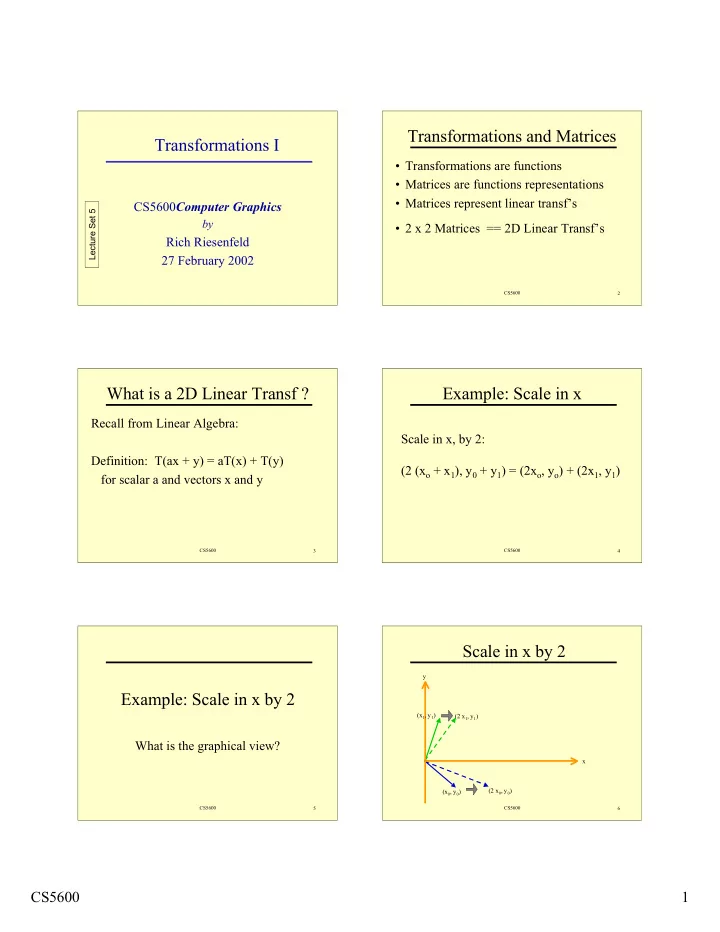

Transformations and Matrices Transformations I • Transformations are functions • Matrices are functions representations • Matrices represent linear transf’s CS5600 Computer Graphics Lecture Set 5 by • 2 x 2 Matrices == 2D Linear Transf’s Rich Riesenfeld 27 February 2002 CS5600 2 What is a 2D Linear Transf ? Example: Scale in x Recall from Linear Algebra: Scale in x, by 2: Definition: T(ax + y) = aT(x) + T(y) (2 (x o + x 1 ), y 0 + y 1 ) = (2x o , y o ) + (2x 1 , y 1 ) for scalar a and vectors x and y CS5600 3 CS5600 4 Scale in x by 2 y Example: Scale in x by 2 (x 1 , y 1 ) (2 x 1 , y 1 ) What is the graphical view? x (x 0 , y 0 ) (2 x 0 , y 0 ) CS5600 5 CS5600 6 CS5600 1
( 2x o + 2x 1 , y 0 + y 1 ) ( 2 (x o + x 1 ), y 0 + y 1 ) y y (x 1 , y 1 ) (2 x 1 , y 1 ) (( x o + x 1 ), y 0 + y 1 ) ( 2 x o + 2 x 1 , y 0 + y 1 ) ( 2 (x o + x 1 ), y 0 + y 1 ) x x (2 x 0 , y 0 ) (x 0 , y 0 ) CS5600 7 CS5600 8 Summary on Scale ( 2 (x o + x 1 ), y 0 + y 1 ) y • “Scale then add,” is same as • “Add then scale” (( x o + x 1 ), y 0 + y 1 ) ( 2 (x o + x 1 ), y 0 + y 1 ) x CS5600 9 CS5600 10 Matrix Representation Matrix Representation Scale in x by 2: Scale in y by 2: 2 0 x = 2x 1 0 x = x 0 1 y y 0 2 y 2y CS5600 11 CS5600 12 CS5600 2
Matrix Representation Matrix Representation Showing Same y 0 + y 1 = 2(x 0 + x 1 ) 2 0 x 0 + x 1 Overall Scale by 2: y 0 + y 1 0 1 2x 0 + 2x 1 2 0 x = 2x = y 0 + y 1 0 2 y 2y CS5600 13 CS5600 14 Rotate by θ y What about Rotation? (0,1) Is it linear? θ θ x (1,0) CS5600 15 CS5600 16 Rotate by θ : 1 st Quadrant Rotate by θ : 1 st Quadrant y (1, 0) (cos θ , sin θ ) (cos θ , sin θ ) sin θ θ x (1,0) cos θ CS5600 17 CS5600 18 CS5600 3
Rotate by θ : 2 nd Quadrant Rotate by θ : 2 nd Quadrant y y (0,1) (0,1) θ cos θ θ θ θ x x (1,0) sin θ CS5600 19 CS5600 20 Rotate by θ : 2 nd Quadrant Summary of Rotation by θ (0, 1) (-sin θ , cos θ ) (1, 0) (cos θ , sin θ ) (0, 1) (-sin θ , cos θ ) CS5600 21 CS5600 22 Summary (Column Form) Using Matrix Notation 1 cos θ cos - sin 1 cos θ θ θ ⇒ = sin cos 0 sin θ θ θ 0 sin θ 0 sin cos - sin 0 - sin − θ θ θ θ = ⇒ sin cos 1 cos θ θ θ 1 cos θ (Note that unit vectors simply copy columns) CS5600 23 CS5600 24 CS5600 4
