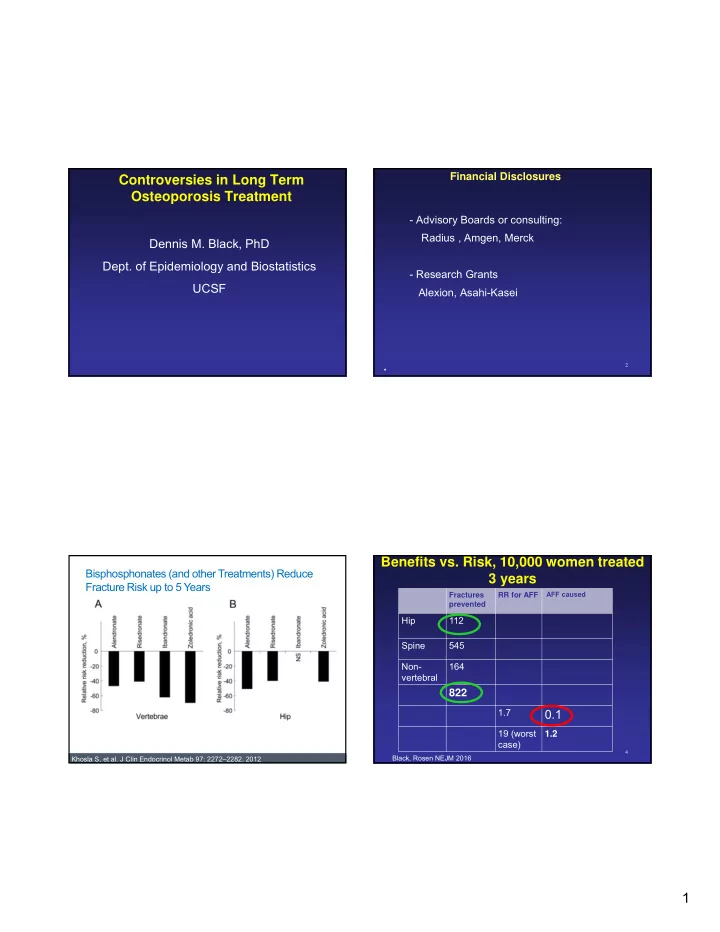

Financial Disclosures Controversies in Long Term Osteoporosis Treatment - Advisory Boards or consulting: Radius , Amgen, Merck Dennis M. Black, PhD Dept. of Epidemiology and Biostatistics - Research Grants UCSF Alexion, Asahi-Kasei 2 * Benefits vs. Risk, 10,000 women treated Bisphosphonates (and other Treatments) Reduce 3 years Fracture Risk up to 5 Years Fractures RR for AFF AFF caused prevented Hip 112 Spine 545 Non- 164 vertebral 822 1.7 0.1 19 (worst 1.2 case) 4 Black, Rosen NEJM 2016 Khosla S, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97: 2272–2282, 2012 1
BP treatment for up to 5 years: Treatment Beyond 5 Years the Bottom Line Benefits for BP treatment (for 3-5 Bisphosphonates years) far outweigh any risks, even Alendronate and Zol allowing for some risk of AFF. Other BPs Denosumab What about treatment beyond 5 years? 5 6 Osteoporosis Treatment Long-term Randomized Design of the FIT Long-Term Extension Extension Studies for Alendronate and ZOL (to 10 years) of Alendronate (FLEX)* FIT N = 6,459 RCT – EXT2 3 RCT – EXT1 2 HORIZON-PFT 1 Z6 (n = 616) Z9 (n = 95) Zoledronic acid ZOL (n = 3889) Mean ALN use: Z3P3 (n = 617) Z6P3 (n = 95) PBO (n = 3876) Placebo N = 3,223 Alendronate N = 3,236 5 years RCT – FLEX 6 FIT 4,5 Alendronate ALN 5 mg (n = 329) or 10 mg (n = 333) ALN (n = 3236) PBO (n = 437) PBO (n = 3223) Randomized in FLEX N = 1,099 FLEX (5 yrs) VERT- MN 7 OL- EXT 9 RCT – EXT 8 RI S 7 yrs (n = 83) Risedronate RIS 2.5 mg (n = 408) RIS (n= 135) PBO 5 yrs/ RI S 2yrs 5 mg (n = 407) PBO (n= 130) (n = 81) PBO (n = 407) 60% 40% Alendronate, 5 or 10 mg 0 2 4 6 8 10 Placebo N = 437 N = 662 Time (Years) ALN = alendronate; DB = double-blind; EXT 1= extension 1; EXT 2= extension 2; FIT = Fracture Intervention Trial; FLEX = FIT Long-term EXtension; HORIZON-PFT = Health Outcomes and Reduced Incidence with Zoledronic acid Once Yearly Pivotal Fracture Trial; OL, Open-label; PBO = placebo; RCT = randomized controlled trial; RIS = risedronate; VERT-MN = Vertebral Efficacy with Risedronate Therapy MultiNational; Z3P3 = zoledronic acid treatment for 3 years followed by placebo for 3 years; Z6 = zoledronic acid treatment for 6 years; ZOL = zoledronic acid. BMD: Primary endpoint 1. Black DM, et al. N Engl J Med . 2007; 356: 1809-1822. 2. Black DM, et al. J Bone Miner Res . 2012; 27: 243-254. 3. The Effect of 6 versus 9 Years of Zoledronic Acid Treatment in Osteoporosis: A Randomized Extension to the HORIZON-Pivotal Fracture Trial (PFT).Presented at ASBMR 2013 (abstract no. SA0389). 4. Black DM, et al. Lancet . 1996; 348: 1535-1541. 5. Cummings SR, et al. JAMA . 1998; 280: 2077–2082. 6. Black DM, et al. JAMA . 2006; 296: 2927-2938. 7. Reginster J-Y, et al. Osteoporos Int . 2000; 11: 83–91. 8. Sorensen OH, et al. Bone . 2003; 32: 120-126. 9. Mellström DD, et al. Calif Tissue Int . 2004; 75: 462-468. Fractures: Exploratory endpoint * Black, et al, JAMA 12/2006 2
