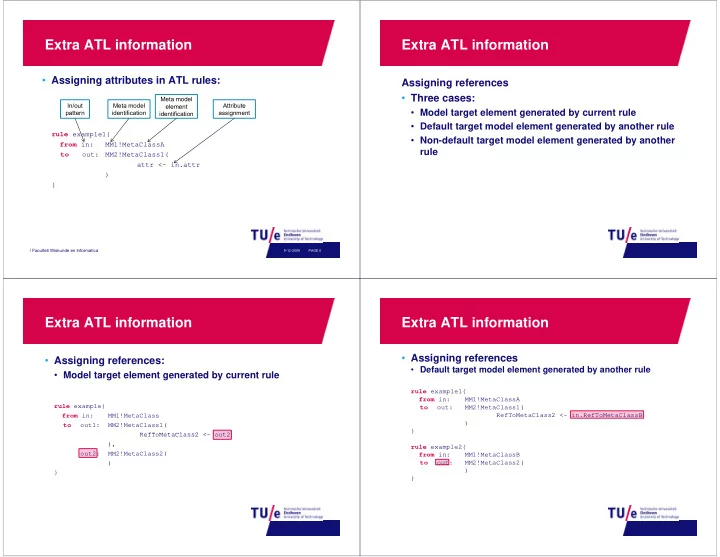

Extra ATL information Extra ATL information • Assigning attributes in ATL rules: Assigning references g g • Three cases: Meta model In/out Meta model Attribute element • Model target element generated by current rule pattern identification assignment identification • Default target model element generated by another rule rule example1{ • Non-default target model element generated by another from in: MM1!MetaClassA rule to to out: out: MM2!MetaClass1( MM2!MetaClass1( attr <- in.attr ) } / Faculteit Wiskunde en Informatica 9-12-2009 PAGE 0 Extra ATL information Extra ATL information • Assigning references • Assigning references: g g • Default target model element generated by another rule D f l d l l d b h l • Model target element generated by current rule rule example1{ from in: from in: MM1!MetaClassA MM1!MetaClassA rule example{ to out: MM2!MetaClass1( from in: MM1!MetaClass RefToMetaClass2 <- in.RefToMetaClassB ) to out1: MM2!MetaClass1( } RefToMetaClass2 <- out2 RefToMetaClass2 < out2 ), rule example2{ out2: MM2!MetaClass2( from in: MM1!MetaClassB ) to out: MM2!MetaClass2( ) } }
Extra ATL information Extra ATL information • Assigning references • Assigning enums g g • Non defa lt target model element generated b Non-default target model element generated by another rule another r le rule example1{ from in: MM1!MetaClassA to out: MM2!MetaClass1( RefToMetaClassN <- thisModule.resolveTemp(in.RefToMetaClassB, ‘out_n’) rule example{ ) } from in: MM1!MetaClassB to to out: t MM2!M t Cl MM2!MetaClass1( 1( rule example2{ enum <- #”Integer” from in: MM1!MetaClassB out: MM2!MetaClass1( to ) ), } out n: _ MM2!MetaClassN( ) } • Quotes are only needed in case of reserved words Rules ATL matched rules • Matched rules • ATL matched rule mechanism provides a mean to rule rule_name{ specify the way target model elements must be from in: MM1!MetaClass( <matching condition> ) generated from source model elements. using { <variable definitions> } to out1: MM2!MetaClass1( • A matched rule enables to specify: • A matched rule enables to specify: <bindings1> 1. which source model element must be matched, ), out2: MM2!MetaClass2( 2. the number and the type of the generated target model yp g g <bindings2> <bindings2> elements, and ) do { <imperative block> } 3. the way these target model elements must be } initialized from the matched source elements initialized from the matched source elements • Matches on all model elements of type MM1!MetaClass , M t h ll d l l t f t similar to ASF’s traversal functions / Faculteit Wiskunde en Informatica 9-12-2009 PAGE 7
ATL matched rules Rules • Each matched rule is identified by its name ( rule_name ). • Lazy matched rules • A matched rule name must be unique within an ATL lazy rule rule_name{ from in: MM1!MetaClass transformation. using { <variable definitions> } • An ATL matched rule is composed of out1: MM2!MetaClass1( to • two mandatory sections <bindings1> ), − from and to parts. out2: MM2!MetaClass2( • two optional sections: two optional sections: <bindings2> <bindings2> − using and do parts. ) do { <imperative block> } • The different variables that may be declared in the scope of a } rule (the source and target pattern elements and the local rule (the source and target pattern elements and the local • Generates new target elements for every call to the rule G t t t l t f ll t th l variables) must have a unique name. • Invoked from other rules as follows: thisModule.rule_name( <model element of type MM1!MetaClass> ) / Faculteit Wiskunde en Informatica 9-12-2009 PAGE 8 Rules Rules • Unique lazy matched rules • Called rules unique lazy rule rule_name{ [entrypoint]? rule rule_name( <parameters> ){ from in: MM1!MetaClass using { <variable definitions> } using { <variable definitions> } to out1: MM2!MetaClass1( to out1: MM2!MetaClass1( <bindings1> <bindings1> ), ), out2: MM2!MetaClass2( out2: MM2!MetaClass2( <bindings2> <bindings2> <bindings2> <bindings2> ) ) do { <imperative block> } do { <imperative block> } } } • Always returns the same target elements for a given Al t th t t l t f i • For generating target elements from imperative code source element, i.e., target elements are generated only once per source element • No from clause
Called rules Called rules • Besides matched rules, ATL defines an additional • A called rule is identified by its name ( rule_name ). • A called rule name must be unique within an ATL kind of rules enabling to explicitly generate target transformation, model elements from imperative code. • must not collide with a helper name • Except for the entrypoint called rule this kind of • Except for the entrypoint called rule, this kind of • a called rule cannot be called "main". rules must be explicitly called from an ATL • A called rule can optionally be declared as the transformation imperative block. entrypoint . entrypoint . • an ATL transformation can include one entrypoint called rule. • it is implicitly invoked at the beginning of the transformation execution once the module initialization phase has execution, once the module initialization phase has completed. / Faculteit Wiskunde en Informatica / Faculteit Wiskunde en Informatica 9-12-2009 PAGE 12 9-12-2009 PAGE 13 Called rules Helpers • A called rule can accept parameters. • Helper with context helper context MM!MetaClass def : helper_name( <parameters> ): return_type = • It is composed of three optional sections: let <variable definition> • the using , in <expression> ; • Invocation: Invocation: • the to and <model element of type MM!MetaClass> .helper_name( <parameters> ) • the do sections. • The context should never be of a collection type • Helper without context • Compared to a matched rule, a called rule has no from p Compared to a matched rule, a called rule has no from helper def : helper_name( <parameters> ): return_type = section, and its to section is optional. let <variable definition> in <expression> ; • • Invocation: Invocation: thisModule.helper_name( <parameters> ) • For OCL functions refer to the ATL user guide • For OCL functions refer to the ATL user guide / Faculteit Wiskunde en Informatica 9-12-2009 PAGE 14
Recommend
More recommend