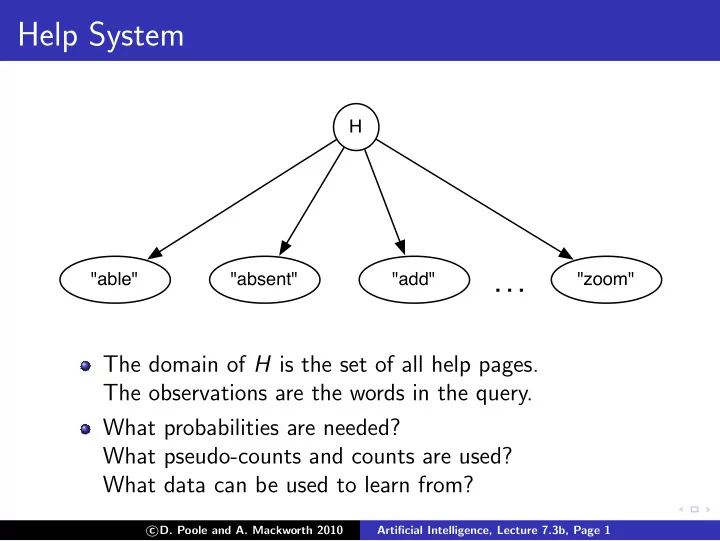

Help System H "able" "absent" "add" "zoom" . . . The domain of H is the set of all help pages. The observations are the words in the query. What probabilities are needed? What pseudo-counts and counts are used? What data can be used to learn from? � D. Poole and A. Mackworth 2010 c Artificial Intelligence, Lecture 7.3b, Page 1
Help System Suppose the help pages are { h 1 , . . . , h k } . Words are { w 1 , . . . , w m } . Bayes net requires: ◮ P ( h i ), these sum to 1 ( � i P ( h i ) = 1) ◮ P ( w j | h i ), these do not sum to one Maintain “counts” (pseudo counts + observed cases): ◮ c i the number of times h i was the correct help page ◮ s = � i c i ◮ u ij the number of times h i was the correct help page and word w j was used in the query. P ( h i ) = c i / s P ( w j | h i ) = u ij / c i � D. Poole and A. Mackworth 2010 c Artificial Intelligence, Lecture 7.3b, Page 2
Learning + Inference Q is the set of words in the query. Learning: if h i is the correct page: Increment s , c i and u ij for each w j ∈ Q . Inference: � � P ( h i | Q ) ∝ P ( h i ) P ( w j | h i ) (1 − P ( w j | h i )) w j ∈ Q w j �∈ Q � c i − u ij expensive c i u ij � � = inference s c i c i w j ∈ Q w j �∈ Q � D. Poole and A. Mackworth 2010 c Artificial Intelligence, Lecture 7.3b, Page 3
Learning + Inference Q is the set of words in the query. Learning: if h i is the correct page: Increment s , c i and u ij for each w j ∈ Q . Inference: � � P ( h i | Q ) ∝ P ( h i ) P ( w j | h i ) (1 − P ( w j | h i )) w j ∈ Q w j �∈ Q � c i − u ij expensive c i u ij � � = inference s c i c i w j ∈ Q w j �∈ Q c i c i − u ij u ij � � = c i − u ij s c i w j w j ∈ Q � expensive u ij � = Ψ i c i − u ij learning w j ∈ Q � D. Poole and A. Mackworth 2010 c Artificial Intelligence, Lecture 7.3b, Page 4
Issues What if the most likely page isn’t the correct page? What if the user can’t find the correct page? What if the user mistakenly thinks they have the correct page? Can some pages never be found? What about common words? What about words that affect the meaning, e.g. “not”? What about new words? What do we do with new help pages? How can we transfer the language model to a new help system? � D. Poole and A. Mackworth 2010 c Artificial Intelligence, Lecture 7.3b, Page 5
Simple Language Models Sentence is a sequence of words: w 1 , w 1 , w 3 , . . . . Modeled as: Set of words Unigram (bag of words): Model P ( W i ). Range of W i is the set of all words. Bigram: Model P ( W i | W i − 1 ) Trigram: Model P ( W i | W i − 1 , W i − 2 ) � D. Poole and A. Mackworth 2010 c Artificial Intelligence, Lecture 7.3b, Page 6
Logic, Probability, Statistics, Ontology over time From: Google Books Ngram Viewer (http://books.google.com/ngrams/) � D. Poole and A. Mackworth 2010 c Artificial Intelligence, Lecture 7.3b, Page 7
Topic Model tools food topics "bolt" "nut" "tuna" words � D. Poole and A. Mackworth 2010 c Artificial Intelligence, Lecture 7.3b, Page 8
Google’s rephil ... 900,000 topics 350,000,000 links "Aaron's "aardvark" ... "zzz" 12,000,000 words beard" � D. Poole and A. Mackworth 2010 c Artificial Intelligence, Lecture 7.3b, Page 9
Recommend
More recommend