FLEX: Alendronate Reductions (RR) for fractures for continuing bisphosphonates: Randomized, Double-blind Treatment Alendronate and ZOL 5 years of ALN followed by 5 more years or PBO Alendronate FLEX: Incidence of Fracture by Treatment Group (FLEX: 5 yrs/5 yrs Fractures Placebo, No. Pooled Relative Risk ( 9 5 % 1.00 (0.8, 1.3) Clinical Fracture ( % ) Alendronate, Confidence I nterval) * ( n= 4 3 7 ) No. ( % ) 0.45 (0.2, 0.85) Vertebral FX ( n= 6 6 2 ) (clinical) Vertebral Zoledronic acid: Clinical 2 3 ( 5 .3 ) 1 6 ( 2 .4 ) 0 .4 5 ( 0 .2 4 – 0 .8 5 ) HORIZON: 3yrs/3 yrs . Morphom etric 4 6 ( 1 1 .3 ) 6 0 ( 9 .8 ) 0 .8 6 ( 0 .6 0 – 1 .2 2 ) Clinical Fracture 0.99 (0.7, 1.5) Clinical Vertebral FX Nonspine 8 3 ( 1 9 .0 ) 1 2 5 ( 1 8 .9 ) 1 .0 0 ( 0 .7 6 – 1 .3 2 ) 0.48 (0.3, 0.9) (morphometric) Hip 1 3 ( 3 .0 ) 2 0 ( 3 .0 ) 1 .0 2 ( 0 .5 1 – 2 .1 0 ) 0.1 1 10 3 Relative Hazard ( ± 95% CI) Favors Bisphosphonate Favors Placebo Black DM, et al. JAMA. 2 0 0 6 ;2 9 6 :2 9 2 7 – 2 9 3 8 . Black JAMA 2006;Black et a. JBMR 2012 Fracture reductions with long-term continuation What about long term safety? Does AFF risk of bisphosphonates (2 RCTs) increase with longer duration of treatment? • Fracture results for Alendronate and Zol • Very controversial question o Continuing lowers vertebral fractures risk vs discontinuing o Continuing vs. discontinuing no effect on non-vertebral • 2012 Kaiser SC case series of AFF − Confidence intervals are wide and allow for possible benefit o Influential but methodologic flaws • 2016 Danish cohort study • What about long term safety? Does AFF risk increase with o Used subtrochanteric/femoral shaft fractures (not adjudicated AFF) longer duration of treatment? o Suggests benefits vs. risks strongly favorable for long term treatment Black JAMA 2006; Black et a. JBMR 2012 Dell JBMR 2012; Abrahamsen BMJ 2016 3
Do Atypical Femur Fractures Increase Do Atypical Femur Fractures Increase with Duration of Treatment? with Duration of Treatment? AFF cases from Kaiser S. Calif* Recent Danish Cohort (81,000 users)* ST/FS: Subtrochanteric/Fem Shaft fracture Incidence of AFF Years of use of bisphosphonates 13 14 Dell et. al. JBMR 12/12 Abrahamsen, et al BMJ 6-16 Is AFF incidence increased with longer Is AFF incidence increased with longer duration of use? duration of use? - Results are mixed, not certain - Most prudent belief: AFF risk increases with treatment duration - Therefore, best to minimize length of treatment And continue to treat only those who will most benefit from longer term treatment Risks of long term osteo therapy 15 16 4
