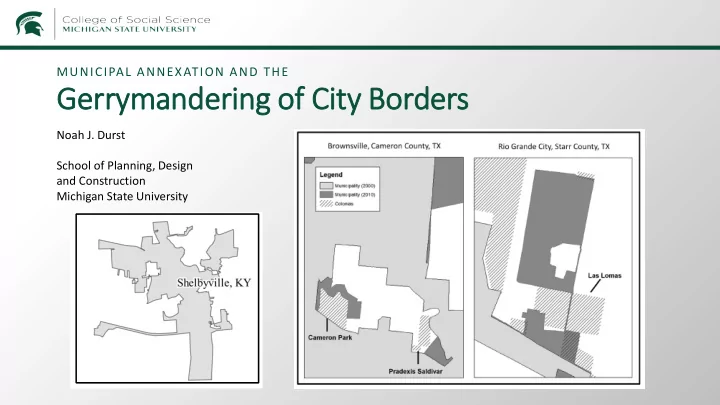

MUNICIPAL ANNEXATION AND THE Gerrymand ndering of C City B Borders Noah J. Durst School of Planning, Design and Construction Michigan State University
Annexation from 2011 to 2018 The Gerrymanderi ring o of City Borders
Selective ve A Annexation CENTRAL RESEARCH QUESTION (Muni nicipa pal Underbo boun undi ding) What factors influence cities’ decision to annex (underbound) specific areas? EMPIRICAL/METHODOLOGICAL ISSUES/CHALLENGES: CAPITALIZING ON INTER-CITY VARIATION Method: regression analysis • Logistic: OLS: Variation in state/federal law matters Y = Annexed/ Y = race, ethnicity, property • When laws give city residents control over annexation, black not annexed (1/0) $ in annexed neighborhoods neighborhoods are less likely to be annexed. • When laws give independent boundary commissions or X = Physical/economic conditions residents on the fringe control over annexation, black neighborhoods are more likely to be annexed (Durst, 2018) Demographics State and federal laws • The invalidation of Section 5 of the Voting Rights Act led to decreases in the annexation of black neighborhoods (Durst, 2019) Durst (2014, 2018, 2019); Lichter et al. (2007); Wilson and Edwards (2014)
Selective ve A Annexation (Muni nicipa pal Underbo boun undi ding) EMPIRICAL/METHODOLOGICAL ISSUES/CHALLENGES: CONTROLLING FOR INTER-CITY VARIATION • The physical, economic, and demographic characteristics of areas “at risk” of annexation vary greatly from city to city. • Failing to control for this leads to biased estimates of the factors that drive municipal underbounding (Durst, 2018) • When inter-city variation is not used as a predictor: • City fixed effects (Durst, 2019) • When inter-city variation is used as a predictor • Spatial first-difference estimators ((Durst, 2018) • Multi-level mixed effects models
Selective ve A Annexation (Muni nicipa pal Underbo boun undi ding) CENTRAL RESEARCH QUESTION EMPIRICAL/METHODOLOGICAL ISSUES/CHALLENGES: THE MODIFIABLE AREAL UNIT PROBLEM Lichter et al. (2007)
Selective ve A Annexation (Muni nicipa pal Underbo boun undi ding) CENTRAL RESEARCH QUESTION EMPIRICAL/METHODOLOGICAL ISSUES/CHALLENGES: What factors influence cities’ decision to annex MEASURING DIFFERENT TYPES OF ANNEXATIONS (underbound) specific areas? 3 Additional data collection Method: regression analysis • Demography Logistic: Y = Annexed/not annexed (1/0) • Socio-Economic Data OLS: Y = race, ethnicity, property $, etc in annexed neighborhoods 4 X = Physical/economic conditions Modeling: Multilevel multinomial logit Demographics State and federal laws 1 Nationwide & Multi-year City 2 Geographic Identification of Durst (2014, 2018, 2019); Lichter et al. (2007); Annexation Variety Boundary Data (IPUMS) Wilson and Edwards (2014)
Recommend
More recommend