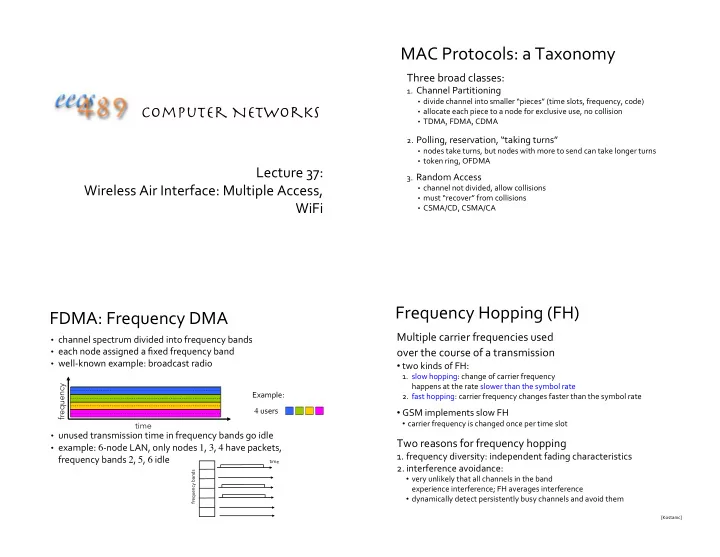

MAC'Protocols:'a'Taxonomy ' Three'broad'classes:' 1. Channel'Partitioning' • divide'channel'into'smaller'“pieces”'(time'slots,'frequency,'code)' Computer Networks • allocate'each'piece'to'a'node'for'exclusive'use,'no'collision' • TDMA,'FDMA,'CDMA' 2. Polling,'reservation,'“taking'turns”' • nodes'take'turns,'but'nodes'with'more'to'send'can'take'longer'turns' • token'ring,'OFDMA' Lecture'37:' 3. Random'Access' Wireless'Air'Interface:'Multiple'Access,' • channel'not'divided,'allow'collisions' • must'“recover”'from'collisions' WiFi' • CSMA/CD,'CSMA/CA' Frequency'Hopping'(FH)' FDMA:'Frequency'DMA' Multiple'carrier'frequencies'used' • channel'spectrum'divided'into'frequency'bands' '' • each'node'assigned'a'fixed'frequency'band' over'the'course'of'a'transmission • wellTknown'example:'broadcast'radio' • two'kinds'of'FH:' 1. slow'hopping:'change'of'carrier'frequency' happens'at'the'rate'slower'than'the'symbol'rate' frequency Example:' 2. fast'hopping:'carrier'frequency'changes'faster'than'the'symbol'rate' 4 'users' • GSM'implements'slow'FH' • carrier'frequency'is'changed'once'per'time'slot' time • unused'transmission'time'in'frequency'bands'go'idle'' Two'reasons'for'frequency'hopping' • example:' 6 Tnode'LAN,'only'nodes' 1 ,' 3 ,' 4 'have'packets,' 1. frequency'diversity:'independent'fading'characteristics' frequency'bands' 2 ,' 5 ,' 6 'idle ' t i m e ' 2. interference'avoidance:' frequency'bands' • very'unlikely'that'all'channels'in'the'band' experience'interference;'FH'averages'interference' • dynamically'detect'persistently'busy'channels'and'avoid'them' [Kostanic]'
Frequency'Diversity' TDMA:'Time'DMA' Mobile'environment'is'characterized'by'small'scale'fading' • channel'divided'into' N 'time'slots,'one'per'node' The'depth'of'signal'fade'is'a'function'of'frequency'' • access'to'channel'in'"rounds"'' • each'node'gets'fixed'length'slot'(length' = 'packet' If'two'signals'are'sufficiently'separated'in'frequency'domain' transmission'time)'in'each'round'' they'fade' independently' frequency Example:' Frequency'diversity' gain'diminishes'for' 4 'users' fast'moving'mobiles ' time • inefficient'with'light'load:'unused'slots'go'idle'' • example:' 6 Tnode'LAN,'nodes' 1 ,' 3 ,' 4 'have'packets,' time'slots' 2 ,' 5 ,' 6 'go'idle'' [Kostanic]' CDMA:'Code'DMA' CDMA'Encode/Decode' Unique'“code”'( c )'assigned'to'each'node; i.e.,'code'set' channel'output' Z i,m Z i,m = d i c m partitioning' data' d 0 = 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 d 1 = -1 bits' All'nodes'share'the'same'frequencies,'but'each'node'has' -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 sender' slot' 0 slot' 1 its'own'“chipping”'sequence'(i.e.,'code)'to'encode'data' code' 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 channel' channel' -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 output' output' Codes'are'orthogonal'or'have'low'cross'correlation' slot' 1 slot' 0 M Encoded'signal'for'bit' i 'with'node’s'code,'of'length' M :' ∑ Z i , m c m Z i,m ' = ' d i c m ;' d i : 'bit' i 'of'data;' c m : 'bit' m 'of'code,' 1 ≤ m ≤ M d i = m = 1 M 'number'of'hosts' , c m received' Decoding:'dotTproduct'of'encoded'signal'and'chipping' 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 d 0 = 1 input' -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 d 1 = -1 sequence'divided'by' ||c m || = d receiver' slot' 0 slot' 1 code' 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 channel' channel' Allows'multiple'users'to'“coexist”'and'transmit' -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 output' output' simultaneously'with'minimal'interference'(because' slot' 1 slot' 0 codes'are'orthogonal'or'have'low'cross'correlation)'
