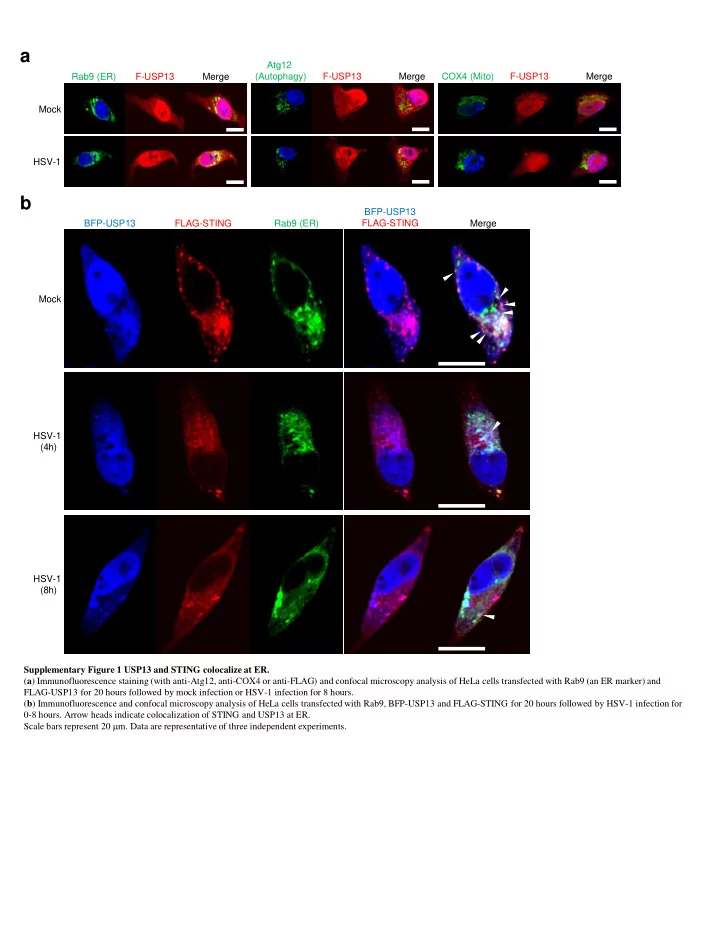

a Atg12 Rab9 (ER) F-USP13 Merge (Autophagy) F-USP13 Merge COX4 (Mito) F-USP13 Merge Mock HSV-1 b BFP-USP13 BFP-USP13 FLAG-STING Rab9 (ER) FLAG-STING Merge Mock HSV-1 (4h) HSV-1 (8h) Supplementary Figure 1 USP13 and STING colocalize at ER. ( a ) Immunofluorescence staining (with anti-Atg12, anti-COX4 or anti-FLAG) and confocal microscopy analysis of HeLa cells transfected with Rab9 (an ER marker) and FLAG-USP13 for 20 hours followed by mock infection or HSV-1 infection for 8 hours. ( b ) Immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy analysis of HeLa cells transfected with Rab9, BFP-USP13 and FLAG-STING for 20 hours followed by HSV-1 infection for 0-8 hours. Arrow heads indicate colocalization of STING and USP13 at ER. Scale bars represent 20 m m. Data are representative of three independent experiments.
