FSM$Modeling State$Diagrams$(SDs)$and$Algorithmic$State$ - PDF document
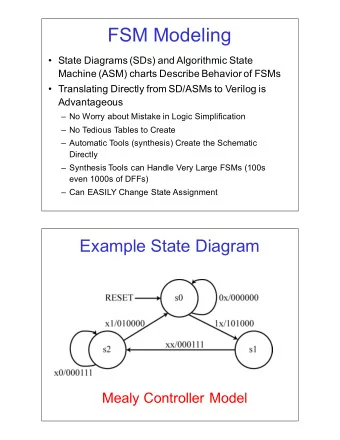
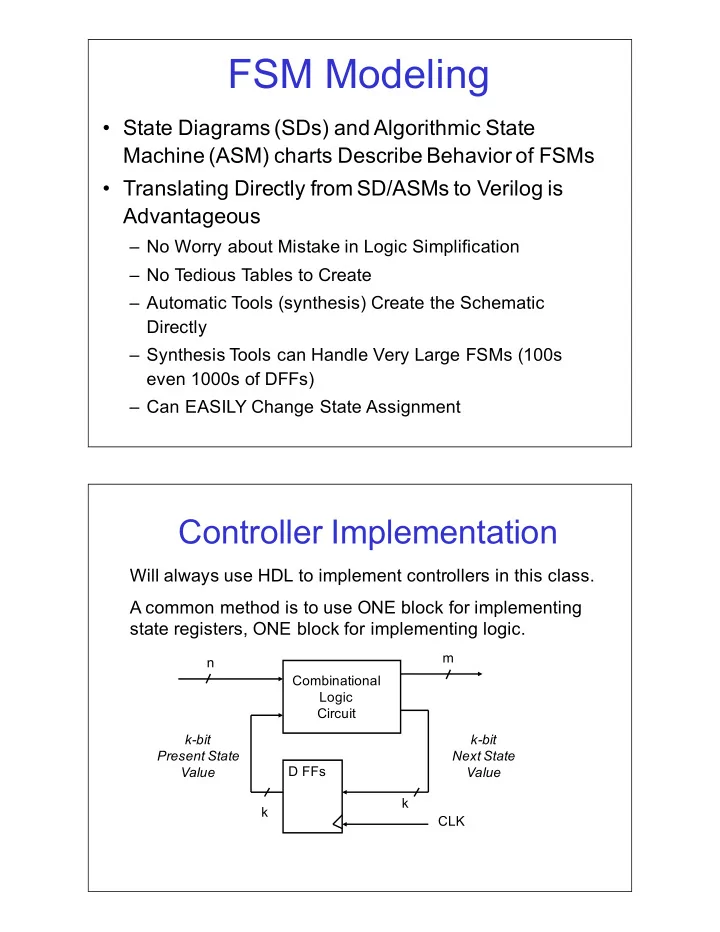
FSM$Modeling State$Diagrams$(SDs)$and$Algorithmic$State$ Machine$(ASM)$charts$Describe$Behavior$of$FSMs Translating$Directly$from$SD/ASMs$to$Verilog$is$ Advantageous No$Worry$about$Mistake$in$Logic$Simplification
FSM$Modeling • State$Diagrams$(SDs)$and$Algorithmic$State$ Machine$(ASM)$charts$Describe$Behavior$of$FSMs • Translating$Directly$from$SD/ASMs$to$Verilog$is$ Advantageous – No$Worry$about$Mistake$in$Logic$Simplification – No$Tedious$Tables$to$Create – Automatic$Tools$(synthesis)$Create$the$Schematic$ Directly – Synthesis$Tools$can$Handle$Very$Large$FSMs$(100s$ even$1000s$of$DFFs) – Can$EASILY$Change$State$Assignment Controller$Implementation Will$always$use$HDL$to$implement$controllers$in$this$class. A$common$method$is$to$use$ONE$block$for$implementing$ state$registers,$ONE$block$for$implementing$logic. m n Combinational Logic Circuit k"bit k"bit Present+State Next+State D$FFs Value Value k k CLK
Controller$Block$Diagrams Blocking/NonSblocking$Example • Assume$Initially$ A=1 ,$ B=2 ,$ C=3 • Assume$the$Following$are$Within$Blocks: B = A; B <= A; C = B + 1; C <= B + 1; Non"Blocking Blocking • When$Blocking$statements$finish$Simulation: A=1 ,$ B=1 ,$ C=2 • When$NonSBlocking$statements$finish$Simulation: A=1 ,$ B=1 ,$ C=3
Blocking/NonSblocking$Example • Consider$the$Following$Blocks: Blocking+Statements Non"Blocking+Statements begin begin A <= B; A = B; B <= A; B = A; end end • When$Blocking$statements$finish$Simulation: A and$ B both$end$up$with$the$value$originally$in B • When$NonSBlocking$statements$finish$Simulation: RHS$of$assignments$first$collected$into$temporary$storage A and$ B content$is$interchanged This$gives$the$effect$of$concurrency Synthesis$Example A D Q A Y D Q D Q B Y clk D Q B always @ (posedge clk) clk begin A <= Y; B <= A; end always @ (posedge clk) begin always @ (posedge clk) A = Y; begin B = A; B = A; end A = Y; end *example from Franzon/Smith book
Blocking/NonSblocking$Rules • Blocking$versus$NonSblocking$statements$can$Produce$ Different$Synthesized$Circuits • Use$NonSblocking$Statements$in$always$Blocks$that$model$ Sequential$Logic • Use$Blocking$Statements$in$always$Blocks$that$model$ Combinational$Logic • Do$Not$Mix$Blocking$and$NonSblocking$statements$in$a$ Single$always$Block • Reasons$are$Subtle$and$Have$to$do$with$Internal$Simulator$ Queue$Scheduling • NonSadherence$to$these$rules$can$Lead$to$Race$ Conditions$or$Inference$of$Incorrect$Logic • See$Link$to$Paper$for$Details One$ always Block$Style Single$ always Block Models$This$Part Concurrent$Assignments Model$This$Part
Verilog$Controller$with$Single$Always$ Block$(Part$1) module ramfsm_ex1 (state, addr_sel, cnt_en, ld_cnt, zero_we, set_busy, clr_busy, clk, reset, zero, cnt_eq); input clk, reset, zero, cnt_eq; output [1:0] state; //state output for debugging output addr_sel, cnt_en, ld_cnt, zero_we; output set_busy, clr_busy; reg [1:0] state; // State Encoding Here parameter S0=2'b00, S1=2'b01, S2=2'b10; Memory$Zeroing$ASM$Chart
