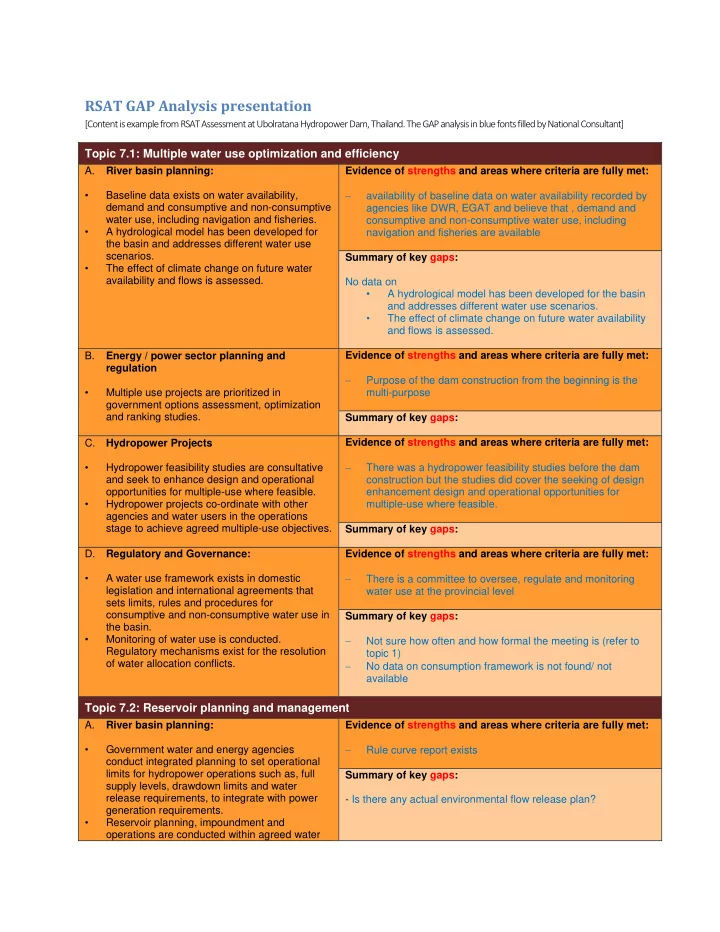

RSAT GAP Analysis presentation [Content is example from RSAT Assessment at Ubolratana Hydropower Dam, Thailand. The GAP analysis in blue fonts filled by National Consultant] Topic 7.1: Multiple water use optimization and efficiency A. River basin planning: Evidence of strengths and areas where criteria are fully met: • Baseline data exists on water availability, availability of baseline data on water availability recorded by demand and consumptive and non-consumptive agencies like DWR, EGAT and believe that , demand and water use, including navigation and fisheries. consumptive and non-consumptive water use, including • A hydrological model has been developed for navigation and fisheries are available the basin and addresses different water use scenarios. Summary of key gaps: • The effect of climate change on future water availability and flows is assessed. No data on • A hydrological model has been developed for the basin and addresses different water use scenarios. • The effect of climate change on future water availability and flows is assessed. B. Energy / power sector planning and Evidence of strengths and areas where criteria are fully met: regulation Purpose of the dam construction from the beginning is the • Multiple use projects are prioritized in multi-purpose government options assessment, optimization and ranking studies. Summary of key gaps: C. Hydropower Projects Evidence of strengths and areas where criteria are fully met: • Hydropower feasibility studies are consultative There was a hydropower feasibility studies before the dam and seek to enhance design and operational construction but the studies did cover the seeking of design opportunities for multiple-use where feasible. enhancement design and operational opportunities for • Hydropower projects co-ordinate with other multiple-use where feasible. agencies and water users in the operations stage to achieve agreed multiple-use objectives. Summary of key gaps: D. Regulatory and Governance: Evidence of strengths and areas where criteria are fully met: • A water use framework exists in domestic There is a committee to oversee, regulate and monitoring legislation and international agreements that water use at the provincial level sets limits, rules and procedures for consumptive and non-consumptive water use in Summary of key gaps: the basin. • Monitoring of water use is conducted. Not sure how often and how formal the meeting is (refer to Regulatory mechanisms exist for the resolution topic 1) of water allocation conflicts. No data on consumption framework is not found/ not available Topic 7.2: Reservoir planning and management A. River basin planning: Evidence of strengths and areas where criteria are fully met: • Government water and energy agencies Rule curve report exists conduct integrated planning to set operational limits for hydropower operations such as, full Summary of key gaps: supply levels, drawdown limits and water release requirements, to integrate with power - Is there any actual environmental flow release plan? generation requirements. • Reservoir planning, impoundment and operations are conducted within agreed water
management limits and thresholds for the basin. B. Energy / power sector planning and Evidence of strengths and areas where criteria are fully met: regulation There is flood rule and flood protection plan • Projects selected for development aim to Irrigation is the first priority and dam is oriented to be a multi- minimise the area flooded per unit of energy. purpose • Schemes make best use of storage characteristics and operations to meet current Summary of key gaps: and future electrical load patterns and other water demands in the basin. C. Hydropower Projects Evidence of strengths and areas where criteria are fully met: • Reservoirs are designed to avoid, mitigate and Need input from EGAT off-set impacts including loss of forest Some planning resources, population displacement and greenhouse gas emissions. Summary of key gaps: • Reservoir filling plans addresses biomass removal, the timing of environmental and social Compensation model does exist plans and downstream impacts. - Not sure the method of resettlement back in 60s • Reservoir filling and operational procedures are - Signification of deforestation ( land conversion from forest to in place to address reservoir management agriculture – now only 15% of remaining forest) issues. D. Regulatory and Governance: Evidence of strengths and areas