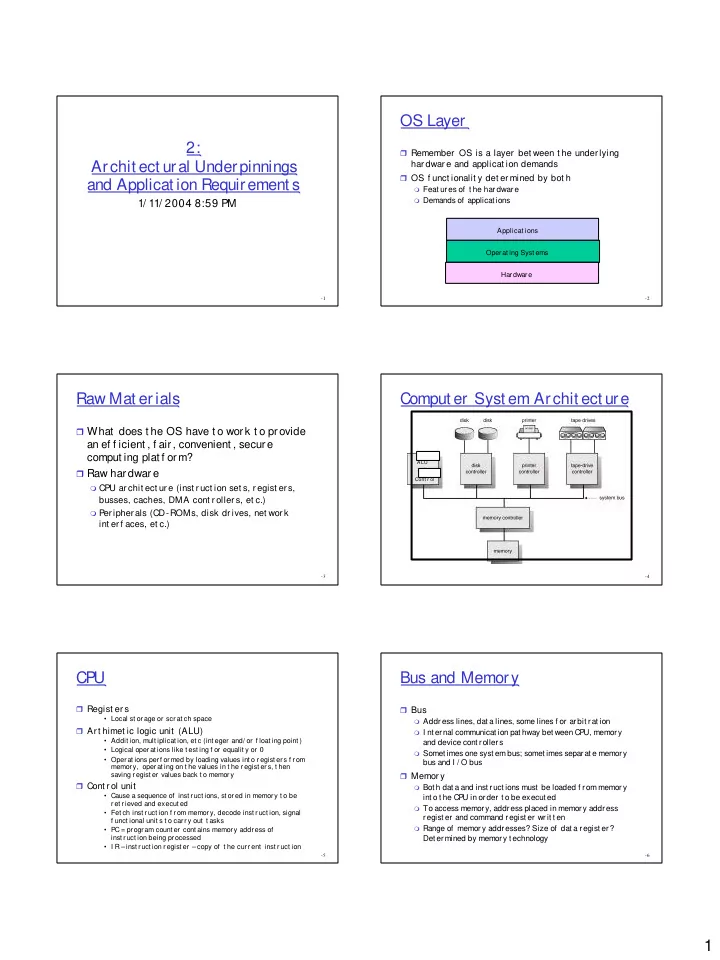

OS Layer 2: � Remember OS is a layer bet ween t he under lying Archit ect ural Underpinnings har dwar e and applicat ion demands � OS f unct ionalit y det er mined by bot h and Applicat ion Requirement s � Feat ur es of t he har dwar e � Demands of applicat ions 1/ 11/ 2004 8:59 PM Applicat ions Operat ing Syst ems Hardware -1 -2 Raw Mat erials Comput er Syst em Archit ect ure � What does t he OS have t o work t o provide an ef f icient , f air, convenient , secure comput ing plat f orm? ALU � Raw har dwar e Cont r ol � CPU ar chit ect ur e (inst r uct ion set s, r egist er s, busses, caches, DMA cont r oller s, et c.) � Per ipher als (CD-ROMs, disk dr ives, net wor k int er f aces, et c.) -3 -4 CP U Bus and Memory � Regist er s � Bus • Local st or age or scr at ch space � Address lines, dat a lines, some lines f or arbit rat ion � Ar t himet ic logic unit (ALU) � I nt ernal communicat ion pat hway bet ween CP U, memory • Addit ion, mult iplicat ion, et c (int eger and/ or f loat ing point ) and device cont rollers • Logical oper at ions like t est ing f or equalit y or 0 � Somet imes one syst em bus; somet imes separat e memory • Operat ions perf ormed by loading values int o regist ers f rom bus and I / O bus memory, operat ing on t he values in t he regist ers, t hen saving regist er values back t o memory � Memor y � Cont r ol unit � Bot h dat a and inst ruct ions must be loaded f rom memory • Cause a sequence of inst ruct ions, st ored in memory t o be int o t he CP U in order t o be execut ed ret rieved and execut ed � To access memory, address placed in memory address • Fet ch inst r uct ion f r om memor y, decode inst r uct ion, signal regist er and command regist er writ t en f unct ional unit s t o car r y out t asks � Range of memory addresses? Size of dat a regist er? • PC = program count er cont ains memory address of inst ruct ion being processed Det ermined by memory t echnology • I R – inst ruct ion regist er – copy of t he cur r ent inst r uct ion -5 -6 1
Devices Bet t er Raw Mat erial? � Device cont r oller s � The “bet t er” t he underlying hardware, t he � Small processing unit s t hat connect a device t o t he bet t er comput ing experience t he OS can syst em bus expose � Regist ers t hat can be read/ writ t en by CPU • command regist er (what t o do), st at us regist er (is t he � Cert ainly t he f ast er t he CP U, t he more device busy? Has t he device complet ed a r equest ?) , dat a regist er t o st ore dat a bring writ t en t o t he device or read memory, et c. t he bet t er experience t he f rom t he device OS can expose t o applicat ions � Device dr iver s � Sof t ware t o hide t he complexit ies of t he device � Also t here are some f eat ures t hat t he cont roller int erf ace behind a higher level logical AP I hardware can provide t o make t he OS’s j ob � Example: read lba 10 inst ead vs. writ e command value much easier 0x30 t o command regist er, address 10 t o address regist er,… � Let s see if we can guess some… -7 -8 Enf orcing P rot ect ion P rot ect ed I nst ruct ions � I f we want t he operat ing syst em t o be able � I f you would look over t he assembly language f or a comput er , you may not ice t hat some inst r uct ions t o enf or ce pr ot ect ion and policies on all look pr et t y danger ous user processes, what can give t he OS t he � Should any applicat ion be allowed t o direct ly execut e t he power t o do t hat ? halt inst ruct ion? Denial of service at t ack? � Pr ot ect ed I nst r uct ions � Should any applicat ion be allowed t o direct ly access I / O devices? Read any ones f iles f rom disk? � Deny applicat ions dir ect access t o t he har dwar e � Har dwar e can help OS by designat ing some � Pr ot ect ed Mode of Execut ion (user vs ker nel) inst r uct ions as pr ot ect ed inst r uct ions t hat only � Memor y pr ot ect ion har dwar e t he OS can issue � How can t he har dwar e t ell whet her it is OS (ker nel) code or user code? -9 -10 P rot ect ed Mode Swit ching Modes � I n addit ion t o designat ing cer t ain inst r uct ions as � So how do we swit ch bet ween an OS pr ot ect ed inst r uct ions, t he har dwar e would need r unning in ker nel mode and an applicat ion t o be able t o dist inguish t he OS f r om user apps r unning in user mode? � Most ar chit ect ur es have a “mode” value