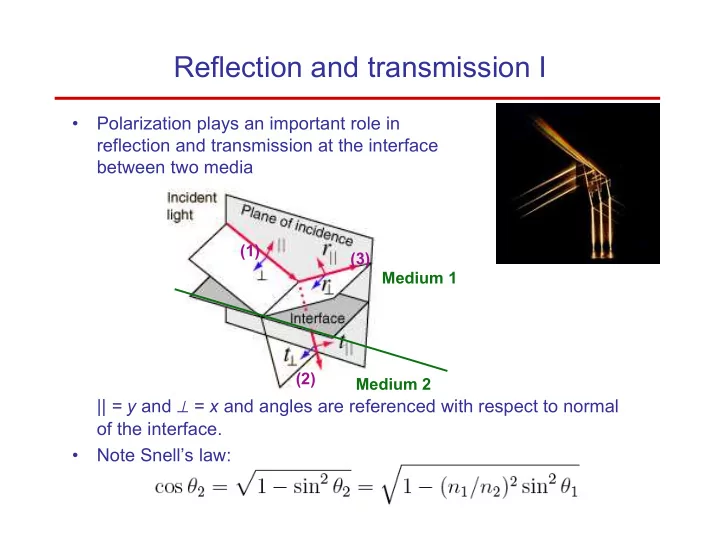

Reflection and transmission I • Polarization plays an important role in reflection and transmission at the interface between two media (1) (3) Medium 1 (2) Medium 2 || = y and ⊥ = x and angles are referenced with respect to normal of the interface. • Note Snell’s law: P. Piot, PHYS 630 – Fall 2008
Reflection and Transmission II • We write • Boundaries condition on E and B gives (Fresnel equations) P. Piot, PHYS 630 – Fall 2008
TE (or s) polarization • External reflection (n1<n2) • Internal reflection (n1>n2) Arg(rx) Arg(rx) |rx| |rx| θ 1 (deg) θ 1 (deg) P. Piot, PHYS 630 – Fall 2008
TM (or p) polarization • External reflection (n1<n2) • Internal reflection (n1>n2) Arg(rx) Arg(rx) |rx| |rx| θ 1 (deg) θ 1 (deg) Brewster angle P. Piot, PHYS 630 – Fall 2008
Optics in anisotropic crystals • A dielectric medium is said to be anisotropic if its optical properties depends on the direction • Anisotropy depends on the crystal structure – If molecules randomly located in space and are isotropic (or oriented along random directions) the medium is isotropi (gases, liquid and amorphous solids) – If the structure takes the form of disjoined crystalline grains randomly oriented, the crystal is a polycrystalline and is in general anisotropic – If the molecules are organized in space according to a regular perioc pattern and oriented in the same direction, as in crystals, the medium is in general anisotropic P. Piot, PHYS 630 – Fall 2008
Permittivity tensor • Only anisotropy is considered • The polarization and dielectric displacement are now given by and wherein χ is a tensor (= a 3x3 array) E x P x χ 11 χ 21 χ 12 χ 31 E y P y χ 22 χ 32 χ 13 χ 23 E z P z χ 33 P. Piot, PHYS 630 – Fall 2008
Principal axes • The elements of the permittivity tensor depend on the choice of coordinate system • However a coordinate system can be found such that the tensor is diagonal i.e. • This coordinate system define the principal axes and principal planes associated to the crystal. • The corresponding refractive indexes are known as principal indexes. P. Piot, PHYS 630 – Fall 2008
Biaxial, Uniaxial & isotropic crystal • Crystals with three different principal refractive indexes are referred to as biaxial crystals • Crystal with two different principal refractive indexes are referred to as uniaxial crystals • For uniaxial crystals, the refractive indexes are n 1 =n 2 =n o , and n 3 =n e where “o” stands for ordinary axis and “e” for extraordinary axis. • If n o >n e the crystal is said to be a positive uniaxial crystal P. Piot, PHYS 630 – Fall 2008
Recommend
More recommend