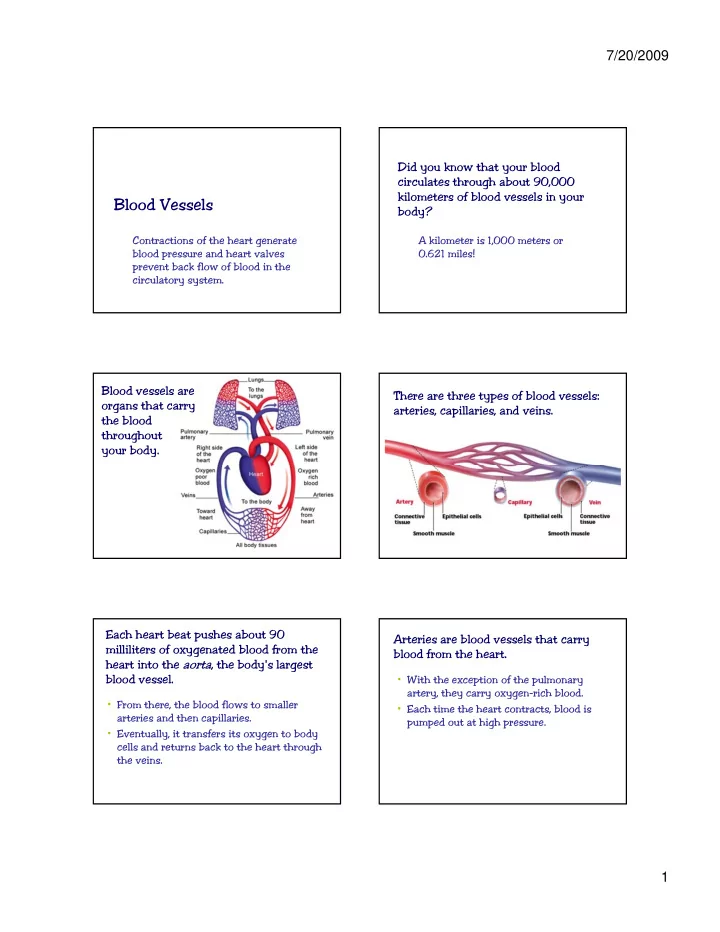

7/20/2009 Did you know that your blood circulates through about 90,000 kilometers of blood vessels in your Blood Vessels body? Contractions of the heart generate A kilometer is 1,000 meters or blood pressure and heart valves 0.621 miles! prevent back flow of blood in the circulatory system. Blood vessels are There are three types of blood vessels: organs that carry arteries, capillaries, and veins. the blood throughout your body. Each heart beat pushes about 90 Arteries are blood vessels that carry milliliters of oxygenated blood from the blood from the heart. heart into the aorta , the body's largest blood vessel. • With the exception of the pulmonary artery, they carry oxygen-rich blood. • From there, the blood flows to smaller • Each time the heart contracts, blood is Each time the heart contracts, blood is arteries and then capillaries. pumped out at high pressure. • Eventually, it transfers its oxygen to body cells and returns back to the heart through the veins. 1
7/20/2009 Veins are blood vessels that carry blood Arteries are made of three layers of toward the heart. tissues that help them withstand that pressure. • With the exception of the pulmonary veins, they carry oxygen- y y yg poor blood. Veins are aided in pushing blood back Like arteries, veins have three tissue toward the heart by the skeletal muscles layers. as they contract and squeeze nearby veins. But veins have thinner walls because Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels they do not receive blood directly from where the exchange of materials with the heart. cells takes place. • They form a net-like structure throughout • The largest veins have one-way valves to your tissues. y keep blood flowing toward the heart keep blood flowing toward the heart. 2
7/20/2009 Contractions of the heart generate blood Capillary walls are only one cell thick and may be so narrow that blood cells must pass pressure. through in single file. • The rhythmic change in blood pressure is • Oxygen and other materials diffuse through called a pulse. capillary walls into the tissues and then • Blood pressure keeps the blood flowing in into cells. th the right direction. i ht di ti • Valves prevent backflow of blood. Blood pressure is a measure of the force Normal blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg. of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries. • The top number is called the systolic pressure; the lower number is called • It is measured in millimeters of mercury diastolic pressure. (mm Hg). • Systolic pressure is the maximum force • Systolic pressure is the maximum force • A pressure of 100 mm Hg means the exerted against artery walls each time the pressure is great enough to push a heart contracts. narrow column of mercury 100 mm • Diastolic pressure is the force exerted on high. the arteries when the heart relaxes. 3
7/20/2009 The number at which blood starts A sphyg·mo·ma·nom·e·ter is used to flowing is the measure of the systolic measure blood pressure. pressure. • The cuff is pumped up with air to restrict blood flow in • Pressure in the cuff continues to release. the arm. • The point at which no sound is heard p • As the pressure in the cuff indicates the pressure in the system when is released, blood starts the heart is relaxed— the diastolic reading flowing again. • You can hear the flow in a stethoscope. Blood pressure increases with age. • The blood vessels of an infant are very elastic. • As the elasticity of a person’s blood • vessels decreases, their blood pressure l d h i bl d increases; this is what typically happens with age. Those arteries branch into smaller and smaller arteries and into capillaries. ( 9 ). From there, blood flows into the lungs where it picks up oxygen ( 4 ). When the left ventricle contracts, blood is pumped through a valve When the right ventricle and into the aorta ( 7 ). contracts, blood is pumped through a valve and into the pulm onary artery ( 3 ). The aorta branches into h b h arteries that lead to upper The inferior vena cava carries and lower parts of the body ( 8 ). oxygen-poor blood from the lower body parts ( 1 ). The now oxygen-rich blood is When the right atrium contracts, carried back to the left atrium the blood goes through a valve and through the pulm onary veins into the right ventricle ( 2 ). ( 5 ). I n the capillaries, blood cells release their When the left atrium contracts, blood oxygen which diffuses into tissues . Carbon goes through a valve into the left dioxide and water are picked up from the body ventricle ( 6 ) cells. The now oxygen-poor blood flows through the capillaries and into small veins ( 1 0 ). 4
Recommend
More recommend