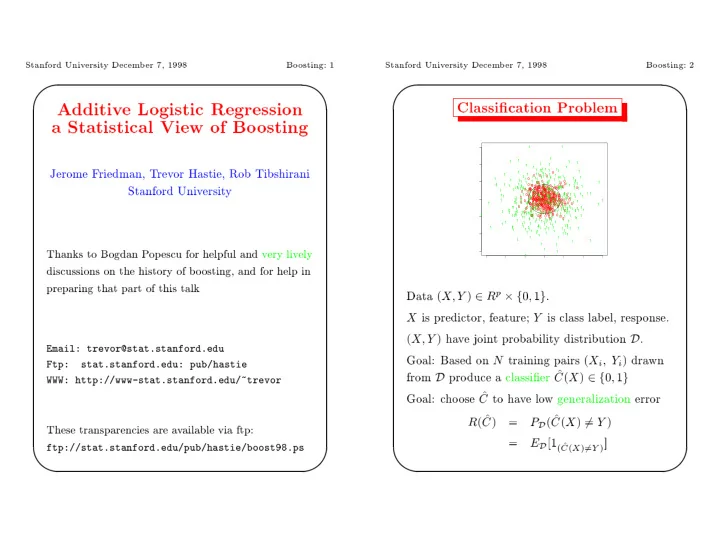

� � � � Stanford Univ ersit y Decem b er �� ���� Bo osting� � Stanford Univ ersit y Decem b er �� ���� Bo osting� � Classi�cation Problem Additiv e Logistic Regression a Statistical View of Bo osting 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Jerome F riedman� T rev or Hastie� Rob Tibshirani 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 Stanford Univ ersit y 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 00 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Thanks to Bogdan P op escu for helpful and v ery liv ely 1 1 discussions on the history of b o osting� and for help in preparing that part of this talk p Data � X � Y � � R � f � � � g � X is predictor� feature� Y is class lab el� resp onse� � X � Y � ha v e join t probabilit y distribution D � Email� trevor�stat�stanford �ed u Goal� Based on N training pairs � X � Y � dra wn Ftp� stat�stanford�edu� pub�hastie i i � from D pro duce a classi�er C � X � � f � � � g WWW� http���www�stat�sta nfo rd� edu �� tre vor � Goal� c ho ose C to ha v e lo w generalization error � � R � C � � P � C � X � � � Y � D These transparencies are a v ailable via ftp� � E �� � D � ftp���stat�stanford �e du� pub �ha sti e� boo st� ��p s � � X � � � Y � C � � � �
� � � � Stanford Univ ersit y Decem b er �� ���� Bo osting� � Stanford Univ ersit y Decem b er �� ���� Bo osting� � Deterministic Concepts Classi�cation T rees 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 94/200 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 x.2<-1.06711 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 x.2>-1.06711 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 11 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 00 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0/34 72/166 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 x.2<1.14988 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 x.2>1.14988 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 40/134 0/32 x.1<1.13632 x.1>1.13632 0 1 p X � R has distribution D � 23/117 0/17 x.1<-0.900735 x.1>-0.900735 C � X � is deterministic function � concept class� 1 0 Goal� Based on N training pairs 5/26 2/91 x.1<-1.1668 x.2<-0.823968 x.1>-1.1668 x.2>-0.823968 � X � Y � C � X �� dra wn from D pro duce a i i i � 1 1 0 0 classi�er C � X � � f � � � g 0/12 5/14 2/8 0/83 x.1<-1.07831 � x.1>-1.07831 Goal� c ho ose C to ha v e lo w generalization error 1 1 � � R � C � � P � C � X � � � C � X �� 1/5 4/9 D � E �� � D � � � X � � � C � X �� C � � � �
� � � � Stanford Univ ersit y Decem b er �� ���� Bo osting� � Stanford Univ ersit y Decem b er �� ���� Bo osting� � Decision Boundary� T ree Bagging and Bo osting Classi�cation trees can b e simple� but often pro duce noisy �bush y� or w eak �stun ted� classi�ers� 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 � Bagging �Breiman� ������ Fit man y large 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 trees to b o otstrap�resampled v ersions of the 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 training data� and classify b y ma jorit y v ote� 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 � Bo osting �F reund � Shapire� ������ Fit man y 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 large or small trees to rew eigh ted v ersions of 1 1 the training data� Classify b y w eigh ted ma jorit y v ote� In general Bo osting � Bagging � Single T ree� �� TM When the nested spheres are in R � CAR T �AdaBo ost � � � b est o��the�shelf classi�er in the pro duces a rather noisy and inaccurate rule � w orld� � Leo Breiman� NIPS w orkshop� ����� C � X �� with error rates around ���� � � � �
� � � � Stanford Univ ersit y Decem b er �� ���� Bo osting� � Stanford Univ ersit y Decem b er �� ���� Bo osting� � Bagging and Bo osting Final classifier sign[ Σα b f b (x)] weighted sample f B (x) weighted sample f 3 (x) f 2 (x) weighted sample �� ���� p oin ts from Nested Spheres in R � Ba y es training sample f 1 (x) error rate is ��� The w eigh ting in b o osting can b e ac hiev ed b y T rees are gro wn Best First without pruning� w eigh ted imp ortance sampling� Leftmost iteration is a single tree� � � � �
Recommend
More recommend