
HbA1c 5.8% 6.5% Duaa Al Ebraheem
HbA1c The term HbA1c refers to glycated haemoglobin. • When the body processes sugar, glucose in the bloodstream naturally attaches to haemoglobin. • The amount of glucose that combines with this protein is directly proportional to the total amount of sugar that is in • your system at that time. By measuring glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c), clinicians are able to get an overall picture of what our average blood • sugar levels have been over a period of weeks/months. For people with diabetes this is important as the higher the HbA1c, the greater the risk of developing diabetes- • related complications.
Principle • Because red blood cells in the human body survive for 8-12 weeks before renewal, measuring glycated haemoglobin (or HbA1c) can be used to reflect average blood glucose levels over that duration, providing a useful longer-term gauge of blood glucose control. • If your blood sugar levels have been high in recent weeks, your HbA1c will also be greater. To convert : From mg/dl to mmol/l : 18 From mmol/l to mg/dl : 18
Who is doing this test ? • Everyone with diabetes mellitus should be offered an HbA1c test at least once a year. • Some people may have an HbA1c test more often. This may be more likely if you have recently had your medication changed or your health team are otherwise wishing to monitor your diabetes control more than once a year. What Are the Limitations to Measuring Hemoglobin A1c? HbA1c tests are usually reliable, there are some limitations to the accuracy of the test. For example: HbA1c may be increased falsely in certain medical conditions: • these conditions include (kidney failure (uremia),chronic excessive alcohol intake, hypertriglyceridemia). Medical conditions that may falsely decrease HbA1c include: • (acute or chronic blood loss, sickle cell disease, thalassemia).
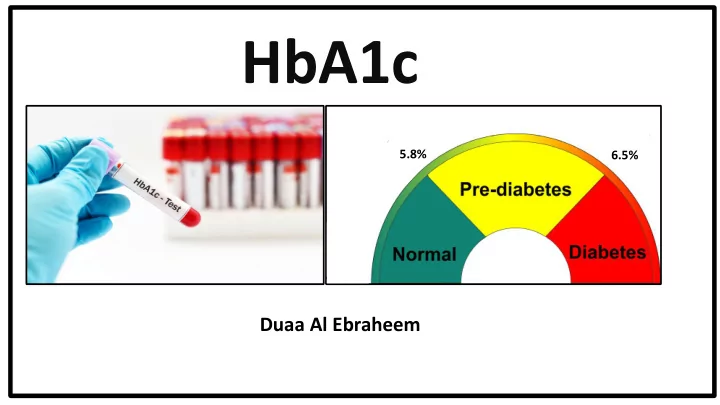
Why do we need to measure HBA1C? HBA1C – Provides accurate picture of Blood Glucose levels over the last two to three months. • High levels of HBA1C indicate high risk of diabetic complications. • HbA1c is typically measured to determine how well a type 1 or type 2 diabetes treatment plan (including • medications, exercise, or dietary changes) is working. HbA1c in diagnosis… HbA1c can indicate people with prediabetes or diabetes as follows: HbA1c % Normal 5.7% Prediabetes 5.8% to 6.4% Diabetes 6.5% or over
How does HbA1c differ from a blood glucose level? • Blood glucose level is the concentration of glucose in your blood at a single point in time. • This is measured using a fasting plasma glucose test, which can be carried out using blood taken from a finger or can be taken from a blood sample from the arm. • Tube used : plain tube or sodium fluoride tube • the HbA1c test serves as an overall marker of what your average levels are over a period of 2-3 months. • Tube used : EDTA tube
Spe c ime n Colle c tion stora g e & Ha ndling Type: whole blood EDTA tube Container/Tube: Lavender top (EDTA) Specimen Volume: 3 mL minimum specimen volume : 2 mL SAMPLE REJECTED IN THE FOLLOWING Condition : 1. Frozen sample 2. Test done less than 3 month Specimen Type Temperature Time Whole Blood EDTA Refrigerated 2-8 c 7 to 14 days Room temperature 24 hours Patient Preparation : No special condition such as fasting or diet are required.
Instrument used in Amiri Biochemistry Lab to measure HbA1c
Pr inc iple of Assa y Tosoh-G8 is based on the principle of high performance in exchange liquid chromatography (HPLC) and LED photometer associated to a micro computer technology. TSK gel Columns are used to separate HB components with different Ionic Charge.
Re a g e nts & Supplie s Elution Buffer – Stored at room temperature. Hemolysis & wash solution – Stored at room temperature. Column – should be replaced when count reaches Filter - Should be replaced when count reaches Printer Paper Waste Bottle
Pr oc e dur e of T e st Analyzer dilute whole blood specimen with Hemolysis & wash solution. Diluted Specimen is injected into the TSK gel column. Hemoglobin Complexes are separated on the column based on Ionic differences. Hemoglobin fractions are separated from column using 3 elution buffers with varied salt concentrations. Eluted Hemoglobin components pass through LED photometer where the changes are absorbance at 415nm is measured. This raw data is converted & calculated by micro computer specific software and results are printed.
Ma inte na nc e Checking and replacing of all reagents and supplies as & when required. Reagent Change
Dr a in F lush - Drain flush - to remove air from the pump
Pr iming of Re a g e nts - Removes air fro buffer lines
Ca libr a tion Tosoh Calibrations set consists of two calibrators Calibrator-1 Calibrator – 2 Calibrators are reconstituted by adding 4ml distilled water. Un-opened calibrators are stored at 2-8 o C. Reconstituted calibrators are stable for one week and stored at 4 o C.
Ca libr a tion Pr oc e dur e Press START Button Select - Calibration Check Calibration Value
QC Polic y There are two levels of Controls to run. 1. Level-1 (Normal) 2. Level-2 (Ab-normal) Whole Blood Control is used for QC 20 µl of blood diluted with 1ml of distilled water Load the QC Rack on sample belt and select start. Recommended to run level 1 QC after 40 samples and run level 2 QC after 80 samples
Re por ting Re sults The printed results are checked by the operator The result also transferred to LIS. Each chromatogram should include six peaks identified as A1A, A1B, F, LA1C+, SA1C and A0. The acceptable retention time for SA1c is 0.57 – 0.61. The acceptable ranges of total area 500 – 4,000 HBA1C results are reported in LIS both in NGSP % and IFCC values according to the following formula started in LIS.
Pr e se nc e of HB Va r ia nt If percentage of HB variant is 30 – 45% then results are reported and saved. If percentage of HB variant is > 45% the report should be given to the incharge Doctor to authenticate.
To know 1- Sample collected in AL Asimah CLINICS transported to Bneid Algar CLINIC. 2- reports are distributed according to clinics name. 3- Sample collected in Amiri Hospital goes to Amiri Lab Biochemistry section .
T ha nk YOU
Recommend
More recommend