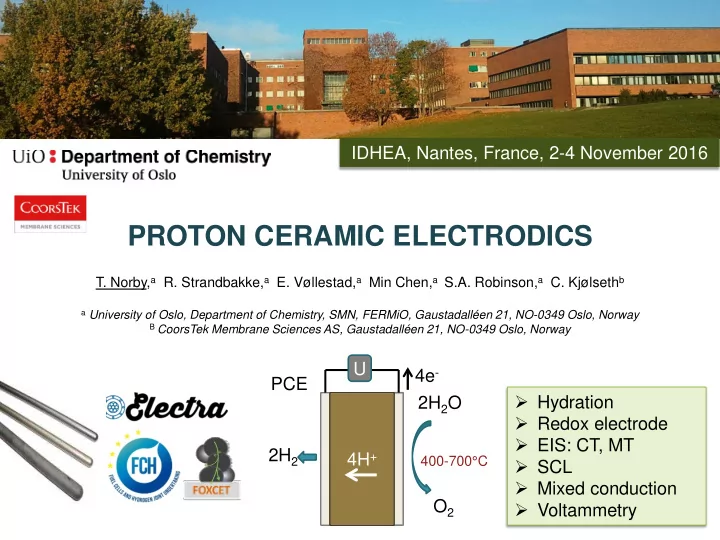

IDHEA, Nantes, France, 2-4 November 2016 PROTON CERAMIC ELECTRODICS T. Norby, a R. Strandbakke, a E. Vøllestad, a Min Chen, a S.A. Robinson, a C. Kjølseth b a University of Oslo, Department of Chemistry, SMN, FERMiO, Gaustadalléen 21, NO-0349 Oslo, Norway B CoorsTek Membrane Sciences AS, Gaustadalléen 21, NO-0349 Oslo, Norway U 4e - PCE Hydration 2H 2 O Redox electrode EIS: CT, MT 2H 2 4H + 400-700°C SCL Mixed conduction O 2 Voltammetry
The electrolyte; example Y-doped BaZrO 3 Doping reaction • • + → + + BaZrO / x 2BaO Y O 2Y v 5O 3 2 3 Zr O O Hydration • • • + + = x H O ( g ) v O 2 OH 2 O O O Note: This is not an electrode redox reaction. The charge carriers do not enter via an electrode reaction They are present in equilibrium with H 2 O(g)
Electrode redox reactions H 2 -side reaction − − − + ↔ + 2 H (g) 2O 2OH 2e 2 O O O 2 +H 2 O-side reaction − − − + + ↔ + 2 O (g) 4OH 4e 2H O(g) 4O 2 O 2 O
Electrode reaction pathways
H 2 -side + ↔ H (g) v H 2 ads 2, ads + ↔ H v 2 H 2, ads ads ads + ↔ + H v H v | 2 ads i i ads ↔ H H | 2 Diffusion i i, int + ↔ H (g) v H 2 ads 2, ads + ↔ H v 2 H 2, ads ads ads ↔ H H | 2 Diffusion ads ads, tpb + − ↔ + − + − 2 H O v OH e | 2 CT ads, tpb/i, int O ads, tpb/i, int O
O 2 +H 2 O side + ↔ O (g) v O 2 ads 2 , ads + ↔ O v 2 O 2 ads ads , ads ↔ O O | 2 Diffusion ads ads, tpb − − − − + + ↔ + + 2 O OH 2 e v OH O | 2 ads, tpb O ads, tpb ads, tpb O − − ↔ CT OH OH | 2 Diffusion ads, tpb ads − + − ↔ − + 2 OH OH O H O | 2 ads O O 2 ads ↔ + H O H O(g) v | 2 2 ads 2 ads
Charge transfer (CT) − − − + ↔ + + 2 H O v OH e ads, tpb/i, int O ads, tpb/i, int O 2 n Fi ( ) n F β − β = = 0 , 1 eq red red 0 red p H 2 - (and p H 2 O?)- G k Q Q red red , , , , ct red ct red react red prod red RT RT dependencies − − − − + + ↔ + + 2 O OH 2 e v OH O ads, tpb O ads, tpb ads, tpb O 2 n Fi ( ) n F β − β = = 0 , 1 eq ox ox 0 ox G k Q Q p O 2 - and pH 2 O- ox ox , , , , ct ox ct ox react ox prod ox RT RT dependencies
Cu and Pt point electrodes on BZCY in H 2 +H 2 O S.A. Robinson, C. Kjølseth, T. Norby, “Comparison of Cu and Pt point-contact electrodes on proton conducting BaZr 0.7 Ce 0.2 Y 0.1 O 3−d “, in pub.
Cu and Pt point electrodes on BZCY in H 2 +H 2 O S.A. Robinson, C. Kjølseth, T. Norby, “Comparison of Cu and Pt point-contact electrodes on proton conducting BaZr 0.7 Ce 0.2 Y 0.1 O 3−d “, in pub.