CDMA:'TwoTSender'Case ' CDMA'Decoding ' Receiver'extraction'works'because'each'bit'of'code'( c m )' is'equally'likely'to'be' -1 'or' +1 ' So'if'the'wrong'code'( c ’ m )'is'used'to'decode,' ∑ c m c ’ m 'is' likely'to'be' 0 ' If'the'right'code'is'used,'the'sign'of' ∑ c m c’ m 'determines' whether'data'is' 1 'or' -1 ' (gives'the'sign' � 'or' + )' Instead'of'lowTcross'correlation'random'code'per' sender,'can'use'orthogonal'codes'which'guarantees' ∑ c m c ’ m = 0 'if'the'wrong'code'is'used'to'decode' CDMA:'Issues ' Orthogonal'Frequency'Division' Multiplexing'(OFDM)' Code'choice:'Barker'( 802.11 ),'Walsh'(cdmaOne),'Orthogonal' Variable'Spreading'Factor'(WCDMA/UMTS) ' Modulation:'changing/modulating'the'carrier' Power'control:'powerful'signal'interferes'with'others' frequency,'phase,'and/or'amplitude'to'carry' • openTloop:'mobile'observe'received'signal,'adjust'its'own'transmit'signal,' information' works'for'TDD,'not'so'well'for'FDD' • closedTloop:'base'station'tells'mobile'to'increase/decrease'power;'requires' Multiplexing:'mixing'information'from'multiple' fast''feedback'time' ' sources'to'share'a'channel' ' RAKE'receiver:' Despite'its'name,'OFDM'is'a'modulation'method,'not' • takes'advantage'of'multipathing:'multiple'copies'of'streams'arrive'at'the' a'multiple'access'method;'but'it’s'a'multiTcarrier' receiver'as'signal'is'bounced'off'the'environment;'with'RAKE'receiver,'late' modulation'method,'i.e.,'signal'is'split'into'subT arriving'copies'used'to'help'strengthen'the'signal' signals'that'are'then'multiplexed'onto'the'channel ' • enables'soft'handoff:'a'mobile'receives'copies'from'multiple'base'stations' during'handoff' [Kwok & Lau] [Langton]'
OFDM' OFDM' Voltage FDM:'data'is'transmitted' Time Carrier'is'split'into'subTcarriers,' over'only'one'carrier' C1, …, C n ,'each'of'a'different' frequency' ' OFDM:'data'is'simultaneously' transmitted'over'several'carriers' Each'subTcarrier'is'modulated'by'data,'in'sequence,' using'a'conventional'modulation'scheme'(QAM,' Advantages'of'OFDM:' PSK,'etc.)'at'a'low,' 1/ n ,'symbol'rate' • robust'against'multiTpath'distortion:'fading'and' • besides,'fast'symbol'rates'are'more' interTsymbol'interference'(ISI)' susceptible'to'multiTpath'distortion' • robust'against'narrowTband'interference' • high'spectral'efficiency,'no'need'for'band'guards' [Langton]' [Dahlman, Keithley] FFT'and'Inverse'FFT' OFDM'Encoding' including'the'sum' C1 C2 C3 C4 I 1 1 -1 -1 1 1 1 -1 F 1 -1 -1 -1 F -1 1 -1 -1 -1 1 1 -1 T' not'to'scale' -1 -1 1 1 treat'bits'as' spectrum' [Langton]' [Langton]'
OFDM' OFDM'Encoding' IFFT' F' F' T' [UCB'EE 225 C]' [Keithley]' OFDM'Decoding' OFDM'Constellation'over'Time' FFT [Keithley]' [Keithley]'
OFDMA:'DL,'UL'Scheduling' OFD'Multiple'Access'(OFDMA)' OFDMA'symbol'number' Time' OFDM'is'a'modulation'method'for'a'single' Dynamic'OFDMA' user:'all'subTcarriers'in'a'channel'are'used' to'carry'a'single'user’s'signal' ' OFDMA'is'a'multipleTaccess'method:'it' SubTchannel' assigns'different'set'of'subTcarriers'to' different'users'the'way'CDMA'assigns' different'chipping'codes'to'different'users' ' Dynamic'OFDMA:'allocation'per'user'is' dynamically'allocated'over'time'(slotted)' � 'OFDMA'with'statistical'multiplexing' Frequency' Scalable'OFDMA:'number'of'subTcarriers' scales'with'bandwidth,'bandwidth'of'subT TDD'Transmission' carriers'is'fixed' base'station'tells'mobiles'who'will'get'to'receive'(DL'map)'' and'who'will'get'to'send'(UL'map),'and'when' Key'Features'of'WiMAX'and'LTE' WiMAX:'DL,'UL'Scheduling' IPTbased' Transmission'frame' Use'OFDMA'and'MIMO' • downTlink'subTframe:'base'station'to'node'' • users'are'allocated'a'slice'in'time'and'frequency' • uplink'subTframe:'node'to'base'station' • flexible,'dynamic'perTuser'resource'allocation' • base'station'schedules'for'uplink'and'downlink'resource'allocation' ' • resource'allocation'information'conveyed'on'a'frameTby'frame'basis' … … Provide'similar'data'rates'and'channel'widths' pream. DL- UL- DL DL DL Initial request SS #1 SS #2 SS #k MAP burst 1 burst 2 burst n maint. conn. Support'both'TDD'(time'division'duplex)'and' MAP … … FDD'(frequency'division'duplex)' downlink subframe uplink subframe TDD:'single'frequency'channel'for'uplink'and'downlink' base'station'tells'mobiles'who'will'get'to'receive'(DL'map)'' and'who'will'get'to'send'(UL'map),'and'when' DL' UL' WiMAX'specifies'mechanism'for'scheduling'of' transmission,'but'not'the'scheduling'algorithm'itself' DL' FDD' Paired'channels' UL' [Mlinarsky&Turner]'
Recommend
More recommend