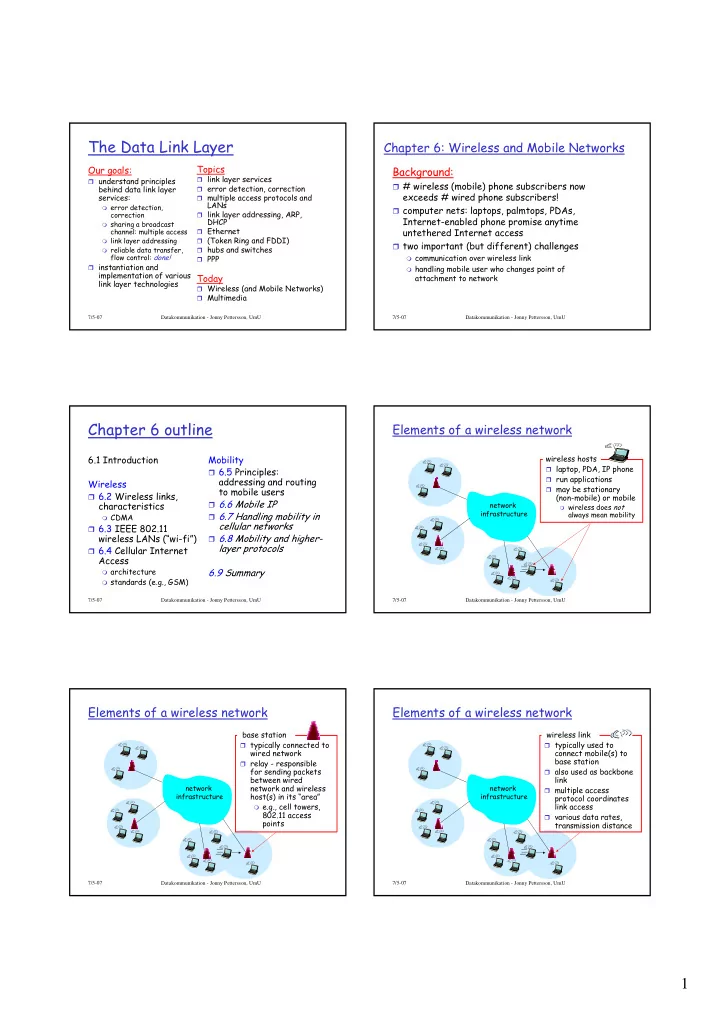

The Data Link Layer Chapter 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Our goals: Topics Background: � link layer services � understand principles � # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now behind data link layer � error detection, correction exceeds # wired phone subscribers! services: � multiple access protocols and LANs � error detection, � computer nets: laptops, palmtops, PDAs, � link layer addressing, ARP, correction Internet-enabled phone promise anytime DHCP � sharing a broadcast � Ethernet untethered Internet access channel: multiple access � (Token Ring and FDDI) � link layer addressing � two important (but different) challenges � hubs and switches � reliable data transfer, flow control: done! � communication over wireless link � PPP � instantiation and � handling mobile user who changes point of implementation of various Today attachment to network link layer technologies � Wireless (and Mobile Networks) � Multimedia 7/5-07 Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU 7/5-07 Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU Chapter 6 outline Elements of a wireless network 6.1 Introduction Mobility wireless hosts � laptop, PDA, IP phone � 6.5 Principles: � run applications addressing and routing Wireless � may be stationary to mobile users � 6.2 Wireless links, (non-mobile) or mobile � 6.6 Mobile IP characteristics network � wireless does not infrastructure � 6.7 Handling mobility in always mean mobility � CDMA cellular networks � 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs (“wi-fi”) � 6.8 Mobility and higher- layer protocols � 6.4 Cellular Internet Access � architecture 6.9 Summary � standards (e.g., GSM) 7/5-07 Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU 7/5-07 Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU Elements of a wireless network Elements of a wireless network base station wireless link � typically connected to � typically used to wired network connect mobile(s) to base station � relay - responsible for sending packets � also used as backbone between wired link network and wireless network network � multiple access host(s) in its “area” infrastructure infrastructure protocol coordinates � e.g., cell towers, link access 802.11 access � various data rates, points transmission distance 7/5-07 7/5-07 Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU 1
Characteristics of selected wireless link Elements of a wireless network standards 54 Mbps infrastructure mode 802.11{a,g} 5-11 Mbps 802.11b .11 p-to-p link � base station connects 1 Mbps mobiles into wired 802.15 network � handoff: mobile 3G changes base station 384 Kbps UMTS/WCDMA, CDMA2000 network providing connection 2G IS-95 CDMA, GSM 56 Kbps infrastructure into wired network Indoor Outdoor Mid range Long range outdoor outdoor 10 – 30m 50 – 200m 200m – 4Km 5Km – 20Km 7/5-07 Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU 7/5-07 Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU Wireless Link Characteristics Elements of a wireless network Ad hoc mode Differences from wired link …. � no base stations � nodes can only � decreased signal strength: radio signal transmit to other attenuates as it propagates through matter nodes within link (path loss) coverage � interference from other sources: standardized � nodes organize wireless network frequencies (e.g., 2.4 GHz) themselves into a shared by other devices (e.g., phone); devices network: route among (motors) interfere as well themselves � multipath propagation: radio signal reflects off objects ground, arriving at destination at slightly different times …. make communication across (even a point to point) wireless link much more “difficult” 7/5-07 Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU 7/5-07 Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU Wireless network characteristics Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Multiple wireless senders and receivers create additional problems (beyond multiple access): � used in several wireless broadcast channels (cellular, satellite, etc) standards � unique “code” assigned to each user; i.e., code set A B C partitioning C � all users share same frequency, but each user has C’s signal A’s signal own “chipping” sequence (i.e., code) to encode data strength B strength � encoded signal = (original data) X (chipping A sequence) Hidden terminal problem space � decoding: inner-product of encoded signal and Signal fading: chipping sequence � B, A hear each other � B, A hear each other � allows multiple users to “coexist” and transmit � B, C hear each other � B, C hear each other simultaneously with minimal interference (if codes � A, C can not hear each other are “orthogonal”) � A, C can not hear each other means A, C unaware of their interferring at B interference at B 7/5-07 7/5-07 Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU 2
CDMA Encode/Decode CDMA: two-sender interference channel output Z i,m Z i,m = d i . c m data d 0 = 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 d 1 = -1 bits sender - - 1 - - - - - - 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 slot 1 slot 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 code channel channel - 1 1 - - 1 - 1 1 - - 1 - 1 1 - output output slot 1 slot 0 M D i = Σ Z i,m . c m m=1 M received 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 d 0 = 1 input - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 d 1 = -1 slot 0 slot 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 code 1 channel channel 1 - - 1 - 1 - 1 - - - - 1 1 1 1 receiver output output slot 1 slot 0 7/5-07 Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU 7/5-07 802.11 LAN architecture IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN � 802.11b � All use CSMA/CA for � wireless host communicates Internet � 2.4-2.485 GHz unlicensed multiple access with base station radio spectrum � All have base-station � base station = access � up to 11 Mbps point (AP) and ad-hoc network � widely deployed, using � Basic Service Set (BSS) versions hub, switch base stations (aka “cell”) in infrastructure or router � 802.11a AP mode contains: � 5.1-5.8 GHz range � wireless hosts BSS 1 � up to 54 Mbps � access point (AP): base AP � 802.11g station � 2.4-2.485 GHz range � ad hoc mode: hosts only � up to 54 Mbps � + more… BSS 2 7/5-07 Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU 7/5-07 Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU IEEE 802.11: multiple access IEEE 802.11 MAC Protocol: CSMA/CA � avoid collisions: 2 + nodes transmitting at same time 802.11 sender � 802.11: CSMA - sense before transmitting 1 if sense channel idle for DIFS then � don’t collide with ongoing transmission by other node sender receiver transmit entire frame (no CD) � 802.11: no collision detection! 2 if sense channel busy then DIFS � difficult to receive (sense collisions) when transmitting due start random backoff time to weak received signals (fading) timer counts down while channel idle � can’t sense all collisions in any case: hidden terminal, fading data � goal: avoid collisions: CSMA/C(ollision)A(voidance) transmit when timer expires if no ACK, increase random backoff SIFS interval, repeat 2 A B C C ACK 802.11 receiver C’s signal A’s signal - if frame received OK B strength strength A return ACK after SIFS (ACK needed due to hidden terminal problem) space 7/5-07 7/5-07 Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU Datakommunikation - Jonny Pettersson, UmU 3
Recommend
More recommend