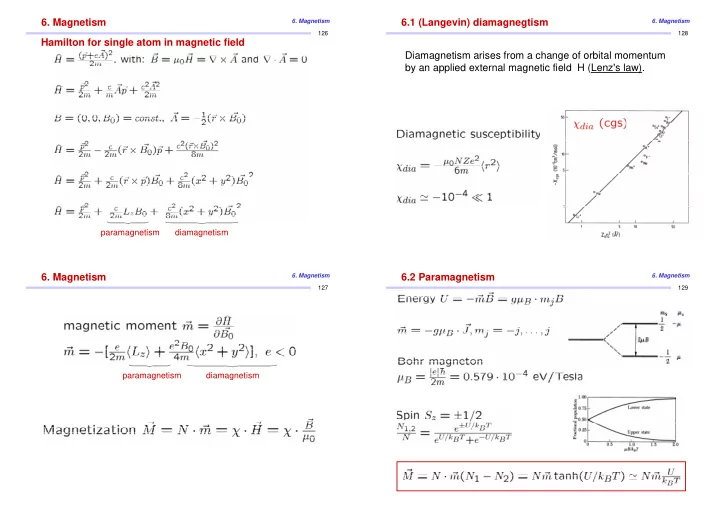

6. Magnetism 6. Magnetism 6.1 (Langevin) diamagnegtism 6. Magnetism 126 128 Hamilton for single atom in magnetic field Diamagnetism arises from a change of orbital momentum by an applied external magnetic field H (Lenz's law). paramagnetism diamagnetism 6. Magnetism 6.2 Paramagnetism 6. Magnetism 6. Magnetism 127 129 paramagnetism diamagnetism
6.2 Paramagnetism 6. Magnetism 6.2 Paramagnetic ions, 4f-electrons 6. Magnetism 130 132 Hund´s rules: 1 / χ M ( μ B ) Gd 3+ , S=7/2 1) S is maximal 2) L is maximal (consistent with S) Fe 3+ , S=5/2 3) J=|L-S| if shell is less than half filled J=|L+S| if shell is more than half filled J = S if shell is half filled Cr 3+ , S=3/2 Trivalent 4f - ions: Gd(C 2 H 5 SO 4 ) 3 ·9H 2 O T (K) B / T (kG / K) 6.2 Paramagnetism 6.2 Paramagnetic ions, 3d-electrons 6. Magnetism 6. Magnetism 131 133 for d-electrons quenching of orbital moments in cubic symmetry
6.2 Pauli paramagnetism of conduction electrons 6. Magnetism 6.3. Exchange interaction 6. Magnetism 134 136 For free electrons: exchange hole = effective charge density seen by a single electron χ (T) direct exchange super exchange ρ eff / en indirect exchange k F r T (K) 6.3. Exchange coupling 6.4. Stoner-Wohlfarth model 6. Magnetism 6. Magnetism 135 137 ⇒ ordering of magnetic moments in absence of external B ⇒ spontaneous magnetization below the Curie temperature T C above T C : paramagnetic behavior
6.5. Tempeature dependence of ferromagnetism 6. Magnetism 6.5. Temperature dependence of ferromagnetism 6. Magnetism 138 140 T < T C : ferromagnetic behavior Ni Ni spin waves 6.5. Temperature dependence 6.6. Mean field theory 6. Magnetism 6. Magnetism 139 141 T > T C : paramagnetic behavior magnetic susceptibility diverges according to Curie-Weiss law: Ni T/°C
6.7. Spin waves - magnons 6. Magnetism 6.9. Magnetic anisotropy 6. Magnetism 142 144 Magnetization M depends not only on external field B but also on crystal orientation M(G) M(G) M(G) Fe Ni Co E ↓ B(G) B(G) B(G) zJ E F E ↑ • crystalline anisotropy (L-S coupling) zJ • shape anisotropy (dipolar interaction, stray fields) • interface anisotropy 6.8. Antiferromagnetic order 6.9. Domains 6. Magnetism 6. Magnetism 143 145 Mn 2+ in MnO a 0 =8.85 Å T=80 K a 0 =4.43 Å MnO neutron 293 K scattering Reduction of magnetic stray field ⇒ magnetic domains χ ⊥ ⇒ reduction of the total energy Domain distribution determined by microscopic and macroscopic properties (shape, anisotropy, exchange interaction) χ || Domain boundaries: continuous spin rotation Width of domain wall in bulk: few 100 lattice constants
Recommend
More recommend