where criteria are fully met: • Project agreements and regulations provide clear institutional arrangements for reservoir Summary of key gaps: ownership, access and management responsibility. Multiple agencies in charge of the Ubolrattana Dam ( Dam • Roles and responsibilities are allocated and infrastructure – EGAT, Water in the dam – Dept. of there is a coordinated approach to managing Fisheries, Pier – Dept. of Marine, Forest – Dept. of Forestry) compliance with reservoir management, operating rules, storage and release commitments. Topic 7.3: Coordinated hydropower operation A. River basin planning: Evidence of strengths and areas where criteria are fully met: • There is allocation of responsibility and institutional arrangements in place for Summary of key gaps: coordinated water management and power generation in the basin amongst multiple Need input from EGAT on hydropower operations projects. coordination • Hydropower operations coordinate with other There are many agencies involve in water management both water users in the basin. at Ubolrattana dam and along the Nam Pong river B. Energy / power sector planning and Evidence of strengths and areas where criteria are fully met: regulation Not applicable • Coordination of the power system, including hydropower cascades, makes optimal use of Summary of key gaps: hydropower capability (peaking, load following) and achieves balanced and equitable water use Not applicable at the sub-basin level. • Project level agreements include provision for coordination of operations amongst projects in a cascade or sub-basin and consistent design and operational mitigation measures.
C. Hydropower Projects Evidence of strengths and areas where criteria are fully met: • Projects coordinate their operations to achieve Coordinating with RID for multipurpose benefit basin objectives, efficient water use and Check on the environmental flow (actual) optimize electricity generation. • Design and operational environmental Summary of key gaps: mitigation measures are consistent and coordinated between projects to optimize No data on environmental flow and effectiveness outcomes. D. Regulatory and Governance: Evidence of strengths and areas where criteria are fully met: • Regulatory framework for hydropower includes Not applicable provision for multiple projects in a cascade to coordinate at all project stages for optimal Summary of key gaps: electricity generation, and efficient resource use. Not applicable • Transboundary mechanisms exist for coordination and cooperation for hydropower operations on international rivers Topic 7.4: Downstream and environmental flows A. River basin planning: Evidence of strengths and areas where criteria are fully met: • Environmental flows assessment has been Overview study conducted by Khon Kean University in 2008 conducted for all river reaches affected or potentially affected by hydropower operations to Summary of key gaps: establish criteria and thresholds for environmental and downstream flows. It We don’t have any data and/or evident on the effectiveness includes assessment of wetlands and floodplains. It is consultative and informed by scientific baseline data. B. Energy / power sector planning and Evidence of strengths and areas where criteria are fully met: regulation Rule curve report • Water management constraints on electricity dispatch are embedded in electricity dispatch and off-taker agreements. Summary of key gaps: • Compliance is monitored and publicly disclosed. • Project agreements include design and We don’t have data on the monitoring and publicity operational performance criteria to deliver Need to find out from EGAT about the environmental flow agreed environmental and downstream flows. C. Hydropower Projects Evidence of strengths and areas where criteria are fully met: • Projects conduct environmental and downstream flow assessments in feasibility stage to inform project design and operations. • Project design and operation rules address commitments made for environmental flows and Summary of key gaps: downstream water releases. • Hydropower projects comply with environmental We don’t know how environmental flow apply at the project and downstream flow commitments. level D. Regulatory and Governance: Evidence of strengths and areas where criteria are fully met: • International agreements, national laws and basin plans relating to water allocation include provision for environmental flows. • ESIA regulations and guidelines include
Recommend
More recommend