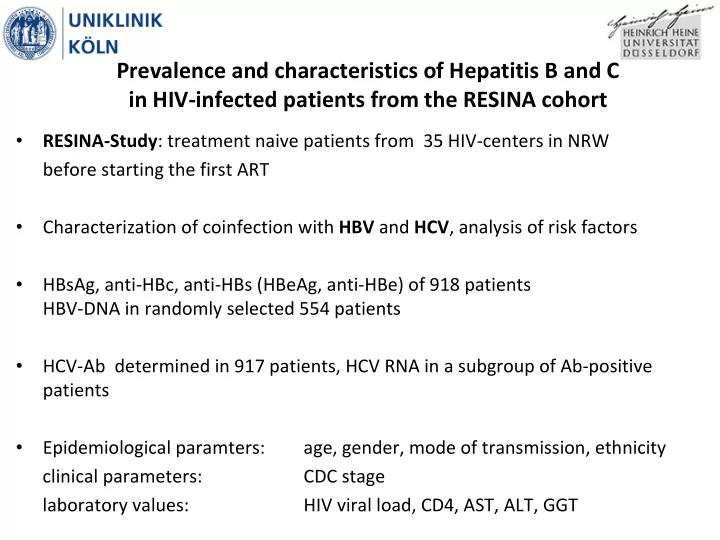

Prevalence and characteristics of Hepatitis B and C in HIV ‐ infected patients from the RESINA cohort • RESINA ‐ Study : treatment naive patients from 35 HIV ‐ centers in NRW before starting the first ART • Characterization of coinfection with HBV and HCV , analysis of risk factors • HBsAg, anti ‐ HBc, anti ‐ HBs (HBeAg, anti ‐ HBe) of 918 patients HBV ‐ DNA in randomly selected 554 patients • HCV ‐ Ab determined in 917 patients, HCV RNA in a subgroup of Ab ‐ positive patients • Epidemiological paramters: age, gender, mode of transmission, ethnicity clinical parameters: CDC stage laboratory values: HIV viral load, CD4, AST, ALT, GGT
HBV ‐ Screening AREVIR ‐ meeting Bonn 2010
Düsseldorf and Cologne n=517 and n=401
Analysis of HBV ‐ DNA n=554 Occult HBV infection (OHBV): HBsAg negative and HBV-DNA positive HBV-DNA pos HBV-DNA neg Total HBsAg pos 3,2 % (18) 1,1 % (6) 4,3 % (24) HBsAg neg 2,9 % (16) --- --- Total 6,1 % (34) --- 7,2 % (40) Anti-HBc + Anti-HBc + Anti-HBc - Anti-HBc - Total Total Anti-HBs + Anti-HBs - Anti-HBs + Anti-HBs - Anti-HBc + Anti-HBc - OHBV 7 3 2 4 10 6 % 4,3 6,4 3,8 1,9 4,6 1,9 (7 / 164) (3 / 47) (2/ 52) (4 / 213) (10 / 217) (6 / 313)
HBV ‐ und HCV coinfections: risk factors and observations • HBV ‐ DNA: significant: higher ALT and AST trend: more MSM, caucasian and CDC ‐ C • OHBV: no parameter showed significant correlation
HBV ‐ und HCV coinfections: risk factors and observations Isolated antiHBc
HBV resistance analysis • 30 / 34 samples sequenced (genotypes): 18 x A 7 x D 3 x G 1 x C 1 x Es • Sequences differing from wild ‐ type in 19 / 30 • 5 patients with mutations conferring to drug resistance I169T, L180M, V191IV, M204V 4 / 13 in patients with OHBV, 1 / 17 in HBsAg positive patients
German HBV ‐ incidence (RKI) NRW HBV ‐ prevalence (RESINA)
HCV ‐ Screening
HBV ‐ und HCV coinfections: risk factors and observations Positive HCV serostatus
HIV primary drug resistance (PDR) • 8,3% (76 / 912) 46% NRTI (35), 47% NNRTI (36), 18% PI (14) • HIV ‐ PDR was significantly correlated with any parameter of active HBV infection (HBV ‐ DNA, HBsAg, OHBV) anti ‐ HCV • patients with HIV ‐ PDR were significantly older more MSM more IVDU caucasian origin showed higher ALT and GGT
CONCLUSIONS • HBV and HCV are frequent co ‐ infections in treatment ‐ naive HIV patients • HCV co ‐ infection influences HIV replication • OHBV constitutes a major proportion of all chronic HBV infections • HIV ‐ PDR associated with active HBV infection
THANK YOU !!! • Frank Clemens Wilhelm • Mark Oette • Rolf Kaiser • Bastian Beggel • Melanie Balduin • Finja Schweitzer • Jens Verheyen • Ortwin Adams • Dieter Häussinger
HBV resistance analysis No. Genotype HBV-polymerase mutations HBsAg mutations 1 A N131DN, I187L, V191IV, L217R, Q101H, K122KR, A159V, S167L, V168AV, W182*W, P217LP, L229M F220L S119PST, F122L, Q130P, L132M, I169T , 2 D L109LQ, T125M, F161L, P203A M171V, A211G 3 E V191IV S167LS, W182*W, L226*L 4 G V142T , L180M, M204V , L229F M133I, Y134H , I195M, C221F 5 D H126R, Y135H, V173L, L180M, L97P, T118A, G130E, E164G, I195M , S204N, S207R M204V , Q215S 6 A L140I N131K 7 A R138K, S219A G130N , S210R 8 A R138KR, S219A G130DGNS , S210R 9 C R153QR, S223A, I224V G145GR , S210N
HBV ‐ Screening and HCV seroprevalence
Recommend
More recommend