Which patients benefit most from Which patients benefit most from long term continuation of ALN (or ZOL) and should ALN (up to 10 years) and should therefore therefore be continued? be continued? • Primary benefit is in reduction of vertebral fractures • Our recommendations from FLEX* (5 years previous ALN). Continue alendronate in: • Therefore, logical to continue those at highest risk of Women with femoral neck BMD T-score <-2.5 vertebral fractures o In women with existing vertebral fractures, continue treatment in those o o NEJM; 5/2012 with fn BMD T-score <-2.0 Others can discontinue with retention of some benefits for up to 5 − Perspective from FDA together with an analysis from FLEX o years o Consider femoral neck BMD and vertebral fracture status at the end of the initial treatment period Black, et al. NEJM 2012 May 31;366(22):2051-3 *Black, et al. NEJM 5/12 Number 5 Yr risk (%) Other factors relevant to deciding to Femoral Neck BMD T- Needed to Clinical Vert. Score (start FLEX) Fx. In PBO Treat discontinue after 5 years FLEX vertebral All women in study fracture benefit: All BMD values 5.5 34 - BMD and vertebral fracture status at time on discontinuation ≤ -2.5 9.3 21 Who to continue? - *Bone markers not useful -2.5 to -2 5.8 33 ≥ -2 2.3 81 - Perhaps other factors such as age and fracture on No prevalent vert. fracture (start of FLEX ) treatment ≤ -2.5 8.0 24 -2.5 to -2 3.0 63 ≥ -2 1.8 102 Prevalent vertebral fracture (start of FLEX) ≤ -2.5 11.1 17 -2.5 to -2 11.1 17 19 ≥ -2 3.7 51 Black, et al. NEJM. 2012 May 31;366(22):2051-3 *Bauer, et al. JAMA IM (5/14) 5
Overview for long-term use of alendronate Summary of benefits vs. risks for and ZOL ALN or ZOL treatment as a function of time Treatment Beyond 10 Treatment Beyond 5 Treatment 3-5 years years with ALN (6 yrs - Some residual benefits after stopping for years with ZOL) alendronate and zoledronic acid - Reductions in spine fractures - Benefits of long-term use are smaller than benefits for short-term use Benefits Risks Benefits: Risks Benefits Risks - On the other hand, risks might be increasing over unproven uncertain Only Hip, non- time spine vertebral reductions and spine - Risk benefit ratio for long term continuation not as reductions favorable as for short-term use Long-term use of non-bisphosphonate Long-term use of other bisphosphonates therapies - Limited data for Risedronate and Ibandronate on - For Teriperatide, Denosumab, Raloxifene, HRT, long term use benefits are rapidly lost after discontinuation - Long term continuation seems to continue - Very different from Alendronate and Zoledronic lowered fracture risk (similar to ALN and ZOL) acid - BUT discontinuation likely results in faster loss of - Need to be continued long-term or switched to benefits of therapy another therapy after discontinuation - Different pharmacologic characteristics - For Risedronate and Ibandronate , after discontinuation, cannot assume same on-going benefits as seen with ALN and ZOL 6
Long-term treatment: Controversies and Thanks! unresolved questions.. • Does longer term treatment ... • Increase risks? • Decrease Benefits? • Value of drug holidays to reduce risks • Can we identify those at higher risks? If yes, then use shorter term therapy • Promising leads.. - Asians (RR=5-10) - Femoral geometry (more bowed femurs) 26 7
Recommend
More recommend