Verilog$Controller$with$Single$Always$ Block$(Part$2) // Register and Combinational Transition logic here always @(posedge clk or posedge reset) begin if (reset == 1'b1) state<=S0; else case (state) S0: if (zero == 1'b1) state <= S1; S1: state <= S2; S2: if (cnt_eq == 1'b1) state <= S0; default: state <= S0; endcase end // Combinational output logic here assign set_busy = (state==S0 && zero==1'b1) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0; assign ld_cnt = (state==S1) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0; assign addr_sel = (state==S2) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0; assign zero_we = (state==S2) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0; assign cnt_en = (state==S2) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0; assign clr_busy = (state==S2 && cnt_eq==1'b1) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0; endmodule One$Process$VHDL$Version library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; -- FSM entity for RAM Zero example entity ramfsm is port ( clk, reset: in std_logic; zero, cnt_eq: in std_logic; -- control inputs set_busy, clr_busy: out std_logic; -- control outputs addr_sel, cnt_en, ld_cnt, zero_we: out std_logic; state: out std_logic_vector(1 downto 0) -- state out for debugging ); end ramfsm; architecture a of ramfsm is signal pstate: std_logic_vector(1 downto 0); -- state encoding CONSTANT S0 : std_logic_vector(1 downto 0) := "00"; CONSTANT S1 : std_logic_vector(1 downto 0) := "01"; CONSTANT S2 : std_logic_vector(1 downto 0) := "10";
One$Process$VHDL$Version$(cont) begin state <= pstate; -- look at present state for debugging purposes stateff:process(clk) -- process has state transistions ONLY begin if (reset = '1') then pstate <= S0; elsif (clk'event and clk='1') then -- rising edge of clock CASE pstate IS WHEN S0 => if (zero = '1') then pstate <= S1; end if; WHEN S1 => pstate <= S2; WHEN S2 => if (cnt_eq = '1') then pstate <= S0 ; end if; WHEN others => pstate <= S0; end case; end if; end process stateff; set_busy <= '1' when (pstate = S0 and zero = ‘1’) else '0'; ld_cnt <= '1' when (pstate = S1) else '0'; addr_sel <= '1' when (pstate = S2) else '0'; zero_we <= '1' when (pstate = S2) else '0'; cnt_en <= '1' when (pstate = S2) else '0'; clr_busy <= '1' when (pstate = S2 and cnt_eq = '1') else '0'; end a; Comments$on$One$always$Block$ Implementation • always block$defines$state$FFs$and$transitions$ between$states • Outputs$of$controller$are$separate$concurrent$ statements$outside$of$synchronous$block • Can$be$confusing$since$you$separate$out$the$FSM$ outputs$from$their$state$definitions$within$the$ CASE$statement
