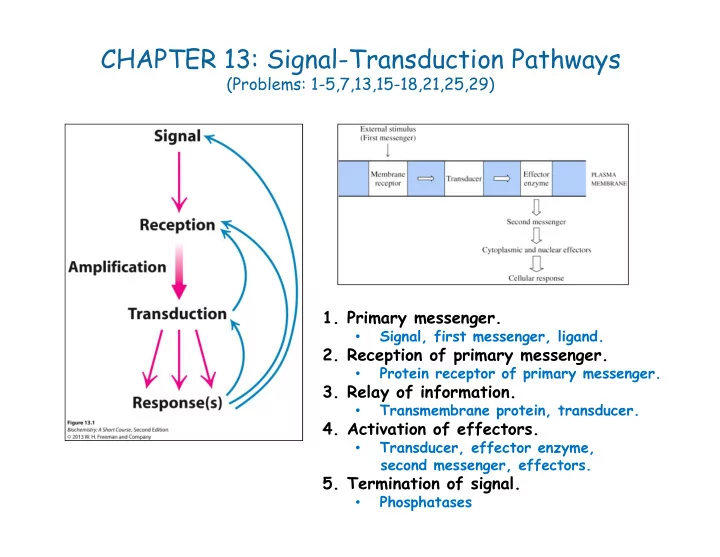

CHAPTER 13: Signal-Transduction Pathways (Problems: 1-5,7,13,15-18,21,25,29) 1. Primary messenger. Signal, first messenger, ligand. • 2. Reception of primary messenger. Protein receptor of primary messenger. • 3. Relay of information. Transmembrane protein, transducer. • 4. Activation of effectors. Transducer, effector enzyme, • second messenger, effectors. 5. Termination of signal. Phosphatases •
13.2. Receptor Proteins Ligand Binding Transmembrane proteins Seven transmembrane helices (7TM proteins) Ligand binding on outside leads to conformational change (new activity) on inside of cell.
Ligand Binding → Activation of G-Proteins → Activation of Effector Proteins Effector ligand enzyme 7TM receptor G s Transducer Second (G-protein) messenger Effector
Activation of Effector Proteins → Phosphorylation of Proteins Protein kinase A Protein kinase A phosphorylates Ser and Thr residues in numerous proteins resulting in activation or inhibition of their functions.
Control of Activation X GTP X G-cycle Chlorera ( Vibrio cholorae ) Whooping Cough ( Bordertella pertussis ) Choleragen → stabilizes G s Toxin → prevents G i ↓ ↓ Open Cl ‐ channel Closes K + channel ↓ ↓ Inhibits Na + ‐ H + exchange Opens Ca 2+ channel ↓ NaCl loss
Reversible Ligand/Receptor Binding
Other Second Messengers 2 nd messenger 2 nd messenger Ligand/Receptor binding leads to G ‐ protein activation
The Phosphoinositide Cascade Ligand + Receptor Active G ‐ Protein Activates C Phosphorylation of Ser and thr on many proteins
13.3. Tyrosine Kinases Epidermal Growth Factor Signaling X Pi Adaptor proteins Tumors
13.4. Insulin Signaling Phosphorylate enzymes in Akt is a glycogen mobile protein synthesis and Insulin-receptor glucose kinase substrates transport (GLUT4) Signaling terminated by protein phosphatases
13.4. Calcium Ion is a Cytoplasmic Messenger CaM-Kinase CaM-Ca 2+ + Inactive CaM-Ca 2+ CaM-Kinase Active Phosphorylation of proteins resulting in regulation of fuel metabolism, ion permeability, neurotransmitters
Recommend
More recommend