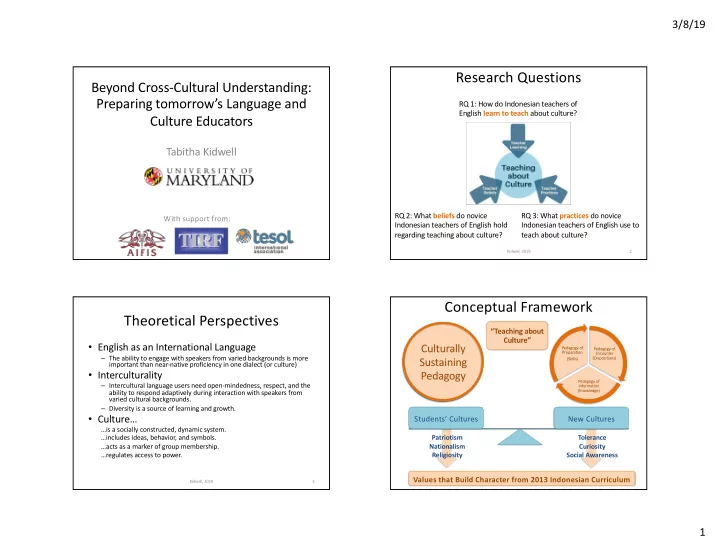

3/8/19 Research Questions Beyond Cross-Cultural Understanding: Preparing tomorrow’s Language and RQ 1: How do Indonesian teachers of English learn to teach about culture? Culture Educators Tabitha Kidwell RQ 2: What beliefs do novice RQ 3: What practices do novice With support from: Indonesian teachers of English hold Indonesian teachers of English use to regarding teaching about culture? teach about culture? Kidwell, 2019 2 Conceptual Framework Theoretical Perspectives “Teaching about Culture” • English as an International Language Culturally Pedagogy of Pedagogy of Preparation Encounter – The ability to engage with speakers from varied backgrounds is more Sustaining (Dispositions) (Skills) important than near-native proficiency in one dialect (or culture) • Interculturality Pedagogy Pedagogy of – Intercultural language users need open-mindedness, respect, and the Information ability to respond adaptively during interaction with speakers from (Knowledge) varied cultural backgrounds. – Diversity is a source of learning and growth. • Culture… Students’ Cultures New Cultures …is a socially constructed, dynamic system. …includes ideas, behavior, and symbols. Patriotism Tolerance …acts as a marker of group membership. Nationalism Curiosity …regulates access to power. Religiosity Social Awareness Values that Build Character from 2013 Indonesian Curriculum Kidwell, 2019 3 1
3/8/19 Study Design Data Collection Primarily RQ 2: Beliefs and RQ 3: Practices Primarily RQ 1: Learning Ethnographic Case Study of teacher preparation practices at Central -CJIU syllabi and course materials Java Islamic University (RQ 1: Learning) -Interviews with 20 novice teachers -33 Observations at CJIU -28 Interviews with 20 faculty members -64 Monthly observations & debrief interviews at 14 novice teachers’ schools Embedded case studies (Yin, 2009) of 14 CJIU alumni in their early years of teaching (RQ 2: Beliefs RQ 3: Practices) Professional Collaborative & -6 Monthly Professional Learning Community sessions Leaning Community Participatory design -Journal entries from 12 teachers -Interviews with 21 current CJIU students Kidwell, 2019 Data Analysis Findings RQ1: Learning CJIU’s English Department provides many Initial Processing & Initial Analysis Reflection Initial Selective Coding curricular opportunities to learn about culture Iterative open & axial coding Transcribe, translate, re- using inductive & deductive Draw from coding to write & read, reflect, journal about codes in Atlas.ti ( Constant revise case descriptions of & discuss data The Concept of Culture Teaching Character Building comparison method, Corbin focal NTs (Yin, 2009) & Strauss, 2014) Sociolinguistics Curriculum and Materials Development Semantics and Pragmatics Design of Language Teaching Cross Cultural Understanding Microteaching Intensive Data Cross-Case Analysis Analysis Member Checking Identify patterns among Review & re-code data set Indonesian Culture Teaching Students from Different Member checks with NT cases & seek general in Atlas.ti ; generate participants and CJIU faculty Cultural Backgrounds explanations (Yin, 2009) Citizenship selective codes (Corbin & Strauss, 2014) Multicultural Education Pancasila (National Philosophy) Foreign Cultures Language Courses (Reading, writing, speaking, listening, vocabulary, structure, translation) 7 8 Kidwell, 2019 2
3/8/19 Findings RQ1: Learning Findings RQ1: Learning Novice teachers have extra-curricular opportunities to learn about culture while at CJIU TK: If you become a teacher, do you know how to teach about culture to your Extracurricular Programs Community Programs students? Lina: Maybe… English Club Indonesia International Work Camp Annisa: Maybe through habits… (IIWC) Homestay Program Niswan: We don’t have the methods, we know it. We can’t – I couldn’t teach culture to my students. TK: So it’s like you know about culture yourself but you don’t know how to teach Other Sources Meeting people from different it? backgrounds Movies, Books, Music Niswan and others: Yes. (Interview with 8 th semester students) “Here I really learn[ed] about tolerance. In