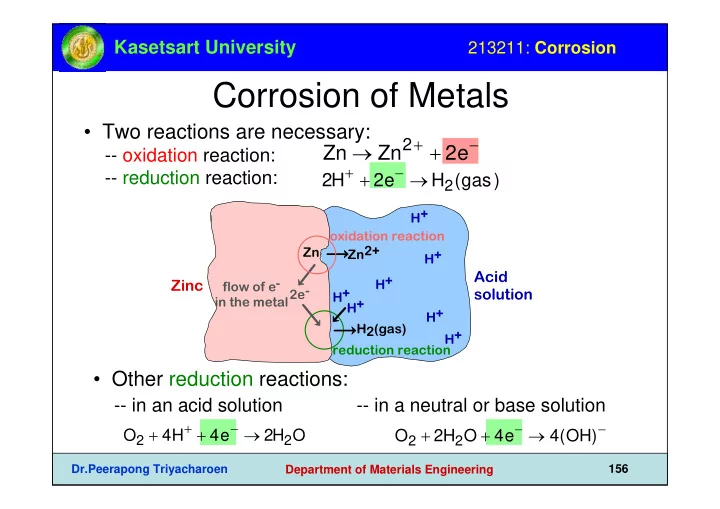

Kasetsart University 213211: Corrosion Corrosion of Metals • Two reactions are necessary: Zn → Zn 2 + + 2e − -- oxidation reaction: 2H + + 2e − → H 2 (gas) -- reduction reaction: H+ oxidation reaction Zn2+ Zn H+ Acid H+ flow of e- Zinc 2e- H+ solution in the metal H+ H+ H2(gas) H+ reduction reaction • Other reduction reactions: -- in an acid solution -- in a neutral or base solution O 2 + 4H + + 4e − → 2H 2 O O 2 + 2H 2 O + 4e − → 4(OH) − Dr.Peerapong Triyacharoen 156 Department of Materials Engineering
Kasetsart University 213211: Corrosion Standard Hydrogen (emf) Test • Two outcomes: --Metal sample mass --Metal sample mass e- e- e- e- H2 (gas) 2e- H+ ne- ne- 2e- H+ Platinum Platinum metal, M metal, M Mn+ Mn+ H+ ions ions H+ 25°C 25°C 1M Mn+ sol’n 1M H+ sol’n 1M Mn+ sol’n 1M H+ sol’n --Metal is the anode (-) --Metal is the cathode (+) o o < 0 (relative to Pt) > 0 (relative to Pt) V metal V metal Standard Electrode Potential Dr.Peerapong Triyacharoen 157 Department of Materials Engineering
Kasetsart University 213211: Corrosion Standard EMF Series • EMF series o V metal metal • Metal with smaller o V corrodes. more cathodic +1.420 V Au metal +0.340 Cu • Ex: Cd-Ni cell - 0.126 Pb - + - 0.136 Sn o - 0.250 Ni DV = - 0.277 Co 0.153V - 0.403 Cd more anodic - 0.440 Fe - 0.744 Cr Cd 25°C Ni - 0.763 Zn - 1.662 Al - 2.262 Mg 1.0 M 1.0 M - 2.714 Na Cd2+ solution Ni2+ solution - 2.924 K Dr.Peerapong Triyacharoen 158 Department of Materials Engineering
Kasetsart University 213211: Corrosion Effect of Solution Concentration • Ex: Cd-Ni cell with • Ex: Cd-Ni cell with standard 1M solutions non-standard solutions o − V Cd o − V Cd − RT nF ln X o = 0.153 o V Ni − V Cd = V Ni V Ni Y - - + + n = #e - per unit oxid/red Cd 25°C Ni Cd Ni T reaction (=2 here) 1.0 M 1.0 M X M Y M F = Cd2+ solution Ni2+ solution Cd2+ solution Ni2+ solution Faraday's • Reduce V Ni - V Cd by constant =96,500 --increasing X C/mol. --decreasing Y Dr.Peerapong Triyacharoen 159 Department of Materials Engineering
Kasetsart University 213211: Corrosion Galvanic Series • Ranks the reactivity of metals/alloys in seawater more cathodic Platinum Gold Graphite (inert) Titanium Silver 316 Stainless Steel Nickel (passive) Copper Nickel (active) Tin more anodic Lead (active) 316 Stainless Steel Iron/Steel Aluminum Alloys Cadmium Zinc Magnesium Dr.Peerapong Triyacharoen 160 Department of Materials Engineering
Kasetsart University 213211: Corrosion Forms of Corrosion • Stress corrosion • Uniform Attack • Erosion-corrosion Stress & corrosion Oxidation & reduction Break down of passivating work together occur uniformly over layer by erosion (pipe at crack tips. surface. elbows). • Selective Leaching • Pitting Forms Preferred corrosion of Downward propagation of one element/constituent of small pits & holes. (e.g., Zn from brass (Cu-Zn)). corrosion • Intergranular Corrosion along grain boundaries, • Galvanic • Crevice Between two often where special Dissimilar metals are pieces of the same metal. phases exist. physically joined. The Rivet holes g.b. more anodic one prec. corrodes.(see Table 17.2) Zn & Mg attacked zones very anodic. Dr.Peerapong Triyacharoen 161 Department of Materials Engineering
Kasetsart University 213211: Corrosion Controlling Corrosion Metal oxide • Self-protecting metals! Metal (e.g., Al, --Metal ions combine with O stainless steel) to form a thin, adhering oxide layer that slows corrosion. • Reduce T (slows kinetics of oxidation and reduction) • Add inhibitors --Slow oxidation/reduction reactions by removing reactants (e.g., remove O 2 gas by reacting it w/an inhibitor). --Slow oxidation reaction by attaching species to the surface (e.g., paint it!). • Cathodic (or sacrificial) protection --Attach a more anodic material to the one to be protected. e.g., zinc-coated nail e.g., Mg Anode Zn 2+ Cu wire e- zinc zinc steel Mg 2+ Mg 2e - 2e - pipe anode steel Earth Dr.Peerapong Triyacharoen 162 Department of Materials Engineering
Kasetsart University 213211: Corrosion Summary • Corrosion occurs due to: --the natural tendency of metals to give up electrons. --electrons are given up by an oxidation reaction. --these electrons then are part of a reduction reaction. • Metals with a more negative Standard Electrode Potential are more likely to corrode relative to other metals. • The Galvanic Series ranks the reactivity of metals in seawater . • Increasing T speeds up oxidation/reduction reactions . • Corrosion may be controlled by: -- using metals which form -- adding inhibitors a protective oxide layer -- painting -- reducing T --using cathodic protection. Dr.Peerapong Triyacharoen 163 Department of Materials Engineering
Recommend
More recommend