General Rotation by Matrix θ cos - sin x x cos - ysin Who had linear algebra? θ θ θ θ = sin cos y x sin y cos θ θ + θ Who understand matrices? CS5600 25 CS5600 26 Off Diagonal Elements 1 a x x ay + What do the off diagonal = elements do? 0 1 y y 1 0 x x = b 1 y bx y + CS5600 27 CS5600 28 Example 1 Example 1 1 0 x T ( x , y ) = y y T ( x , y ) = 0 . 4 1 y x ( 1 , 1 ) ( 0 , 1 ) ( 0 , 1 ) 0 . 4 x y x ( 1 , 1 ) + = 0 . 4 x y S S + x x ( 1 , 0 ) ( 1 , 0 ) ( 0 , 0 ) ( 0 , 0 ) CS5600 29 CS5600 30 CS5600 5
Example 1 Example 2 1 0 . 6 x T ( x , y ) = y y ( 1 , 1 . 4 ) T ( x , y ) = 0 1 y x ( 0 , 1 ) ( 0 , 1 ) 0 . 4 x y ( 1 , 1 ) x 0 . 6 y + + T(S) = y S ( 1 , 0 . 4 ) x x ( 1 , 0 ) ( 0 , 0 ) ( 0 , 0 ) CS5600 31 CS5600 32 Example 2 Example 2 T ( x , y ) x 0 . 6 y = y + y T ( x , y ) = x 0 . 6 y y + ( 0 , 1 ) ( 0 . 6 , 1 ) y ( 0 , 1 ) ( 1 , 1 ) ( 1 . 6 , 1 ) S T(S) x x ( 1 , 0 ) ( 1 , 0 ) ( 0 , 0 ) ( 0 , 0 ) CS5600 33 CS5600 34 Summary Double Shear Shear in x: 1 a 1 0 ( ab) a 1 1 a x x ay + + Sh x = = = 0 1 b 1 b 1 0 1 y y Shear in y: 1 0 1 a a 1 1 0 x x = b 1 0 1 b ( ab) 1 Sh y + = = b 1 y bx y + CS5600 35 CS5600 36 CS5600 6
Sample Points: unit inverses Geometric View of Shear in x 1 a a 0 − = ( a , 1 ) − 0 1 1 ( 0 , 1 ) ( 1 , 1 ) 1 1 0 1 1 ( 1 , 0 ) ( 1 , 0 ) = b 1 b 0 − CS5600 37 CS5600 38 Another Geometric View of Another Geometric View of Shear in x Shear in x y y y x x x 39 40 Another Geometric View of Geometric View of Shear in y Shear in y y y ( 1 , 1 ) ( 0 , 1 ) ( 0 , 1 ) ( 0 , 0 ) ( 0 , 0 ) ( 1 , 0 ) ( 1 , b ) − x 42 x h h CS5600 41 CS5600 7
Another Geometric View of “Lazy 1” Shear in y y x x 0 1 0 y y 0 1 0 = 0 0 1 1 1 x 43 CS5600 44 Translation in x Translation in x x x x d x d 0 1 0 1 0 + x x y y 0 1 0 y d y y d 0 1 = = + y 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 CS5600 45 CS5600 46 Homogeneous Coordinates Homogeneous Coordinates x x λ x x 1 0 0 x y , for 0 y ↔ λ ≠ λ = y y 0 1 0 = y 1 λ 0 0 1 1 1 CS5600 47 CS5600 48 CS5600 8
Homogeneous Coordinates Homogeneous Coordinates For 0, λ ≠ An infinite number of points correspond to (x,y,1). They constitute the whole line (tx,ty,t). x x x 0 1 0 λ w (tx,ty,t) x λ y y y 0 1 0 = = λ ↔ y λ w = 1 (x,y,1) 0 0 1 1 1 1 y λ λ Homogeneous term effects overall scaling x CS5600 49 Next Class: Compound Transformations We’ve got Affine • Build up compound transformations Transformations by concatenating elementary ones • Use for complicated motion Linear + Translation • Use for complicated modeling CS5600 51 CS5600 52 CS5600 9
Recommend
More recommend