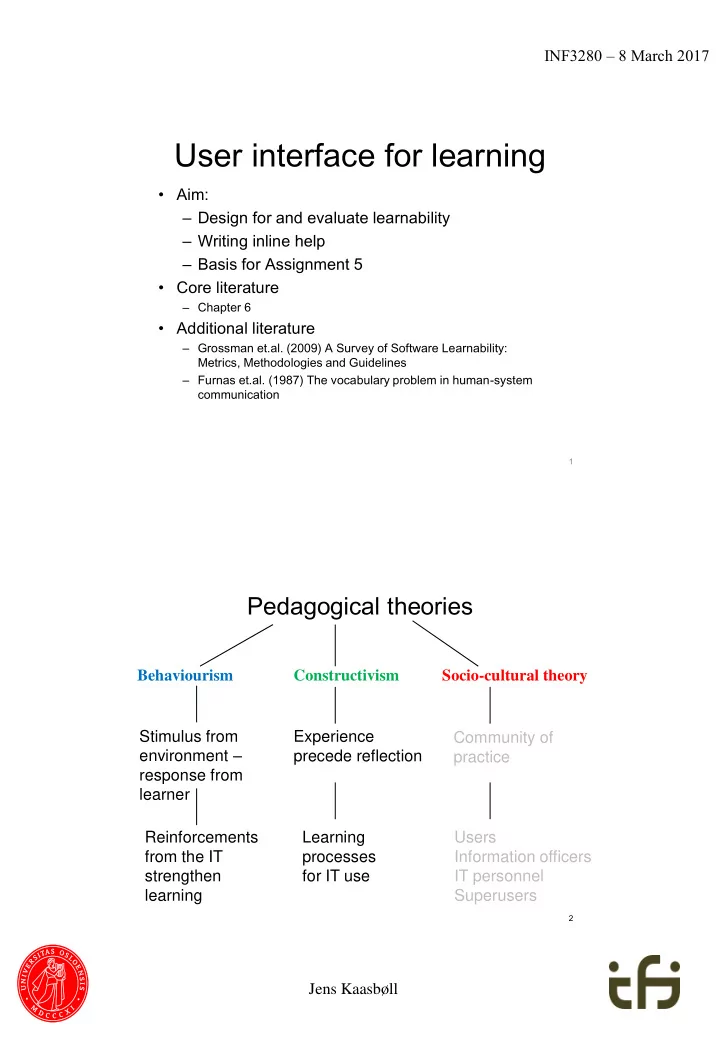

INF3280 – 8 March 2017 User interface for learning • Aim: – Design for and evaluate learnability – Writing inline help – Basis for Assignment 5 • Core literature – Chapter 6 • Additional literature – Grossman et.al. (2009) A Survey of Software Learnability: Metrics, Methodologies and Guidelines – Furnas et.al. (1987) The vocabulary problem in human-system communication 1 Pedagogical theories Behaviourism Constructivism Socio-cultural theory Stimulus from Experience Community of environment – precede reflection practice response from learner Reinforcements Learning Users from the IT processes Information officers strengthen for IT use IT personnel learning Superusers 2 Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 – 8 March 2017 Behaviourism – 1920 • Observable behaviour – No concern for thinking • The learning cycle – Stimulus from the environment • Login: • Password: – Response from the learner • Writing user name and password • If this response differed from previous ones and the new response is repeated, learning has occurred – Reinforcement from the environment • Other windows appear 3 Behaviourism Reinforcement and learning Reinforc orcem emen ent strengthens learning Punishm hment nt weakens learning A wanted event or the removal of an Unwanted event or removal of a wanted unwanted one one Wanted • > prnt rapport.text Output which we wanted ILLEGAL USER ACTION! PRINTER DAMAGED! Removal of unwanted • Extinction No more error messages • Informative reinforcement – No new stimulus from the • environment You are now logged in Immediate reinforcement > cd MyFiles • < 1 second > Repeated reinforcement at • variable ratio or interval 4 Behaviourism Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 – 8 March 2017 Design gn for learnabi nability ity kidosphere.com • Some computer applications are complex – Additional help needed 5 Inline help in the program • Responding to users’ current problem Guidance 1a. Imitate Not a tutorial primarily designed for teaching • Users want to do do, not read Minimal distraction from task 1b. Repeat and functionality 2a. Compare task Short output 2c. Compare input and Recognizable language Recognizable graphics 2b. Compare model and experience 2d. Conceptualise 6 Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 – 8 March 2017 Help – Types Inline ine – Cont ntext ext-sen sensi siti tive ve Cont ntext ext-free free • Tooltip • Help system • Wizard • Web • Help button Search if you don’t know • System-initiated where to go Help where you are 7 Balloon help • Appeared immediately on mouseover • Cluttered the screen 8 Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 – 8 March 2017 Tooltip – Screentip • Help where the user is at the moment • No need for search 1 s delay Avoiding distraction Minimal manual? Instructions? c Functional model? Structural model? 9 Wizards carrying out the operations Minimal manual? Instructions? c Functional model? Structural model? 10 Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 – 8 March 2017 Help button Document Minimal Manual? Instructions? c Functional model? Structural model? 11 System initiated – Clippy • Annoying • Irrelevant • Too trivial help 12 Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 – 8 March 2017 Help system 1. Click Help in the application 2. Wait for the help system to start 3. Select software 4. Search 5. Select hit Minimal Manual? Instructions? c Functional model? Structural model? 13 1a. Imitate Searchable Context-sensitive/free context-free help video Wizard 1b. Repeat and functionality 2a. Compare task output 2c. Compare input and Tooltip Tooltip 2b. Compare model and experience 2d. Conceptualise Context-sensitive/free document help 14 Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 – 8 March 2017 Qualities of IT applications • Learnability – From novice to expert user • Time from first encounter to use • Time before understanding what the application can be used for • Time before understanding how the representation system of the information enables and restricts operations – Intermittent users • Time to recall • Usability – Efficiency • Time and effort used to achieve the result – Satisfaction • Comfort and acceptability amongst users • Usefulness – Effectiveness – The quality of the result achieved 15 Qualitie ities s of help • Way of accessing the help One click Separate search system • Contents – scaffold for Skill Understanding 16 Jens Kaasbøll
Recommend
More recommend