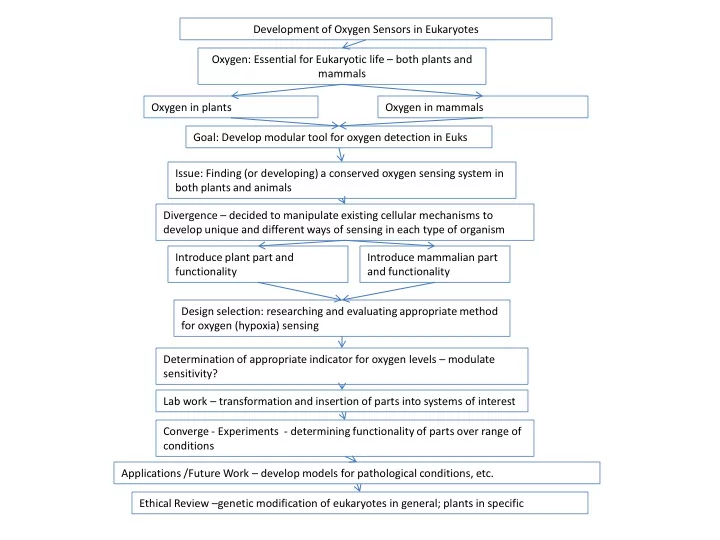

Development of Oxygen Sensors in Eukaryotes Oxygen: Essential for Eukaryotic life – both plants and mammals Oxygen in plants Oxygen in mammals Goal: Develop modular tool for oxygen detection in Euks Issue: Finding (or developing) a conserved oxygen sensing system in both plants and animals Divergence – decided to manipulate existing cellular mechanisms to develop unique and different ways of sensing in each type of organism Introduce plant part and Introduce mammalian part functionality and functionality Design selection: researching and evaluating appropriate method for oxygen (hypoxia) sensing Determination of appropriate indicator for oxygen levels – modulate sensitivity? Lab work – transformation and insertion of parts into systems of interest Converge - Experiments - determining functionality of parts over range of conditions Applications /Future Work – develop models for pathological conditions, etc. Ethical Review – genetic modification of eukaryotes in general; plants in specific
The Idea: Oxygen Sensing for Eukaryotes
Function of Oxygen in Eukaryotes • Final electron acceptor in Cellular Respiration for Aerobic Metabolism • Determines the progression of respiration • Essential for harnessing energy in the cell • Influences all energy-requiring reactions of the cell Image Source: biologycorner.com
Problems in Oxygen Availability • Waterlogged plants and • Mammalian cells – halts Anaerobic fermentation metabolism • Energy Availability • Molecular signaling cascade • Effects on the plant • Effects on the mammal: – Senescence, chlorosis, – Cell death, fermentation, stunting, death vasculogenesis/angiogenesis Image Source: Heddleston, et al. 2009
Objective: Develop Oxygen Sensitive Biological Devices • Subsequent change in cellular activity • Responsive to low oxygen levels • Modular device
Problems in Developing Modular Oxygen Sensing Devices • Incompatibility between plants and animals • Evolutionary divergence • Complex pathways • Diverse responses to the same stimulus
Analogous Devices for Oxygen Sensing in Plants and Animals
Plant Device • Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) promoter • Nuclear localization sequence, Kozak sequence • Reporter protein (fluorescent protein, luminescent protein)
Mammalian Device • Constitutive promoter (CMV) • Nuclear localization sequence, Kozak sequence • Protein domain – oxygen dependent degradation • Reporter protein (luminescent)
Divergence in Paths Plants Mammals 200 μ m Image Source: http://pested.ifas.ufl.edu/ Model : A. Thaliana Model: Immortalized human GBAM1 cell line (stem cell-like glioma cells)
Plants: Development Criteria • Why ADH promoter? – Well-characterized in literature – Up-regulated in hypoxia – Directly involved in respiration pathway – Other options less feasible Image Source: Meuser, J. 2004.
Plants: Indicating Oxygen Concentration • Choice of reporter protein: – Fluorescent proteins – easily visualized in roots – Luminescent proteins (luciferase) require luciferin substrate – Practical quantification Image Source: WikiVisual
Plants: Assembly and Insertion of Device Transforming DNA A. thaliana 3A and Process for A. transferred to grown until standard Thaliana : agrobacterium Floral dip flowering (30 assembly Agrobacterium via days) tumefaciens electroporation A. Thaliana grown in mist room pots A. Thaliana cultured on agar plates
Plants: Determining Oxygen Sensitivity • Experiments to include: – Plant response to low oxygen, varying time, concentration – Quantifying GFP production at different oxygen Image Source: biospherix.com concentrations – Model development
Mammals: Development Criteria • Why a degradation domain? – Limits undiminished signal – Mimics the activity of proteins involved in hypoxia response – Constitutively up- regulates reporter – Terminates response in normoxia – Real time hypoxia sensor Image Source: dbs.umt.edu
Mammals: Indicating Oxygen Concentration • Choice of reporter proteins – Bright, measurable signal – Luciferase (bioluminescence) - tissue penetration – Easily visualized – Luciferin in cell media Preliminary transformations using luciferase
Mammals: Assembly and Insertion of Device • Synthesized active sequence of oxygen dependent degradation (ODD) domain • 3A assembly – modified with protein fusion • For insertion into mammalian cells – transfection by electroporation Confirmation of Parts for assembly -
Mammals: Determining Oxygen Sensitivity • Experiments to include: – Incubation at various oxygen concentrations – Expression in differentiated versus proliferative cells – Model to predict reporter activity – Modeling hypoxia in 3D Image Sources: Dirks, Peter B. 2004 solid tumor cultures
Applications • Crop stabilization – food production • Physiological conditions in plants • Predictive models for cancer hypoxia • Spatial models – tissue engineering Image Source: venturebeat.com
Ethical Review • Weedy or invasive species • Reductionist philosophy • Homogenization of plant species • Uncontrolled transfer of genetic material
• Binary vector systems – Formerly, transforming agrobacterium meant recovering, manipulating, and reincorporating the tumor-inducing plasmid – In a binary vector system, the plasmid containing the DNA of interest can be manipulated and copied in the more robust E. coli – The vector can then be transferred via electroporation to an agrobacterium with virulence genes on a separate plasmid • Agrobacterium strain GV3101::pMP9 – Disarmed strain; does not produce tumors – Expresses rifampicin resistance genes – Binary vector pCB302 – Many advantages for plant transformation:Includes antibacterial (kanamycin) and herbicide (glufosinate ammonium) resistance for selection on appropriate media
Recommend
More recommend