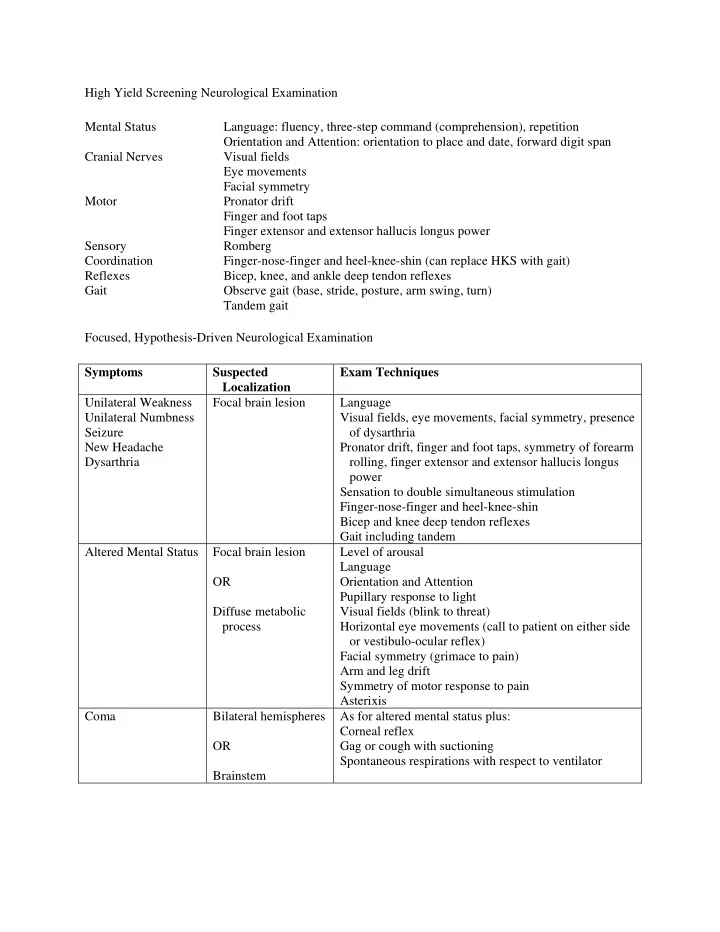

High Yield Screening Neurological Examination Mental Status Language: fluency, three-step command (comprehension), repetition Orientation and Attention: orientation to place and date, forward digit span Cranial Nerves Visual fields Eye movements Facial symmetry Motor Pronator drift Finger and foot taps Finger extensor and extensor hallucis longus power Sensory Romberg Coordination Finger-nose-finger and heel-knee-shin (can replace HKS with gait) Reflexes Bicep, knee, and ankle deep tendon reflexes Gait Observe gait (base, stride, posture, arm swing, turn) Tandem gait Focused, Hypothesis-Driven Neurological Examination Symptoms Suspected Exam Techniques Localization Unilateral Weakness Focal brain lesion Language Unilateral Numbness Visual fields, eye movements, facial symmetry, presence Seizure of dysarthria New Headache Pronator drift, finger and foot taps, symmetry of forearm Dysarthria rolling, finger extensor and extensor hallucis longus power Sensation to double simultaneous stimulation Finger-nose-finger and heel-knee-shin Bicep and knee deep tendon reflexes Gait including tandem Altered Mental Status Focal brain lesion Level of arousal Language OR Orientation and Attention Pupillary response to light Diffuse metabolic Visual fields (blink to threat) process Horizontal eye movements (call to patient on either side or vestibulo-ocular reflex) Facial symmetry (grimace to pain) Arm and leg drift Symmetry of motor response to pain Asterixis Coma Bilateral hemispheres As for altered mental status plus: Corneal reflex OR Gag or cough with suctioning Spontaneous respirations with respect to ventilator Brainstem
Vertigo Brainstem or Detailed cranial nerve exam with special attention to the Imbalance cerebellum following: Horner’s syndrome OR Unidirectional vs. gaze-evoked nystagmus Vertical nystagmus Inner ear Head thrust maneuver Pronator drift, finger and foot taps, symmetry of forearm rolling, finger extensor and extensor hallucis longus power Sensation intact to light touch in all four limbs Finger-nose-finger and heel-knee-shin Gait including tandem Dix-Hallpike maneuver Back Pain Spinal cord Pronator drift, finger and foot taps, symmetry of forearm Bowel or Bladder rolling Incontinence Muscle tone in the legs Bilateral Leg Strength of deltoids, biceps, triceps, finger extensors, Weakness or iliopsoas, quadriceps, hamstrings, foot and toe Numbness dorsiflexion Sensory level on trunk Rectal tone Diffuse Weakness High spinal cord, Pupillary response to light neuropathy, Eye movements, presence of ptosis neuromuscular Facial strength (check for bifacial weakness) junction, or Count to 30 in one breath, check NIF and FVC myopathy Strength of neck flexion, neck extension, deltoids, biceps, triceps, finger extensors, iliopsoas, quadriceps, hamstrings, foot and toe dorsiflexion Sensory gradient to pain from feet to thighs Sensory level on trunk Romberg Bicep, knee, and ankle deep tendon reflexes Ability to stand without using arms, walk on heels and toes *NIF = negative inspiratory force (normal < -60 cm H 2 O); FVC = forced vital capacity (normal > 2.0 L)
Key Teaching Points in Localization Weakness Pattern of Tone Bulk Reflexes Sensory Other weakness Loss Upper Motor Pyramidal Spastic Normal Increased Varies Neuron Anterior Horn Pyramidal or Spastic or Atrophy Increased or None Fasciculations Cell myotomal normal decreased Peripheral In Normal or Atrophy Decreased Prominent Nerve distribution reduced of root or nerve Neuromuscular Diffuse Normal Normal Normal None Ptosis and Junction (myasthenia) ophthalmo- or Absent paresis (botulism) Muscle Proximal > Normal Normal or Normal None Distal patterned atrophy Aphasia Fluency Repetition Comprehension Expressive (Broca’s) Impaired Impaired Intact Receptive (Wernicke’s) Intact Impaired Impaired Global Impaired Impaired Impaired Conductive Intact Impaired Intact References: Kamel et al, A randomized trial of hypothesis-driven vs screening neurologic examination. Neurology Oct 2011, 77(14) 1395-1401.
Recommend
More recommend