a b c THP-1 shCon siRNA: N.C. #1 #2 #3 4000 IFNB shCon shUSP13#1 shUSP13#1 kDa shUSP13#2 -USP13 3000 90 SeV: 0 4 8 12 0 4 8 12 h - 50 - MW (kDa) - b -Actin -pI k B a 34 - 2000 d -I k B a 34 - -pIRF3 IFNB TNFA 1000 50 5000 - 30 siN.C. -IRF3 50 - Rel. mRNA Level siUSP13#2 0 50 4000 - -pERK 20 50 - -ERK 3000 80 10 TNFA 50 Rel. mRNA Level - -pJNK * 500 *** 6 60 50 -JNK - -p-p65 250 40 50 3 - -p65 * 50 - 20 -USP13 0 90 - 50 - - b -Actin 0 1000 e f THP-1 THP-1 siN.C. siUSP13#2 siN.C. siUSP13#2 IL6 750 SeV: 0 6 12 0 6 12 h HSV-1: 0 6 12 0 6 12 h MW (kDa) -pI k B a MW (kDa) -pI k B a 34 500 - 34 - -I k B a -I k B a 34 34 - - 250 -pIRF3 -pIRF3 50 50 - - -IRF3 -IRF3 50 0 - 50 - SeV: 0 4 8 12 h -USP13 90 -USP13 - 90 - 50 50 - - - b -Actin - b -Actin Supplementary Figure 2 Knockdown of USP13 did not affect SeV-triggered signaling. ( a ) qRT-PCR analysis of IFNB , TNFA , and IL6 in THP-1 cells stably transfected with control shRNA, shUSP13#1 or shUSP13#2, then infected with HSV-1 for 0-24 hours. ( b ) Immunoblot analysis of phosphorylated and total IRF3, I k B a , ERK, p38, and JNK and b -Actin in THP-1 cells stably transfected with control shRNA or shUSP13#1, then infected with HSV-1 for 0-12 hours. ( c ) Immunoblot analysis (with anti-USP13 or anti- β -Actin) of THP-1 cells transfected siRNAs targeting USP13 (#1, #2, #3) or non-targeting control siRNA(N.C.) for 36 hours. ( d ) qRT-PCR analysis of IFNB and TNFA in THP-1 cells transfected with siUSP13#2 or N.C. for 36 hours, then infected with HSV-1 or SeV for 0-8 hours. ( e-f ) Immunoblot analysis of phosphorylation of IRF3 and I k B a , total IRF3 and I k B a , USP13 and b -Actin in THP-1 cells transfected with siUSP13#2 or N.C. for 36 hours, then infected with SeV (e) or HSV-1 (f) for 0-8 hours. * P < 0.05; *** P <0.001 (analysis of two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test). Data are representative of three independent experiments (mean S.D. in a and d ).
a ATG Usp13 allele exon1 exon2 exon3 5’···CATATGCCCACGATCCGCGTGCCCAGGTCGGGGGACCGCGTCT···3’ 3 ’··· GGTGCTAGGCGCACGGGTCCAGC···5 ’ Cas9 gRNA sequence: PAM Cas9-gRNA Wild-type Usp13 allele: 5’···CATATGCCCACGATCCGCGTGCCCAGGTCGGGGGACCGCGTCT···3’ 5’···CATATGCCCACGA C TCCGCGTGCCCAGGTCGGGGGACCGCGTCT···3’ Mutant Usp13 allele: Insertion c b Bone marrow Reading frame +/+ m/m Usp13: 91 CCC ACG ATC CGC ……C TCT GAA CTC ….. AGCTAA 2577 bp +/+ MW (kDa) 31 P T I R …… S E L ....… S * 858aa (full length) 120- -USP13 90- -NS GCCCACGATCCGCGTGC 50- 34- +/m 26- 50- - b -Actin GCCCACGATCCGCGTGC CTCCGCGTG 91 CCC ACG ACT CCG …….CTC TGA 171 bp m/m 31 P T T P …… L * 56aa (early termination) GCCCACGACTCCGCGTG Supplementary Figure 3 Generation of Usp13 m/m mice. ( a ) A scheme for CRIPSR/Cas9-mediated genome editing of the Usp13 gene locus. ( b ) Gene sequence and reading frame of Usp13 +/+ , Usp13 +/m and Usp13 m/m mice. ( c ) Immunoblot analysis of USP13 in bone marrow cells from Usp13 +/+ and Usp13 m/m mice. Data are representative of two ( c ) independent experiments.
a b 24 F -Usp13 +/+ Usp13 +/+ Usp13 +/m Usp13 m/m Genotype F- Usp13 m/m Body Weight (g) 21 M- Usp13 +/+ Number 121 258 110 M- Usp13 m/m Percentage 24.7% 52.8% 22.5% 18 15 12 Weeks after birth 6 7 8 9 c d GM-CSF culture Flt3L culture Usp13 +/+ Usp13 m/m Usp13 +/+ Usp13 m/m 2.24 Thymus 100 79.0 78.2 79.7 Cell number (x 10 6 ) Usp13 +/+ 80 SSC 67.5 68.3 6.79 60 CD11c 2.43 M-CSF culture CD11c 40 80.9 23.3 22.9 Usp13 m/m 20 CD8 96.2 97.9 6.08 CD11b 0 CD11b Usp13 : +/+ m/m 66.7 69.1 CD4 F4/80 B220 e Spleen 35.8 21.4 31.2 1.44 400 53.9 Cell number (x 10 6 ) Usp13 +/+ 300 19.3 55.5 53.6 200 34.3 23.3 32.3 1.36 100 51.6 Usp13 m/m CD25 CD44 CD3 CD8 19.7 57.6 0 52.9 Usp13 : +/+ m/m CD19 CD4 CD4 CD62L f Peripheral lymph nodes 48.8 7.01 72.6 8 4.32 48.5 Cell number (x 10 6 ) Usp13 +/+ 6 31.9 72.9 22.6 4 46.3 7.62 66.4 4.41 2 47.3 Usp13 m/m CD25 CD44 CD3 CD8 31.6 70.8 0 28.0 Usp13 : +/+ m/m CD19 CD4 CD4 CD62L Supplementary Figure 4 USP13 deficiency did not alter the homeostasis of immune cells. ( a ) Mice numbers and percentages of each genotype. ( b ) Mice body weight of each genotype. F, Female; M, Male. ( c ) Flow cytometry analysis of GM-CSF, M-CSF or Flt3L induced DCs, Macrophage cells or pDCs from Usp13 +/+ and Usp13 m/m mice. ( d-f ) Flow cytometry analysis of immune cells and quantitative data in thymus ( e ), spleen ( f ) and peripheral lymph nodes from Usp13 +/+ and Usp13 m/m mice. Data are representative of two ( c-f ) independent experiments (n=3) (mean S.D. in b, d-f ).
