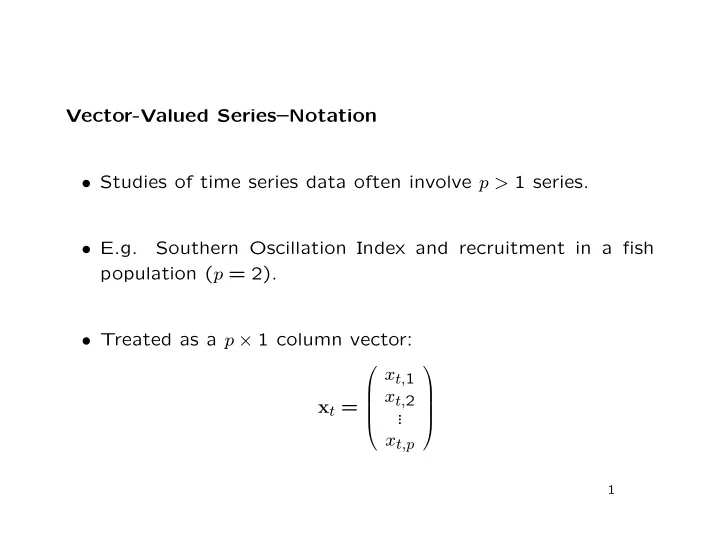

Vector-Valued Series–Notation • Studies of time series data often involve p > 1 series. • E.g. Southern Oscillation Index and recruitment in a fish population ( p = 2). • Treated as a p × 1 column vector: x t, 1 x t, 2 x t = . . . x t,p 1
Mean Vector • Assume jointly weakly stationary. • mean vector: � � E x t, 1 µ 1 � � E x t, 2 µ 2 µ = E ( x t ) = = . . . . . . µ p � � E x t,p 2
Autocovariance Matrix • Autocovariance matrix contains individual autocovariances on the diagonal and cross-covariances off the diagonal: �� � ( x t − µ ) ′ � Γ( h ) = E x t + h − µ γ 1 , 1 ( h ) γ 1 , 2 ( h ) γ 1 ,p ( h ) . . . γ 2 , 1 ( h ) γ 2 , 2 ( h ) γ 2 ,p ( h ) . . . = . . . ... . . . . . . γ p, 1 ( h ) γ p, 2 ( h ) γ p,p ( h ) . . . 3
Sample mean and autocovariances • sample mean: n x = 1 � ¯ x t n t =1 • sample autocovariance: n − h Γ( h ) = 1 � � x ) ′ ˆ � x t + h − ¯ x ( x t − ¯ n t =1 Γ( h ) ′ . for h ≥ 0, and ˆ Γ( − h ) = ˆ 4
Multidimensional Series (Spatial Statistics) • Some studies involve data indexed by more than one variable. • E.g. soil surface temperatures in a field • Notation: x s is the observed value at location s ( s for s patial). 5
Soil temperatures 10 Temperature 8 6 60 4 rows 40 30 20 20 c o l u m n s 10 6
Autocovariance and Variogram � � • Stationary : E ( x s ) and cov do not depend on s . x s + h , x s • For a stationary process, the autocovariance function is � � �� �� �� γ ( h ) = cov = E x s + h − µ x s − µ x s + h , x s � � � � • Intrinsic : E x s + h − x s and var x s + h − x s do not depend on s . • For an intrinsic process, the (semi-)variogram is V x ( h ) = 1 � � 2var x s + h − x s 7
• A stationary process is intrinsic (see Problem 1.26), but an intrinsic process is not necessarily stationary. • In one dimension, the random walk is intrinsic but not sta- tionary. • When stationary, V x ( h ) = γ ( 0 ) − γ ( h ). • Isotropic : an intrinsic process is isotropic if the variogram is a function only of | h | , the Euclidean distance between s + h and s . 8
Recommend
More recommend