Two$ always Blocks$Style Second$ always Block Models$These$Parts First$ always Block Models$This$Part Controller$Verilog$with$Two$Always$Blocks$ (Part$1) module ramfsm_ex2 (pstate, addr_sel, cnt_en, ld_cnt, zero_we, set_busy, clr_busy, clk, reset, zero, cnt_eq); input clk, reset, zero, cnt_eq; output [1:0] pstate; //state output for debugging output addr_sel, cnt_en, ld_cnt, zero_we; output set_busy, clr_busy; reg addr_sel, cnt_en, ld_cnt, zero_we, set_busy, clr_busy; reg [1:0] pstate, nstate; // State Encoding Here parameter S0=2'b00, S1=2'b01, S2=2'b10; // Register logic here always @(posedge clk or posedge reset) begin if (reset == 1'b1) pstate <= S0; else pstate <= nstate; end
Controller$Verilog$with$Two$Always$Blocks$ (Part$2) // Combinational transition and output logic here always @(pstate or zero or cnt_eq) begin // We must include default values here // to avoid inferred latches set_busy = 1'b0; ld_cnt = 1'b0; clr_busy = 1'b0; addr_sel = 1'b0; zero_we = 1'b0; cnt_en = 1'b0; // Transition and output logic in case statement case (pstate) S0: if (zero == 1'b1) begin nstate = S1; set_busy = 1'b1; end else nstate = S0; Controller$Verilog$with$Two$Always$Blocks (Part$3) S1: begin nstate = S2; ld_cnt = 1'b1; end S2: begin if (cnt_eq == 1'b1) begin nstate = S0; clr_busy = 1'b1; end else nstate = S2; addr_sel = 1'b1; zero_we = 1'b1; cnt_en = 1'b1; end default: nstate = S0; endcase end endmodule
Two$Process$VHDL$Version architecture a of ramfsm is signal pstate, nstate: std_logic_vector(1 downto 0); -- state encoding CONSTANT S0 : std_logic_vector(1 downto 0) := "00"; CONSTANT S1 : std_logic_vector(1 downto 0) := "01"; CONSTANT S2 : std_logic_vector(1 downto 0) := "10"; begin state <= pstate; -- look at present state for debugging purposes stateff:process(clk) -- process has DFFs only begin if (reset = '1') then pstate <= S0; elsif (clk'event and clk='1') then pstate <= nstate; -- update pres. w. next state endif; end process stateff; Two$Process$VHDL$Version comblogic: process (zero, cnt_eq, pstate) begin -- default assignments nstate <= pstate; set_busy <= '0'; clr_busy <= '0'; ld_cnt <= '0'; addr_sel <= '0'; zero_we <= '0'; cnt_en <= '0'; CASE pstate IS WHEN S0 => if (zero = '1') then set_busy <= ‘1’; nstate <= S1; end if; WHEN S1 => ld_cnt <= ’1'; nstate <= S2; WHEN S2 => zero_we <= '1'; cnt_en <= '1' ; addr_sel <= '1’; if (cnt_eq = '1') then clr_busy <= '1’; nstate <= S0 ; end if; WHEN others => nstate <= S0; end case; end if; end process comblogic; end a;
Comments$on$Two$always$block$ Implementation • First$ always block$process$defines$only$FFs • Second$ always block$defines – State$transitions – Output$assertions – Has$natural$mapping$from$ASM$chart$to$CASE$statement • Default$assignments$to$outputs$in$Combinational$ always Block$(VHDL$Comblogic$process)$very$ important$to$Prevent$Inferred$Latches Two$ always Blocks$with$Concurrent$ Output$Logic$Style Second$ always Block Models$This$Part First$ always Block Concurrent$Assignments Models$This$Part Model$This$Part
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.