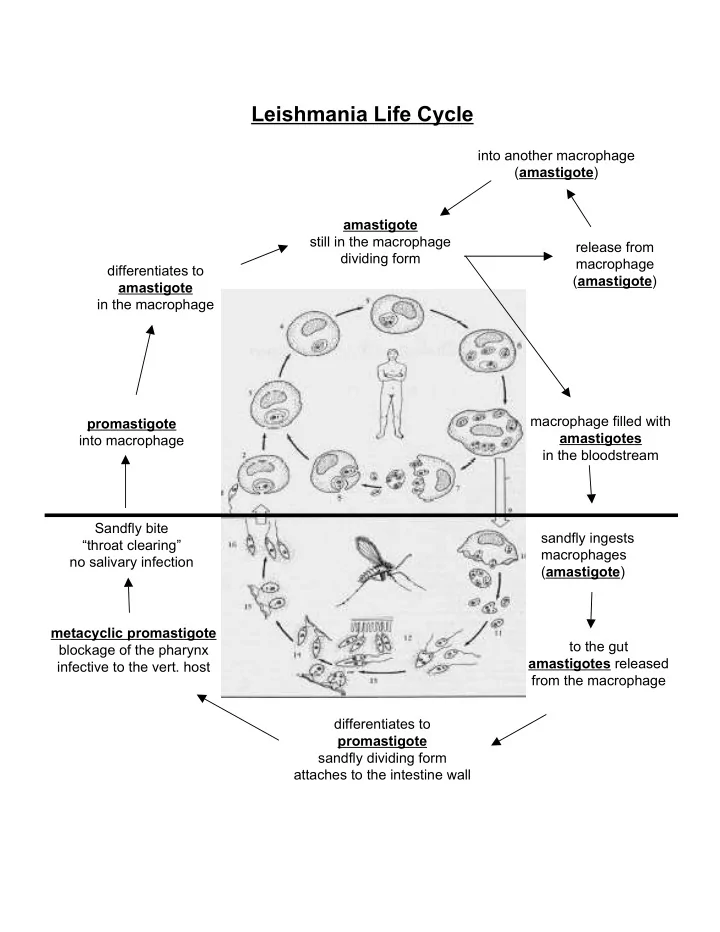

Leishmania Life Cycle into another macrophage ( amastigote ) amastigote still in the macrophage release from dividing form macrophage differentiates to ( amastigote ) amastigote in the macrophage macrophage filled with promastigote amastigotes into macrophage in the bloodstream Sandfly bite sandfly ingests “throat clearing” macrophages no salivary infection ( amastigote ) metacyclic promastigote to the gut blockage of the pharynx amastigotes released infective to the vert. host from the macrophage differentiates to promastigote sandfly dividing form attaches to the intestine wall
Agglutination – a decreased number of free promastigotes compared to the control Peanut (PNA) and ricin (RCA) are two-D-galactose-binding lectins Left panels : percent agglutination using PNA and RCA agglutinin log-phase promastigotes – solid line stationary promastigotes – dashed line 100% agglutination with PNA and RCA in log-phase cells 50% agglutination using stationary cells Right panel : Percent infectivity (macrophage survival) at various growth time points Solid bars - % of promastigotes surviving thru change to amastigotes Open bars - % unagglutinated (infective) promastigotes of total recovered Conclusions: Only stationary phase promastigotes (metacyclic) are able to survive in the macrophage (~50%). Virtually all surviving cells are stationary phase, PNA non-binding (non-agglutinated.) Non-agglutination is the result of a change in surface binding sites. Changes in the cell surface (lengthening of the coat) are part of the metacyclic pre-adaption.
Lectins (Ricin, peanut agglutinin, PpGalectin ) : Bind to D-Galactose ProcyclicPromastigote LPG (fly midgut) Metacyclic Promastigote LPG (fly midgut) Hence, the metacyclic promastigote LPG does not bind the PpGalectin in the midgut and out it goes
LPG: Lipophosphoglycan Pro Meta •GPI anchored phospholipid chain polymer with branching sugar moeities •Major surface L.donovani molecule of the parasite •Different LPGs in Metacyclic vs Procyclic promastigotes •This change corresponds to different infectivities in different life stages! L. Major •Procyclic Promastigotes(Insect midgut) =Not infective to Mammals •Metacyclic Promastigotes (Insect Salivary gland = Infective to mammals
LPGs in the insect
Recommend
More recommend