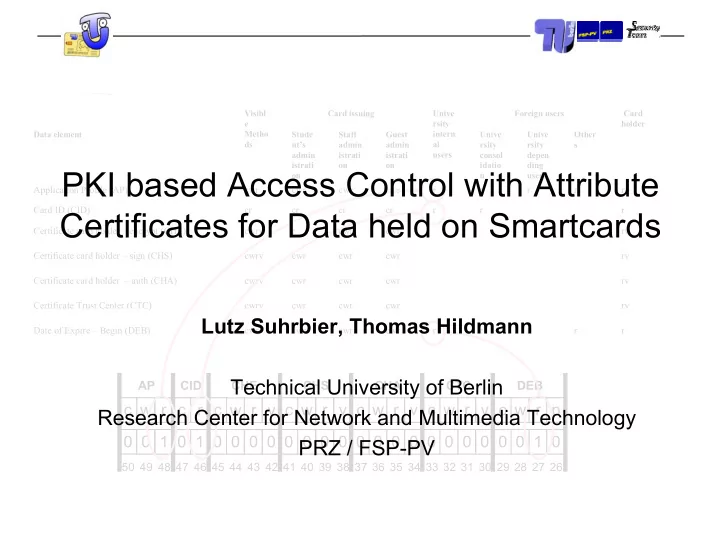

Visibl Card issuing Unive Foreign users Card e rsity holder Metho intern Data element Stude Staff Guest Unive Unive Other ds al nt’s admin admin rsity rsity s admin istrati istrati users consol depen istrati on on idatio ding PKI based Access Control with Attribute on n users Application Profile (AP) cwr cwr cwr cwr r r r r r Card ID (CID) cr cr cr cr r r r Certificates for Data held on Smartcards Certificate card holder – encrypt (CHE) cwrv r cwr cwr rv Certificate card holder – sign (CHS) cwrv cwr cwr cwr rv Certificate card holder – auth (CHA) cwrv cwr cwr cwr rv Certificate Trust Center (CTC) cwrv cwr cwr cwr rv Lutz Suhrbier, Thomas Hildmann Date of Expire – Begin (DEB) cwr cwr cwr cwr r r r r r Date of Expire – End (DEE) cwr cwr cwr cwr r r r r r List of DES-Keys (DES) cw cw cw cw Technical University of Berlin AP CID CHE CHS CHA CTC DEB Card holder identification (OM) cr cr cr cr r r r c w r c r c w r v c w r v c w r v c w r v c w r p Research Center for Network and Multimedia Technology Status-group (PS) cwr cwr cwr cwr r r r Personal Identification Number (PIN) cw c c c w 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 PRZ / FSP-PV PIN Failure counter (FVZ) c c c c 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 Secret Key – encrypt (SKE) cwd cw cw d
Content • Current problems – State of the art • An approach – Attribute certificates – Security level – Integration of security level into certificates • Implementation – Operating sequence : Data access • More advanced access control – Delegation of rights and credentials • Conclusion
Current problems • State of the art – Access control using symmetric keys (common secret) – Problem of key-exchange (old known problems) – Only flat 1:1 mapping of permissions and keys – Keeping the keys secret – A compromise of a single key compromises the whole infrastructure – Can not be used on insecure terminals because of loosing the control of the key • How to realize access control using a public-key infrastructure?
Visibl Card issuing Unive Foreign users Card e rsity holder Metho intern Data element Stude Staff Guest Unive Unive Other ds al nt’s admin admin rsity rsity s admin istrati istrati users consol depen istrati on on idatio ding on n users Application Profile (AP) cwr cwr cwr cwr r r r r r Card ID (CID) cr cr cr cr r r r Certificate card holder – encrypt (CHE) cwrv r cwr cwr rv Certificate card holder – sign (CHS) cwrv cwr cwr cwr rv Certificate card holder – auth (CHA) cwrv cwr cwr cwr rv Certificate Trust Center (CTC) cwrv cwr cwr cwr rv Date of Expire – Begin (DEB) cwr cwr cwr cwr r r r r r Date of Expire – End (DEE) cwr cwr cwr cwr r r r r r List of DES-Keys (DES) cw cw cw cw Card holder identification (OM) cr cr cr cr r r r Status-group (PS) cwr cwr cwr cwr r r r Personal Identification Number (PIN) cw c c c w PIN Failure counter (FVZ) c c c c Secret Key – encrypt (SKE) cwd cw cw d Secret Key – sign (SKS) cs c c c s Secret Key – auth (SKA) cwa cw cw cw a
Attribute certificates • Attribute certificates are just like public-key certificates with the following differences: – Instead of a public-key they contain structured data which can be used for role, group, access control or other mappings. – An attribute certificate is a binding of attribute data to a subject. – A public-key certificate is a binding of a public-key to a subject. – Both are signed by a certification authority which guarantees the correctness of the binding.