in a � OS could set t he mode bit t o a dif f erent mode pr ot ect ed r egist er bef or e allowing t he applicat ion t o r un on t he � When user applicat ions execut e, t he mode value is set t o CPU one t hing � I f an applicat ion needs t o access a pr ot ect ed � When t he OS kernel execut es, t he mode value set t o r esour ce t o accomplish it s t ask (like r ead a f ile somet hing else � I f code running in user mode, an at t empt t o execut e or send a message on t he net wor k), how can it prot ect ed inst ruct ions will generat e an except ion do t hat at user mode? � Swit ching t he mode value must of course be prot ect ed � Once an applicat ion is r unning how can we � Some ar chit ect ur es suppor t mor e pr ot ect ion f orce it t o relinquish cont rol? modes t han j ust user / ker nel -11 -12 2
Syst em Calls Syst em Call I llust rat ed File.open(“/ home/ README”) Resume applicat ion wit h f ile � I f an applicat ion legit imat ely needs t o access a opened or er r or pr ot ect ed f eat ur e (Ex. r ead a f ile f r om disk, it calls a special OS pr ocedur e called a “syst em call” � Syst em call inst ruct ion execut ed wit h a paramet er t hat Syst emCall (SYS_OPEN, “/ home/ README”) designat es specif ic call desired and any ot her paramet ers needed User mode � The st at e of t he user program is saved so t hat it can be Kernel mode rest ored (cont ext swit ch t o t he OS) � Cont rol passed t o an OS procedure t o accomplish t he Save user r egist er s and mode, lookup t ask and mode bit changed! SYS_OPEN in a t able of syst em call pr ocedur es, Change mode bit , j ump t o t he ker nelOpen procedure � OS procedure runs at t he request of t he user program but can verif y t he user program’s “right s” and ref use t o Rest ore user perf orm t he act ion if necessary mode and � On complet ion of t he syst em call, t he st at e of user applicat ion’s program including t he old mode bit is rest ored kernelOpen(“/ home/ README”, regist ers et c. t his applicat ions access right s) -13 -14 Simple Memory P rot ect ion Memory P rot ect ion Hardware � Give each pr ocess a cont iguous set of memor y � All code t hat execut es on t he CPU must be loaded addr esses t o use and dedicat e t wo r egist er s t o int o memor y (it s code, it s dat a, et c.) specif ying t he t op and t he bot t om of t his r egion � I t is execut ed by set t ing t he program count er regist er � Of course, changing t he base and limit regist er must be t o point t o t he memory locat ion of t he next inst ruct ion prot ect ed! t o execut e (add, j ump, load, st ore, et c.) When pr ocess 1 execut ing, base and OS � OS has it s code in memor y and so does each limit set t o point t o process 1’s memory Base regist er region if process 1 t ries t o load r unnable user pr ocess Process 1 Limit regist er or st ore t o addresses out side t his � Would we want a pr ocess t o st or e r andom dat a r egion t hen har dwar e will t r ansf er Process 2 int o t he OS’s code or dat a segment s? What about cont r ol t o t he OS int o anot her pr ocesses code or dat a segment s? � Memor y pr ot ect ion har dwar e gener ally mor e � What pr event s t his? power f ul t hat base and limit r egist er s (page t ables, TLB, et c.) -15 -16 Transf erring Cont rol t o t he OS Concret e Example: I nt el CP U � Dur ing OS init ializat ion: � A syst em call causes cont rol t o be � I nt errupt Descript or Table (I DT) loaded wit h handlers t ransf erred t o t he OS at t he applicat ion’s f or each kind of int errupt request � Syst em call is int errupt vect or 128 (0x80) � Ot her t hings can cause cont rol t o be � Kernel code segment is set t o have privilege level 0 (user t ransf erred t o t he OS but not at t he code runs at 3) � Ent r y in I DT cor r esponding t o vect or 128 is set applicat ion’s request wit h: � Could be t hat t he applicat ion did somet hing � P oint er t o t he kernel code segment and of f set of t he wr ong like t r ied t o addr ess memor y it shouldn’t syst em call handler in t his segment or t ries t o divide by 0, et c. � P ermission f or code running at level 3 t o invoke it � Could be t hat a har dwar e device is r equest ing � To make syst em call, user level app: ser vice � Set s eax regist er t o t he syst em call number � Execut es “int 0x80” inst ruct ion -17 -18 3
Recommend
More recommend