a MEF- Ifnb MEF- Ifna4 MEF- Tnf MEF- Ccl5 *** Rel. mRNA Level *** *** Usp13 +/+ 8000 4000 150 2000 Usp13 m/m 2000 4000 1000 100 * *** *** *** *** *** *** 50 * ** 500 100 200 * * 0 0 0 0 BMDM- Ifnb BMDM- Ifna4 BMDM- -Tnf BMDM- Ccl5 400 250 1000 * Rel. mRNA Level 3000 ** ** *** 200 *** 800 300 2000 ** *** *** *** 200 *** *** * *** *** ** 100 400 *** ** 1000 *** ** 100 0 0 0 0 b MEFs MEFs WT Usp13 m/m WT Usp13 m/m SeV: 0 4 8 0 4 8 h 8 0 4 8 h HSV-1: 0 4 MW (kDa) MW (kDa) -pI k B a -pI k B a 34 34 - - -I k B a 34 -I k B a 34 - - -p-IRF3 -p-IRF3 50 50 - - -IRF3 50 -IRF3 50 - - 90 90 -USP13 - - -USP13 50 50 - - - β -Actin - β -Actin c d e MEFs 2.5 Usp13 +/+ Usp13 +/+ 50000 Usp13 m/m HSV-1 UL30 Rel.mRNA Level HSV-1-GFP Usp13 m/m HSV-1 titer (x 10 4 PFU/ml) * Mock MOI=0.05 MOI=0.1 *** 2.0 40000 0.082 3.62 7.68 1.5 30000 WT 1.0 20000 *** 300 0.5 200 0.041 2.29 5.27 100 Usp13 m/m 0 0 SSC GFP Supplementary Figure 5 USP13 deficiency potentiated HSV-1- but not SEV-triggered signaling in MEFs or BMDMs. ( a ) qRT-PCR analysis of Ifnb , Ifna4 , Tnf or Ccl5 mRNA in Usp13 +/+ and Usp13 m/m MEFs or BMDMs left uninfected (Mock) or infected with HSV-1, SeV, HCMV or EMCV for 0-8 hours, or mock transfected (Lipo) or transfected with ISD45, DNA90 or poly(I:C) for 6 hours. ( b ) Immunoblot analysis of phosphorylation of IRF3 and I k B a , total IRF3 and I k B a , USP13 and β -Actin in Usp13 +/+ and Usp13 m/m MEFs infected with SeV or HSV-1 for 0-8 hours. ( c ) Flow cytometry analysis of Usp13 +/+ and Usp13 m/m MEFs infected with HSV-1-GFP for 24 hours. Numbers adjacent to outlined areas indicate the percentages of GFP + MEFs. ( d ) qRT-PCR analysis of HSV-1 -UL30 mRNA in Usp13 +/+ and Usp13 m/m MEFs infected with HSV-1 for 1 hour followed by twice PBS wash and subsequent incubation in full medium for 0-24 hours. ( e ) Viral plaque assay of HSV-1 in Usp13 +/+ and Usp13 m/m MEFs infected with HSV-1 for 1 hour followed by twice PBS wash and cultured in full medium for 32 hours. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P <0.001 (analysis of two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test). Data are representative of three ( a, b ) or two ( c-e ) independent experiments (mean S.D. in a, d-e ).
Recommend
More recommend