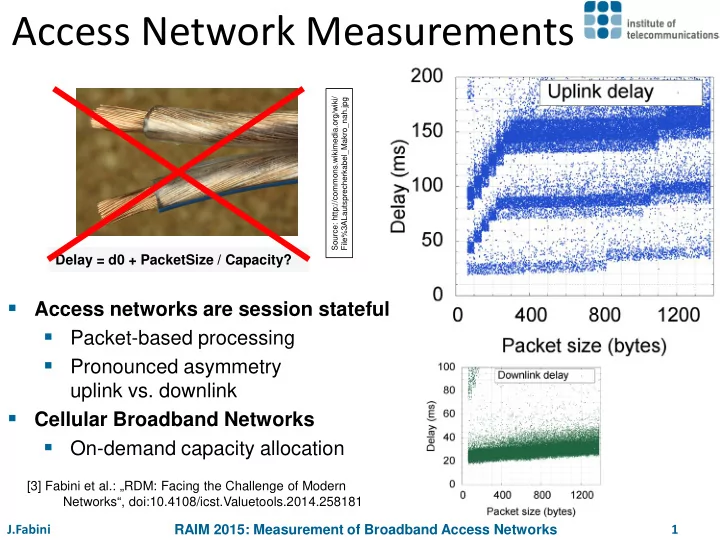

Access Network Measurements Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/ File%3ALautsprecherkabel_Makro_nah.jpg Delay = d0 + PacketSize / Capacity? Access networks are session stateful Packet-based processing Pronounced asymmetry uplink vs. downlink Cellular Broadband Networks On-demand capacity allocation [3] Fabini et al.: „RDM: Facing the Challenge of Modern Networks“, doi:10.4108/icst.Valuetools.2014.258181 J.Fabini RAIM 2015: Measurement of Broadband Access Networks 1
On-Demand Capacity Allocation (a) HSPA low avg. bit rate (b) HSPA higher avg bit rate Observations: Stream patterns matter! (application, measurements, …) Packet inter-departure time, average bit rate, packet size, … Packet start-time matters (details at HOPS-NG IRTF meeting)! Start-time randomness imperative for unbiased results! J.Fabini RAIM 2015: Measurement of Broadband Access Networks 2
Delay vs. Capacity Reasoning (a) VDSL UL (768 kbit/s) (b) VDSL DL (8 Mbit/s) Observations: Delay not necessarily (inverse) proportional to link capacity! Reason in this case: interleaving activated on VDSL downlink [1] Fabini and Zseby: „M2M communication delay challenges: Application and measurement perspectives“, doi: 10.1109/I2MTC.2015.7151564 J.Fabini RAIM 2015: Measurement of Broadband Access Networks 3
Conclusion Networks and middleboxes bias on communications At low load, when operating within specifications State vs. Coding HSDPA 384k UL middlebox? Access networks: middleboxes “Dormant” middlebox: time-domain vs. value-domain Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/ File%3ALautsprecherkabel_Makro_nah.jpg Main conclusion: Think (at least) twice before abstracting access link behavior Contact: Joachim.Fabini@tuwien.ac.at J.Fabini RAIM 2015: Measurement of Broadband Access Networks 4
Bibliography [1] Fabini and Morton: IETF RFC 7312 “Advanced Stream and Sampling Framework for the IPPM” [2] Fabini and Abmayer: “Delay Measurement Methodology Revisited: Time-slotted Randomness Cancellation“, doi:10.1109/TIM.2013.2263914 [3] Fabini et al.: „RDM: Facing the Challenge of Modern Networks“, doi:10.4108/icst.Valuetools.2014.258181 [4] Fabini and Zseby: „M2M communication delay challenges: Application and measurement perspectives“, doi: 10.1109/I2MTC.2015.7151564 [5] Fabini and Zseby: „The Right Time: Reducing Effective End-to-End Delay in Time- Slotted Packet-Switched Networks“, doi:10.1109/TNET.2015.2451708 Contact: Joachim.Fabini@tuwien.ac.at J.Fabini RAIM 2015: Measurement of Broadband Access Networks 5
Recommend
More recommend