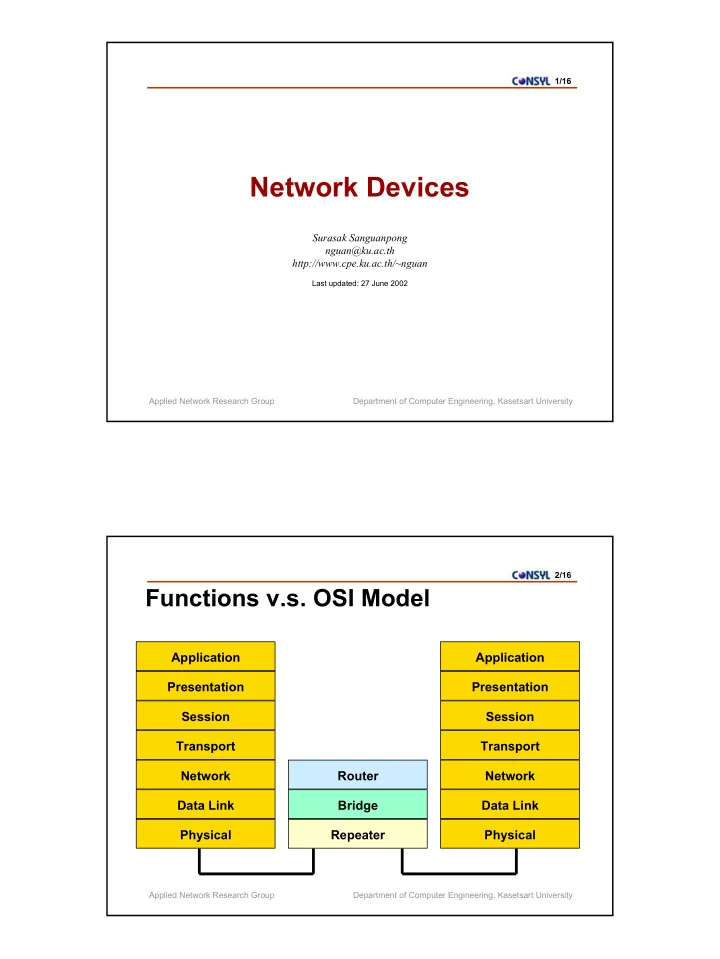

1/16 Network Devices Surasak Sanguanpong nguan@ku.ac.th http://www.cpe.ku.ac.th/~nguan Last updated: 27 June 2002 Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 2/16 Functions v.s. OSI Model Application Application Presentation Presentation Session Session Transport Transport Network Router Network Data Link Bridge Data Link Physical Repeater Physical Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
3/16 Hub/Repeater hub The frame is repeated out all the other ports A sends a frame to D D D D D A B C D Attempt to forward all Frames � Error Frames will be forwarded � A hub regenerates signals; it does not an amplifier � Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 4/16 Hub characteristics collision domain, broadcast domain Hubs create a single hub hub collision domain and a broadcast domain A B C D E F G H All devices connected to hub : � � share the same collision domain � share the same broadcast domain Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
5/16 Hub Model Application Application Presentation Presentation Session Session Transport Transport Network Network Data Link Data Link Physical Repeater Physical � Deal with signaling : operate at the Physical Layer Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 6/16 Bridge operations Filtering segment 2 2 The frame A-to-B A to B 1 C is blocked 4 segment 1 segment 4 3 D G H A B 2 Forwarding 1 4 2 The frame A-to-B A to C 1 is forwarded 3 4 to port 2 Station port E 3 A 1 B 1 F C 2 Flooding D 2 segment 3 E 3 Forwarding Table 2 The frame A-to-B G 4 (F and H is currently unknown) A to F 1 is flooded to all ports 4 Selectively forwards frames � 3 Error Frames will not be forwarded � Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
7/16 Bridge characteristics collision domain collision domain bridge B C D A broadcast domain � All devices connected to bridges share the same broadcast domain � Networks are segmented; each segment is its own collision domain Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 8/16 Bridge Model Application Application Presentation Presentation Session Session Transport Transport Network Network Data Link Bridge Data Link Physical Repeater Physical � Deal with Data Link Frame : operate at the Data Link Layer Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
9/16 Bridge operations 2 1 Initially, the bridge’s table is empty station port C D A B bridge 1 2 Station A transmits to Station C. The station port bridge starts building its bridging A 1 A B C D bridge table and forward the packet. A-to-C C A Station D transmits to Station A. The 2 1 station port bridge forward the packet and A 1 A B C D bridge continues building its table. D 2 D-to-A A D 1 2 station port Station B transmits to Station A, the bridge does not forward the frame, A 1 C D A B bridge D 2 since A also resides on port 1 B-to-A B 1 A B Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 10/16 Loop in Bridge Packet is infinite looping! � The learning bridge concept works for any tree (loop free) topology Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
11/16 Loop Avoidance with algorithm Spanning-tree algorithms disable some interfaces to break the loop Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 12/16 Type of bridge � Transparent Bridges � Same Topologies � Translational Bridges � Converts frame types from one topology to another � For example, Ethernet to FDDI � Source Route Bridges � Token Ring Only � IBM Legacy Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
13/16 Bridge A B C D B B The frame to B is blocked A C D B C C C The frame to C is forwarded Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 14/16 Router Network is partitioned in to a small subnetwork � Each node has its own � � Data Link Layer address (e.g. Ethernet MAC address) � Network Layer address (e.g. IP Address) network 1 network 2 network node 1 1,2,3 1.2 1.3 2.2 2.3 2 1,2,3 3 1 1.1 2.1 3.1 No node inside Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
15/16 Router characteristics broadcast domain broadcast domain collision domain collision domain broadcast domain collision domain Collision domains are isolated � Broadcast domains are isolated (do not forward layer 2 � broadcast) Error Frames will not be forwarded � Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 16/16 Router Model Application Application Presentation Presentation Session Session Transport Transport Router Network Network Data Link Bridge Data Link Physical Repeater Physical � Deal with Network Frame : operate at the Network Layer Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
Recommend
More recommend