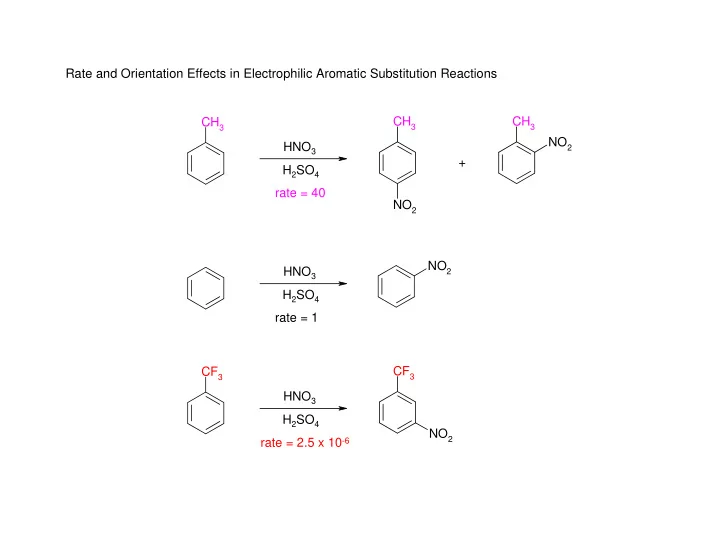

Rate and Orientation Effects in Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 NO 2 HNO 3 + H 2 SO 4 rate = 40 NO 2 NO 2 HNO 3 H 2 SO 4 rate = 1 CF 3 CF 3 HNO 3 H 2 SO 4 NO 2 rate = 2.5 x 10 -6
Activating Substituents Deactivating Substituents ortho , para meta ortho , para .. .. NH 2 .. : X –C � N .. O O OH .. S OH O O O .. N R OR OH , H .. O OR .. R –R O + N O X X X
Nitration of anisole The resonance donating effects of the OCH 3 substituent make it an activating substituent .. . O . + + O O O + .. - - .. . . - • The aromatic ring is more nucleophilic than benzene • The resonance delocalization of the electron density of the aromatic ring is lumpy: � There is greater electron density at the o - and p - carbons
Nitration of anisole: ortho -attack of nitronium ion O + O O O O H H H H + NO 2 NO 2 NO 2 NO 2 + O + O N + +
Nitration of anisole: ortho -attack of nitronium ion O + O O O O H H H H + NO 2 NO 2 NO 2 NO 2 + O + O N + + meta -attack of nitronium ion O O O O + + + O + O N H H H + NO 2 NO 2 NO 2
Nitration of anisole: ortho -attack of nitronium ion O + O O O O H H H H + NO 2 NO 2 NO 2 NO 2 + O + O N + + meta -attack of nitronium ion O O O O + + + O + O N H H H + NO 2 NO 2 NO 2 para -attack of nitronium ion O + O O O O + + O + O N + + H NO 2 H NO 2 H NO 2 H NO 2
Nitration of anisole: ortho -attack of nitronium ion O + O O O O H H H H + NO 2 NO 2 NO 2 NO 2 + O + O N + + meta -attack of nitronium ion all octets filled! O O O O + + + O + O N H H H + NO 2 NO 2 NO 2 para -attack of nitronium ion O + O O O O + + O + O N + + H NO 2 H NO 2 H NO 2 H NO 2 all octets filled!
m -arenium ion o - and p -arenium ions NO 2 O 2 N NO 2 + CH 3 O CH 3 O CH 3 O + + NO 2 CH 3 O
Where would the E vs reaction coordinate diagram of the nitration of benzene be placed relative to this one? m -arenium ion o - and p -arenium ions NO 2 O 2 N NO 2 + CH 3 O CH 3 O CH 3 O + + NO 2 CH 3 O
Nitration of nitrobenzene The inductive and resonance withdrawing effects of the NO 2 substituent make it a deactivating substituent O O O O O O O O N N N N + + + + + + + • The aromatic ring is less nucleophilic than benzene • The resonance delocalization of the electron density of the aromatic ring is lumpy: � There is greater electron density at the m - carbons
Nitration of nitrobenzene: ortho -attack of nitronium ion O O O O O O O O N + N N N + + + H H H + NO 2 + O NO 2 NO 2 + O N + +
Nitration of nitrobenzene: ortho -attack of nitronium ion O O O O O O O O N + N N N + + + H H H + NO 2 + O NO 2 NO 2 + O N + + meta -attack of nitronium ion O O O O O O O O N N N N + + + + + + + O + O N H H H + NO 2 NO 2 NO 2
Nitration of nitrobenzene: ortho -attack of nitronium ion O O O O O O O O N + N N N + + + H H H + NO 2 + O NO 2 NO 2 + O N + + meta -attack of nitronium ion O O O O O O O O N N N N + + + + + + + O + O N H H H + NO 2 NO 2 NO 2 para -attack of nitronium ion O O O O O O O O N N N + N + + + + + O + O N + + H NO 2 H NO 2 H NO 2
Nitration of nitrobenzene: ortho -attack of nitronium ion O O O O O O O O N + N N N + + + H H H + NO 2 + O NO 2 NO 2 + O N + + � meta -attack of nitronium ion O O O O O O O O N N N N + + + + + + + O + O N H H H + NO 2 NO 2 NO 2 para -attack of nitronium ion O O O O O O O O N N N + N + + + + + O + O N + + H NO 2 H NO 2 H NO 2 �
o - and p -arenium ions m -arenium ion NO 2 O 2 N NO 2 + O 2 N O 2 N O 2 N + + NO 2 O 2 N
Where would the E vs reaction coordinate diagram of the nitration of benzene be placed relative to this one? o - and p -arenium ions m -arenium ion NO 2 O 2 N NO 2 + O 2 N O 2 N O 2 N + + NO 2 O 2 N
Use the same method of analysis to explain why the Cl substituent is a deactivating, o -, p -directing substituent: 1:1 Cl Cl Cl HNO 3 : H 2 SO 4 + NO 2 O 2 N
Recommend
More recommend