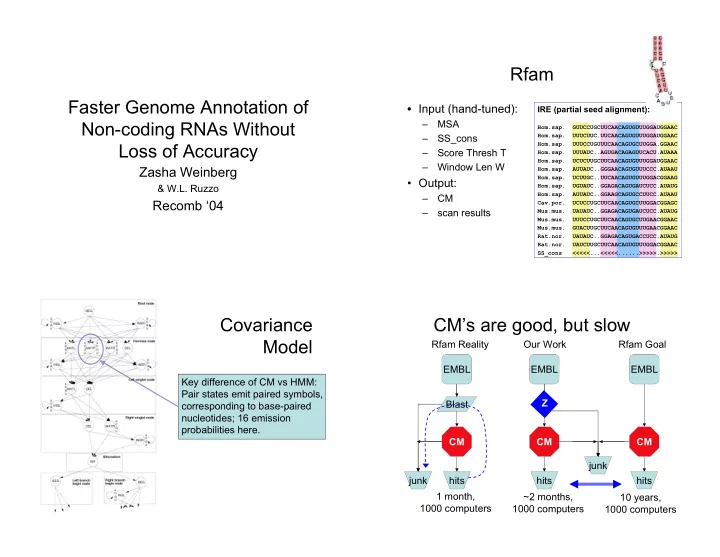

Rfam Faster Genome Annotation of • Input (hand-tuned): IRE (partial seed alignment): Non-coding RNAs Without – MSA Hom.sap. GUUCCUGCUUCAACAGUGUUUGGAUGGAAC Hom.sap. UUUCUUC.UUCAACAGUGUUUGGAUGGAAC – SS_cons Loss of Accuracy Hom.sap. UUUCCUGUUUCAACAGUGCUUGGA.GGAAC – Score Thresh T Hom.sap. UUUAUC..AGUGACAGAGUUCACU.AUAAA Hom.sap. UCUCUUGCUUCAACAGUGUUUGGAUGGAAC – Window Len W Zasha Weinberg Hom.sap. AUUAUC..GGGAACAGUGUUUCCC.AUAAU Hom.sap. UCUUGC..UUCAACAGUGUUUGGACGGAAG • Output: & W.L. Ruzzo Hom.sap. UGUAUC..GGAGACAGUGAUCUCC.AUAUG Hom.sap. AUUAUC..GGAAGCAGUGCCUUCC.AUAAU – CM Recomb ‘04 Cav.por. UCUCCUGCUUCAACAGUGCUUGGACGGAGC – scan results Mus.mus. UAUAUC..GGAGACAGUGAUCUCC.AUAUG Mus.mus. UUUCCUGCUUCAACAGUGCUUGAACGGAAC Mus.mus. GUACUUGCUUCAACAGUGUUUGAACGGAAC Rat.nor. UAUAUC..GGAGACAGUGACCUCC.AUAUG Rat.nor. UAUCUUGCUUCAACAGUGUUUGGACGGAAC SS_cons <<<<<...<<<<<......>>>>>.>>>>> Covariance CM’s are good, but slow Model Rfam Reality Our Work Rfam Goal EMBL EMBL EMBL Key difference of CM vs HMM: Pair states emit paired symbols, Z Blast corresponding to base-paired nucleotides; 16 emission probabilities here. CM CM CM junk junk hits hits hits 1 month, ~2 months, 10 years, 1000 computers 1000 computers 1000 computers
Oversimplified CM CM to HMM (for pedagogical purposes only) A A A A C C C C A A G G G G C C U U U U G G – – – – U U – – CM HMM A A A A C C C C A A G G G G C C U U U U G G – – – – U U – – 25 emisions per state 5 emissions per state, 2x states Key Issue: 25 scores � 10 Viterbi/Forward Scoring A A A A • Path � defines transitions/emissions C C C C CM HMM G G G G • Score( � ) = product of “probabilities” on � U U U U – – – – • NB: ok if “probs” aren’t, e.g. !"# • E.g. in CM, emissions are odds ratios vs 0th- order background • For any nucleotide sequence x: • Need: log Viterbi scores CM � HMM – Viterbi-score(x) = max{ score( � ) | � emits x} – Forward-score(x) = !$ score( � ) | � emits x}
P AA � L A + R A P AC � L A + R C Key Issue: 25 scores � 10 Rigorous Filtering P AG � L A + R G P AU � L A + R U P A– � L A + R – … • Any scores satisfying the linear A A A A C C C C CM HMM inequalities give rigorous filtering G G G G U U U U – – – – NB:HMM not a prob. model Proof: • Need: log Viterbi scores CM � HMM CM Viterbi path score � “corresponding” HMM path score P AA � L A + R A P CA � L C + R A … P AC � L A + R C P CC � L C + R C … � Viterbi HMM path score P AG � L A + R G P CG � L C + R G … (even if it does not correspond to any CM path) P AU � L A + R U P CU � L C + R U … P A– � L A + R – P C– � L C + R – … Some scores filter better Optimizing filtering P UA = 1 � L U + R A • For any nucleotide sequence x: P UG = 4 � L U + R G Viterbi-score(x) = max{ score( � ) | � emits x } Forward-score(x) = !$ score( � ) | � emits x } Assuming ACGU � 25% • Expected Forward Score Option 1: Opt 1: E(L i , R i ) = ! x Forward-score(x)*Pr(x) L U = R A = R G = 2 L U + (R A + R G )/2 = 4 – NB: E is a function of L i , R i only Under 0th-order background model • Optimization: Option 2: Opt 2: Minimize E(L i , R i ) subject to score L.I.s L U = 0, R A = 1, R G = 4 L U + (R A + R G )/2 = 2.5 – This is heuristic (“forward � � Viterbi � � filter � ”) – But still rigorous because “subject to score L.I.s”
Calculating E(L i , R i ) Minimizing E(L i , R i ) E(L i , R i ) = ! x Forward-score(x)*Pr(x) • Calculate E(L i , R i ) symbolically , in terms of emission scores, so we can do • Forward-like: for every state, calculate partial derivatives for numerical convex expected score for all paths ending optimization algorithm there, easily calculated from expected � E ( L 1 , L 2 ,...) scores of predecessors & transition/ emission probabilities/scores � L i Results: buried treasures Estimated Filtering Efficiency # found # found # new (139 Rfam 4.0 families) rigorous Name BLAST filter + CM + CM Filtering # families # families Pyrococcus snoRNA 57 180 123 fraction (compact) (expanded) Iron response element 201 322 121 < 10 -4 105 110 Histone 3’ element 1004 1106 102 Purine riboswitch 69 123 54 10 -4 - 10 -2 8 17 Retron msr 11 59 48 .01 - .10 11 3 Hammerhead I 167 193 26 Hammerhead III 251 264 13 .10 - .25 2 2 U4 snRNA 283 290 7 S-box 128 131 3 .25 - .99 6 4 U6 snRNA 1462 1464 2 U5 snRNA 199 200 1 .99 - 1.0 7 3 U7 snRNA 312 313 1
Results: With additional work # with # with rigorous # new BLAST+CM filter series + CM Rfam tRNA 58609 63767 5158 Group II 5708 6039 331 intron tRNAscan- 608 729 121 SE (human) tmRNA 226 247 21 Lysine 60 71 11 riboswitch And more…
Recommend
More recommend