force − Per Contact Bump Per Contact Bump Boltzmann Boltzmann dkT e = f(n) Charge Charge = 4 πσβ 2 2 + ∞ n e f c Distribution Distribution − ∑ dkT e = −∞ n = πσβ Average Number Average Number Total Capillary Total Capillary F 4 N n ≈ 2 . 37 d of Charge of Charge c c Force Force ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi 2
Diffusion Charging Diffusion Charging Boltzmann Charge Distribution Charge Distribution Boltzmann π Average Absolute Diameter Neutral dkT d c = + Number of Charges Fraction 2 i n ln( 1 e N t ) d ( µ m ) f(0) diff i 2 2 e 2 kT 5 0.0606 5.29 10 0.0428 7.46 ε 2 3 Ed Field Field = 15 0.0349 9.17 n ε + Charging Charging field 2 4 e 20 0.03 10.55 ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi Spherical Particles Spherical Particles Diffusion and Field Charging Diffusion and Field Charging Diameter Number of Charges 2 q = − F qE { πε d ( µ m ) e 2 Diffusion Field Combined 16 y 1 4 2 4 3 o Coulomb 5 407 4340 4747 Im age 10 874 17361 18235 πε 3 6 2 qEd 3 d E + − o 15 1365 39062 40427 3 4 16 y 128 y 1 2 3 1 42 4 43 4 20 1870 69444 71314 dielectrop horetic Polarizati on ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi 3
= − F 1 . 5 qE e ⎡ ⎤ − + 2 2 2 2 q ( 1 3 / N ) [( 4 n 1 )( 3 / N ) − + Charge Charge b ⎢ ⎥ πε β + 2 2 2 3 / 2 ⎣ ⎦ 4 d 3 ( 4 n 1 ) o b − πε β 2 2 72 E o ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi π µ 3 f dC πµ 2 2 f d V = d = F V Hydrodynamic Hydrodynamic m Drag Force M Drag Force t t C Torque Torque C c c = + 0 . 687 C 1 0 . 15 Re d + = dV + ( ) dy Near Wall Near Wall = ρµ 1 u M 1 . 72 y 2 F 1 . 61 d V Lift Force 2 Lift Force l 1 Peak Velocity Peak Velocity 2 dV dy ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi 4
F Rolling Rolling l M t d + ≥ + + β M F (F F F )0.58n h h ad e c b F 2 t ≥ + + Sliding Sliding F k(F F F ) h ad c e Electrostatic Electrostatic + ≥ + + + F F F F F F F a ec ed ad ei ep c F F c e ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi + = + u y Saturation Saturation Charge Charge + + + = − β 2 ≤ v y , y 1 . 85 o + + + = β w 2 y z o β o = 0 . 01085 ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi 5
q=20 µ µ C/g C/g Neutral q=20 Neutral Particles Particles ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi Boltzmann Saturation Boltzmann Saturation Charge Charge Charge Charge ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi 6
q=20 µ µ C/g C/g Saturation q=20 Saturation Charge Charge ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi Boltzmann Saturation Boltzmann Saturation Charge Charge Charge Charge ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi 7
F l M t F d / 2 t a F a F e ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi N − 2 c ( 1 ) 2 3 q 0 . 13 N = − − N + r c F 1 . 5 qE ( ) πε β e 2 2 2 4 d N o − π β ε 2 2 2 24 N E . c o β 2 ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi 8
Boltzmann Saturation Boltzmann Saturation Charge Charge Charge Charge Rough Rough Rough Rough Particles Particles Particles Particles ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi Rough Rough Particles Particles ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi 9
� Rolling detachment is the dominant mechanism � Rolling detachment is the dominant mechanism for bumpy particle removal in turbulent flows. for bumpy particle removal in turbulent flows. � � Drag and hydrodynamic torque are dominant for Drag and hydrodynamic torque are dominant for particle detachment from the wall. particle detachment from the wall. � � Electrical Electrical forces forces contribute contribute significantly significantly to to particle particle adhesion. adhesion. � increasing the number of bumps reduces the � increasing the number of bumps reduces the adhesion force. adhesion force. � � Patch charge model presents a more realistic Patch charge model presents a more realistic picture picture of surface charge distribution. of surface charge distribution. ME 437/537 Ahmadi ME 437/537 Ahmadi 10
Recommend
More recommend