Mass transfer (MT) Adsorption Dissociation Dissolution Diffusion 2 ( 2 ) F = 0 1 / 2 eq G K p , , mt red mt red H RT 2 2 ( 4 ) F = 0 eq n m G K p p , , mt ox mt ox O H O RT 2 2
Cu and Pt point electrodes on BZCY in H 2 +H 2 O + − ↔ + − + − 2 H O v OH e ads, tpb/i, int O ads, tpb/i, int O 2 n Fi ( ) n F β − β = = 0 , 1 eq red red 0 red G k Q Q red red , , , , ct red ct red react red prod red RT RT CT MT 2 ( 2 ) F = 0 1 / 2 eq G K p mt , red mt , red H RT 2 S.A. Robinson, C. Kjølseth, T. Norby, “Comparison of Cu and Pt point-contact electrodes on proton conducting BaZr 0.7 Ce 0.2 Y 0.1 O 3−d “, in pub.
Electrode space charge layer (SCL) ∆ ϕ 2 ( 0 ) F red Fc u Fc u + + H H + + RT = ≈ eq H H G λ ∆ ϕ , ∆ ϕ scl red ( 0 ) F ( ) F x ∫ λ exp red exp dx RT RT 0
B+GB+SCL+CT for nanograined Ni on BZY in H 2 +H 2 O Min Chen, T. Norby, “Space Charge Layer Effect at the Ni/BaZr 0.9 Y 0.1 O 3- δ Electrode Interface in Proton Ceramic Electrochemical Cells”, under publication
Mixed conduction – example O 2 +H 2 O-side electrode Typical Ideal H + Ideal H + Ideal Model Typical PCFC PCFC oxide H + conductor PCFC conductor cathode cathode cathode conductor e - e - 4e - 4e - 2O 2- 2O 2- O 2 4e - 4H + 4H + 4e - O 2 O 2 4H + 4H + O 2 2H 2 O 2H 2 O 2H 2 O
PCFC oxygen electrodes (cathodes) Mixed conductivity: protons, oxide ions, electrons (holes) Typical Typical PCFC oxide H + cathode conductor e - e - 4e - 2O 2- 2O 2- O 2 4e - 4H + O 2 R. Strandbakke, V. Cherepanov, A. Zuev, D.S. Tsvetkov, C. Argirusis, G. Sourkouni-Argirusis, 2H 2 O S. Prünte, T. Norby, “Gd- and Pr-based double perovskite cobaltites as oxygen side electrodes for proton ceramic fuel cells and electrolyser cells”, Solid State Ionics , 278 (2015) 120.
Perovskite electrode on BaZr 0.7 Ce 0.2 Y 0.1 O 3 (BZCY) Impedance spectra yield apparent -1.2 electrode polarisation resistances -1.0 -0.8 Z // ( Ω cm 2 ) Electrolyte Electrode -0.6 -0.4 S1 S2 S0 R p 2 R p 1 -0.2 0.0 14.0 14.5 15.0 / ( Ω cm 2 ) Z
Perovskite electrode on BaZr 0.7 Ce 0.2 Y 0.1 O 3 (BZCY) …but a more correct treatment is required -1.2 needs more input parameters and assumptions -1.0 -0.8 Z // ( Ω cm 2 ) Electrolyte Electrode -0.6 -0.4 S1 S2 S0 R p 2 R p 1 -0.2 0.0 14.0 14.5 15.0 / ( Ω cm 2 ) Z Recipe: Get individual R v ’s from conductivity data Calibrate to R v at S0 Calculate properly R v +R p,1 at S1 Calculate properly R v +R p,1 +R p,2 at S2 Express and fit 4 unknown R p ’s to variations in T , p O 2 , p H 2 O
Perovskite electrode on BaZr 0.7 Ce 0.2 Y 0.1 O 3 (BZCY) Modelling by fitting all data T ( ° C) Protons vs oxide ions 700 600 500 400 Effect of electronic conduction 1 10 CT and MT(d) 0 1 2 )) 2 ) log( R ( Ω cm R ( Ω cm R p ,O 2- R p,H + -1 0.1 R p,d,H + R p,ct,H + R p R p,app -2 0.01 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 -1 ) 1000/T (K
Voltammetry Tafel plot displays the kinetics of only the forward or backward reaction Yields β , n, i 0 May require EIS to deconvolute R ’s and η ’s Example: Ni on BZY
Summary • • • + + = x Hydration H O ( g ) v O 2 OH 2 O O O + − ↔ − + − 2 H (g) 2O 2OH 2e Redox-reactions 2 O O − − − + ↔ + + 2 Reaction paths and CT H O v OH e ads, tpb/i, int O ads, tpb/i, int O EIS Separate into G+GB, (SCL?), CT, MT Pre-exponential: Microstructure Activation energy: Kinetics pH 2 , pH 2 O, pO 2 dependencies: Mechanistics D. Poetzsch, R. Merkle, J. Maier, J. Electrochem. Soc., 162 [9] (2015) F939. Mixed conduction Voltammetry
Acknowledgements The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Union's Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) for the Fuel Cells and Hydrogen Joint Technology Initiative under grant agreement n° 621244, and from the Research Council of Norway through the PROTON (225103), FOXCET (228355), and ROMA (219194) projects.
Recommend
More recommend