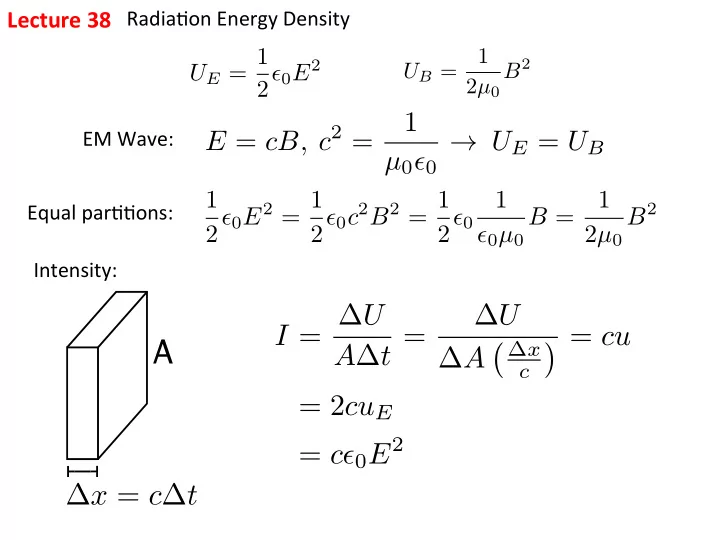

Lecture ¡38 ¡ Radia%on ¡Energy ¡Density ¡ U E = 1 1 B 2 2 ✏ 0 E 2 U B = 2 µ 0 1 E = cB, c 2 = EM ¡Wave: ¡ → U E = U B µ 0 ✏ 0 2 ✏ 0 E 2 = 1 1 2 ✏ 0 c 2 B 2 = 1 1 1 Equal ¡par%%ons: ¡ B 2 B = 2 ✏ 0 ✏ 0 µ 0 2 µ 0 Intensity: ¡ I = ∆ U ∆ U � = cu A ∆ t = � ∆ x A ∆ A c = 2 cu E = c ✏ 0 E 2 ∆ x = c ∆ t
Time ¡dependence ¡of ¡I ¡at ¡x ¡= ¡x 0 : ¡ I 0 I 0 I ( x 0 , t ) = 2 Time ¡averaged ¡value: ¡ ¯ I = c ✏ 0 E 2 max cos 2 ( ! t − kx ) I 2 = c ✏ 0 E 2 p ¯ ∴ ¯ E 2 E rms = max 2
Intensity ¡Vector ¡(Poyn%ng ¡Vector) ¡ E × ~ ~ B ~ S = EB Show ¡that: ¡ = cu = c ✏ 0 E 2 µ 0 µ 0 Energy-‑Momentum ¡Rela%onship: ¡Rela%vis%c ¡Kinema%c ¡ 1 1 − β 2 , β = v For ¡a ¡par%cle ¡will ¡mass ¡ m : ¡ γ = ⇢ Energy p c U = mc 2 γ Momentum p = mv γ Light ¡par%cle: ¡photon ¡ m = 0 , v = c p = mc 2 γ mv γ = c 2 U c = c, or U = pc
Radia%on ¡Pressure ¡ dU/C ⇢ ∆ U absorptive : ∆ tcA = u dtA = Pressure = F A = dp dt / A reflective : 2 u Geometry ¡Dependent ¡A: ¡Reflec%ve ¡Example ¡ F = 2 uA Geometric ¡considera%on: ¡ I = ∆ U ∆ tA = Power A I = Power Light ¡beam ¡shining ¡on ¡a ¡book: ¡ ∆ A A Bulb ¡shining ¡on ¡a ¡book: ¡ I = Power ∆ A ∆ A 4 π R 2 ∆ A ✓ Power ∆ A ◆ I book = / ∆ A 4 π R 2
Polariza%on ¡ Define: ¡Direc%on ¡of ¡polariza%on ¡= ¡direc%on ¡of ¡oscilla%on ¡of ¡E ¡ Metal ¡perpendicular ¡ strips: ¡ ~ E E-‑parallel ¡drives ¡electron ¡oscilla%on ¡ E ⊥ ¡Large ¡induced ¡current ¡ Energy ¡absorbed ¡by ¡medium ¡ E k E-‑perp. ¡Negligible ¡induced ¡current ¡ This ¡component ¡can ¡be ¡transmiVed ¡ The ¡strip ¡setup ¡serves ¡as ¡a ¡polarizer. ¡ ¡ If ¡the ¡incident ¡light ¡is ¡unpolarized ¡(i.e. ¡polariza%on ¡is ¡uniformly ¡distributed ¡in ¡the ¡ azimuthal ¡direc%on) ¡the ¡outgoing ¡light ¡will ¡be ¡polarized ¡in ¡the ¡ver%cal ¡direc%on ¡– ¡direc%on ¡ of ¡E-‑parallel ¡ ¡ If ¡the ¡incident ¡light ¡is ¡polarized ¡along ¡E ¡where ¡there ¡is ¡angle ¡θ ¡between ¡E-‑perp ¡and ¡E, ¡then ¡ E-‑perp ¡= ¡E ¡cosθ, ¡ Outgoing ¡Intensity: ¡ I out = I in cos 2 θ This ¡is ¡Malus’ ¡law. ¡
Metal ¡Strip ¡Analyzer ¡ • Rota%ng ¡the ¡strip ¡can ¡check ¡polariza%on ¡of ¡the ¡incident ¡light. ¡ • Unpolarized ¡incident ¡light, ¡if ¡no ¡varia%on ¡in ¡intensity ¡ • Unpolarized ¡light ¡may ¡be ¡represented ¡by ¡two ¡equal ¡weight ¡mutually ¡ perpendicular ¡polarized ¡lights ¡ ¡ • Two ¡mutually ¡perpendicular ¡analogues ¡can ¡fully ¡block ¡out ¡an ¡ polarized ¡light ¡ Radia%on ¡from ¡a ¡charged ¡par%cle ¡ini%ally ¡at ¡rest: ¡ D E ~ v × ~ q ~ F = q ~ h ~ v i = B E D E D E D E D E q ~ v × ~ v × ~ E × ~ ~ q ~ ~ q > 0 case, F B B B = = = Direc%on ¡of ¡magne%c ¡force ¡on ¡q ¡ini%ally ¡at ¡rest: ¡ HINT: ¡ q ¡> ¡0 ¡ q ¡< ¡0 ¡ ~ v × ~ F = q ~ B 1) ¡ Le^ ¡ Le^ ¡ h v i = h qE i 2) ¡ Right ¡ Le^ ¡ 3) ¡ Le^ ¡ Right ¡ h F i = q 2 D E E ⇥ ~ No%ce: ¡ ¡ B X 4) ¡ Right ¡ Right ¡
The ¡polarized ¡sky ¡light ¡ Sunlight: ¡Unpolarized ¡light ¡ ¡RescaVered ¡light ¡observed ¡by ¡ground ¡ ¡observer ¡is ¡polarized ¡along ¡z ¡ Fig(mi) ¡24.51 ¡ Intensity ¡of ¡scaVered ¡light: ¡ I = cu = c ( u E + u B ) = c · 2 u E = c ✏ 0 E 2 , E ↵ a ⊥ ∝ ! 2 z Compare ¡Intensity ¡of ¡rescaVered ¡light ¡with ¡frequencies ¡ω 1 ¡and ¡ω 2 : ¡ ◆ 2 ◆ 2 ◆ 4 ◆ 4 = E 2 ✓ ω 2 ✓ a ⊥ 1 ✓ ω 1 ✓ λ 2 I 1 1 z 1 = = = = E 2 ω 2 ω 2 λ 1 I 2 a ⊥ 2 2 z 2 ◆ 4 λ r = 700 nm 400 nm = 1 . 75 , I b ✓ λ r I blue = (1 . 75) 4 ≈ 9 = I red λ b λ b I r
Recommend
More recommend