my village, there is only one religion, and there Novice Teachers had few formal opportunities to is only one stream of religion itself… But here, after coming here, I see… there are many kind of Islam itself, and we can accept one another without any clash, without any offense, learn how to TEACH about culture even not only in Islam itself, but in also other religion, too. In [this town], I learn about that.” (Harto, interview, 8-31-2017) Kidwell, 2019 10 9 Findings RQ2: Beliefs Findings RQ2: Beliefs Novice teachers could be classified within two groups Definitions of culture Locally-Oriented Globally-Oriented Locally-Oriented Globally-Oriented • Retained strong ties to their Active in CJIU community “Culture is a heritage from Culture includes “knowledge, • local, rural communities during undergrad group of people. It is influence belief, art, moral, law, habit, • Returned to that the way of life in society… It etc.” and “culture is the Accepted teaching positions • community to teach was became heritage from ensemble of stories we tell in new communities ancient to future until now. ourselves about ourselves . It • Participated in intercultural So, we as a new generation is related with how we experiences should keep this culture in our communicate with the society believe, so that the culture and surely related with will not disappear .” (Aril, language. ” (Siti journal 5) journal 5) Kidwell, 2019 11 Kidwell, 2019 12 3
3/8/19 Findings RQ2: Beliefs Findings RQ3: Practices Globally-Oriented Teachers Locally-Oriented Teachers Globally-Oriented Locally-Oriented • The goal of teaching about Teachers should teach • 11 of 41 lessons were 9 of 23 lessons were • • culture is to foster appropriate about culture. entirely linguistically entirely linguistically (Javanese) behavior. focused. • Culture is interesting and focused. • Local culture should be motivating to students. • 14 of 41 lessons connected 13 of 23 lessons connected • protected from foreign to students’ lives & local The goals of teaching about • to students’ lives & local cultures. cultures. culture are to prepare cultures. • Linguistic objectives should be • 16 of 41 lessons included students to meet foreigners • 1 lesson included cultural cultural content from an prioritized. and to help them develop content from an unfamiliar unfamiliar context. tolerance for other cultures. “At the elementary school I teach about context. • Typical practices: culture, that when you speak with your – Discussing a proverb “If students are not introduced to foreign cultures, I – Discussing texts teacher or to someone older, you need to think that will be dangerous. Because, you know, use polite Javanese or proper Indonesian . – Direct instruction they only know their own culture, and they're going I educate them little by little so that my – Contextualizing language to believe that "mine is the best." And, like, the students speak politely to someone who others are wrong… So , to learn foreign culture, practice in unfamiliar context is older than them.” (Muhay interview 10- make you more tolerant .” (Nita, PLC 3, 11-11-2017) Kidwell, 2019 14 4-2017; translated) 13 Kidwell, 2019 Implications for Teacher Educators Implications for Teacher Education programs • Integrate cultural content within your class; Novice • Programs could require intercultural experiences teachers need to see models of effective teaching (i.e. study abroad, internship with refugees, “language pal”) about culture in language classes. • Program assessments could require evidence of • Be explicit when you are modeling techniques for intercultural competence on program integrating cultural content. assessments. • Go beyond models of culture à Also discuss how to • Program assessments could require evidence of use these models with students à Also discuss ability to teach about culture. models for teaching about culture. • Program curriculum could include a course on Methods of teaching about culture in addition to (or within) Cross cultural understanding or Multicultural education courses. (from ACTFL standards, 2015) Kidwell, 2018 17 Kidwell, 2018 4
Recommend
More recommend