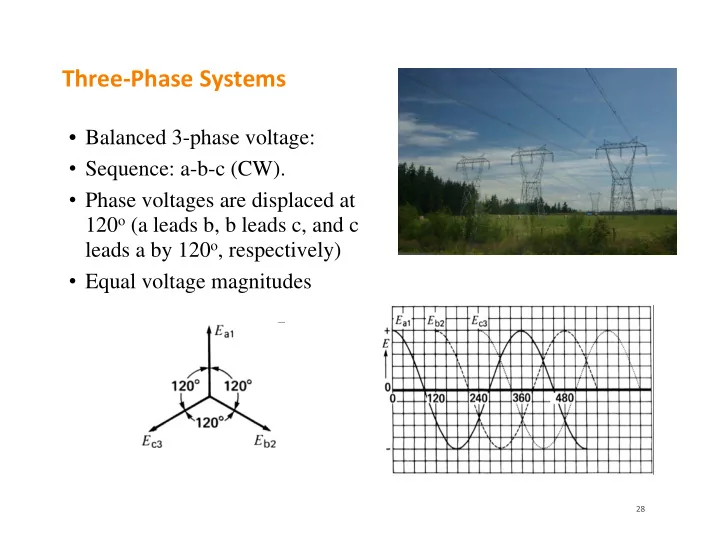

Three ‐ Phase Systems • Balanced 3-phase voltage: • Sequence: a-b-c (CW). • Phase voltages are displaced at 120 o (a leads b, b leads c, and c leads a by 120 o , respectively) • Equal voltage magnitudes 28
3 ‐ Phase, 4 ‐ Wire AC System I a + I b + I c = E a1 / R + E b2 / R + E c3 / R =( E a1 + E b2 + E c3 ) / R = 0 29
3 ‐ Phase, 3 ‐ Wire AC System (balanced) • Line currents: | I a |=| I b |=| I c |= I L • Phase voltages (phase-to-neutral or line-to-neutral): Nodes 1, 2, 3 Node n |E an |=| E bn |=| E cn |= E LN • From KVL, line voltages (line-to-line or phase-to-phase): E L = 3 E LN E LN E ab = E an + E nb = E an - E bn 1.73 E LN E bc = E bn + E nc = E bn - E cn E ca = E cn + E na = E cn - E an | E ab |=| E bc |=| E ca |= E L 30
a a Wye (Y) Connection • Each line current ( I a , I b and I c ) equals the phase current. ab I L = I Z ca • Each line voltage is 3=1.73 times of b a phase voltage in magnitude b bc E L = 3 E LN ( |E ab |= 3 | E an | ) c c • Apparent power of each phase: E L | S | E I I Z LN Z L 3 • Total 3-phase apparent, active and reactive power: 2 E E 2 L L | S | 3 I 3 E I 3 I | Z | 3 L L L L Y | Z | 3 Y Z | Z | P 3 E I cos is the power factor angle Y Y 3 L L and load impedance angle Q 3 E I sin 3 L L 31
Delta ( ) Connection a • From KCL: I ca I ab I a = I ab - I ca I b = I bc - I ab b I c = I ca - I bc I bc Because three equations are symmetric, and I a leads I b , I b leads I c and I c leads I a all by 120 o , we may easily conclude: c 1. | I ab |=| I bc |=| I ca |= I Z 2. I ab leads I bc , I bc leads I ca , and I ca leads I ab by 120 o , respectively • Each line current is 3=1.73 times of a phase current in magnitude I L = 3 I Z ( |I a |= 3 | I ab | ) • Each phase voltage equals the line voltage E LN = E L 32
a Delta ( ) Connection I ca I ab • Apparent power of each phase: I b L | S | E I E Z L Z L 3 I bc • Total 3-phase apparent, active and reactive power: c 2 I 3 E 2 L L | S | 3 E 3 E I I | Z | 3 L L L L | Z | | Z Y |=| Z |/3 3 P 3 E I cos Z | Z | is the power factor angle 3 L L and load impedance angle Q 3 E I sin 3 L L • Given line voltage E L , line current I L and power factor cos , calculation of power is independent of the connection (Y / ) 33
Examples 8 ‐ 8 & 8 ‐ 11 34
Summary • Important questions: Exp 2-16, Prob 2-26, Exp 7-2&7-3, Prob 7-11, Exp 8-11 • j X L =j L , j X C = -1j/( C ) • KVL: E 14 =E 12 +E 23 +E 34 or E 41 +E 12 +E 23 +E 34 =0 • How many KVL & KCL are needed for N-node B-branch network? – Keep adding new KVL and KCL equations until no new E or I can be introduced (# of KCLs: N-1; # of KVLs: B-N+1) • Source or Load? 1. Treat the branch with the (+) terminal receiving I as the load for calculation of power S = P +j Q P >0 active load; P <0 active source; 2. Q >0 reactive load = inductive load; Q <0 reactive source = capacitive load • Do calculations with all complex numbers to avoid confusion among RMS, phasor, peak and apparent values (Saadat’s Example 2.2). – Most basic formulas S = EI * and E = IZ – Understand the power triangle for load ( S = P +j Q , Z = R +j X , E leading I by ) • Three-phase system: here to put 3 35
Recommend
More recommend