
Protein Folding
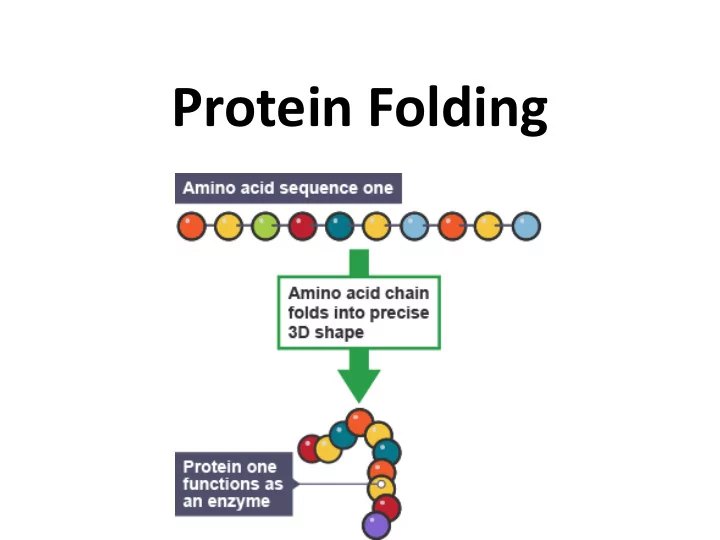
Protein Folding • Proteins have unique 3-dimensional shapes created by the twisting or folding of one or more polypeptide chains • The structure of a protein enables it to recognize and bind to other molecules
Protein Folding
Shape Determines Function
Shape Determines Function
Shape Determines Function
Protein Structure • Primary Structure • Secondary Structure • Tertiary Structure • Quaternary Structure
Primary Structure • Determined by the sequence of a chain of amino acids held together by peptide bonds
Secondary Structure • Involves regions of coiling ( α -helices) or folding ( β -pleated sheets) of the polypeptide • Stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of amino acids
Tertiary Structure • Results from interactions between the various side chains (R groups) • Ionic bonds between positive (+) and negative (-) side chains • Hydrophobic interactions between nonpolar side chains (repelled by water), clump together • Hydrogen bonds between polar side chains • Disulfide bridges between the sulfhydryl groups of cysteine amino acids
Tertiary Structure
Quaternary Structure • Occurs in proteins that are composed of more than one polypeptide • Results from the combination of hydrogen bonding, ionic bonding, and hydrophobic interactions between polypeptide chains
Protein Folding Control • Chaperones and proteasomes are molecules that act jointly to regulate protein folding and control the selective removal of misfolded proteins from the cell • Chaperones control the conformational folding and unfolding of proteins released from ribosomes • Proteasomes degrade unneeded or damaged proteins
Diseases Caused by Misfolded Proteins • Alzheimer’s Disease • Parkinson’s • Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) • Huntington’s Disease
Sickle-Cell Anemia Mutation • Causes hemoglobin molecules to crystallize when oxygen levels are low
Insulin Receptor – Type 2 Diabetes
Recommend
More recommend