Attribute Certificates vs. Public-Key Certificates attribute�certificate Public-key�certificate data data issuer issuer validity validity subject subject public-key attribute 1 attribute 2 signature signature
We are using combined certificates attribute�certificate combined�certificate data data issuer issuer Public-key�certificate validity validity data subject subject issuer public-key attribute 1 validity attribute 2 subject attribute 1 public-key signature attribute 2 signature signature
Security level AP CID CHE CHS CHA CTC DEB c w r c r c w r v c w r v c w r v c w r v c w r p 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 FV DEE DES OM PS PIN SKE SKS SKA Z c w r p c w e c r p c w r p c w c c w d c s c w a 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01
Visibl Card issuing Unive Foreign users Card e rsity holder Metho intern Data element Stude Staff Guest Unive Unive Other ds al nt’s admin admin rsity rsity s admin istrati istrati users consol depen istrati on on idatio ding on n users Application Profile (AP) cwr cwr cwr cwr r r r r r Card ID (CID) cr cr cr cr r r r Certificate card holder – encrypt (CHE) cwrv r cwr cwr rv Certificate card holder – sign (CHS) cwrv cwr cwr cwr rv Certificate card holder – auth (CHA) cwrv cwr cwr cwr rv Certificate Trust Center (CTC) cwrv cwr cwr cwr rv Date of Expire – Begin (DEB) cwr cwr cwr cwr r r r r r Date of Expire – End (DEE) cwr cwr cwr cwr r r r r r List of DES-Keys (DES) cw cw cw cw AP CID CHE CHS CHA CTC DEB Card holder identification (OM) cr cr cr cr r r r c w r c r c w r v c w r v c w r v c w r v c w r p Status-group (PS) cwr cwr cwr cwr r r r Personal Identification Number (PIN) cw c c c w 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 PIN Failure counter (FVZ) c c c c 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 Secret Key – encrypt (SKE) cwd cw cw d Secret Key – sign (SKS) cs c c c s Secret Key – auth (SKA) cwa cw cw cw a
Integration of security level into certificates • Security level is a base64 encoded bitmap concatenated to the subject name – No extensions are needed to a standard X.509v3 certificate – Subject names are clear text fields and are human readable without any needed of additional software cn=reregistration.tu-berlin.de,�o=Technische� Universitaet Berlin,�c=DE,�sl=00000001fAngkH08
Operating sequence : Data access 1:�(req,�rcert)�=�sym_decrypt(cryptreq,�skey) 2:�verify_cert(rcert,�CTC) 3:�rpubkey =�extract_public_key(rcert) 4:�verify_data(req,�rpubkey) 5:�seclevel =�extract_seclevel(rcert) 6:�return =�execute_req(req,�seclevel) 7:�signedreturn =�sign(return,�SKA) 8:�cryptreturn =�asym_encrypt(signedreturn,�rpubkey)
1. The foreign-university requires access to data elements Foreign getData(x) University Home Smartcard University
2: Generate random number and send to foreign- university Foreign University 2:�reqestForCredential(rnd) Home Smartcard University 1:�rnd =�randomize()
3: forwarding request for credential Foreign University reqestForCredential (rnd,�getData(x)) Home Smartcard University
4: home-university is proving the permission Foreign University 3:�cred Home Smartcard University 1:�checkPermission(getData(x)) 2:�cred =�signCredential (HomeCERT,�rnd,� getData(x))
5: foreign-university is sending credential to smartcard Foreign University cred Home Smartcard University
6: validate rnd, check signature and security level, encrypt and return Foreign University 3:�cryptreturn Home Smartcard University 1:�(HomeCERT,�getData(x))�=�checkSignature(req) 2:�**�the�data�access�algorithm�as�see�before�** cryptreturn =�asym_encrypt(signedreturn,�HomeCERT)
7: foreign-university is sending the encrypted values to the home-university Foreign University cryptreturn Home Smartcard University
8: home-university decrypts and re-encrypts for foreign- university Foreign 3:�funiCryptedSignedX University Home Smartcard University 1:�signedX =�decrypt(HomePRIV,�cryptreturn) 2:�funiCryptedSignedX =�encrypt(ForeignUniCERT,� signedX)
Conclusion • Using combined attribute-/public-key-certificates enables a flexible and effective protection of data elements on smartcards. • This infrastructure was implemented successfully at Technical University of Berlin. • There are solutions for environments constituted by several organisations with different access rights.
For contact and further information / discussion • Lutz Suhrbier http://www.prz.tu-berlin.de/~lusu/ • Thomas Hildmann http://www.prz.tu-berlin.de/~hildmann/ • German Homepage of the Project Campuskarte http://campuskarte.tu-berlin.de/
Recommend
More recommend