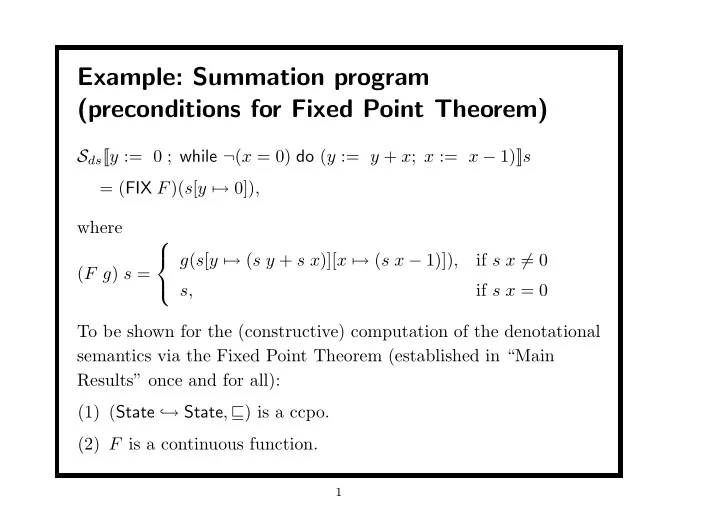

Example: Summation program (preconditions for Fixed Point Theorem) S ds [ [ y := 0 ; while ¬ ( x = 0) do ( y := y + x ; x := x − 1)] ] s = ( FIX F )( s [ y �→ 0]), where g ( s [ y �→ ( s y + s x )][ x �→ ( s x − 1)]) , if s x � = 0 ( F g ) s = if s x = 0 s, To be shown for the (constructive) computation of the denotational semantics via the Fixed Point Theorem (established in “Main Results” once and for all): (1) ( State ֒ → State , ⊑ ) is a ccpo. (2) F is a continuous function. 1
Example: Summation program (constructive fixed point computation (1)) ( g ( s [ y �→ ( s y + s x )][ x �→ ( s x − 1)]) , if s x � = 0 ( F g ) s = if s x = 0 s, Notation: s ′ = s [ y �→ ( s y + s x )][ x �→ ( s x − 1)] Hence: s ′ x = 0 ⇐ ⇒ s x = 1 ( if s x � = 0 undef , ( F 0 ⊥ ) s = undef , ( F 1 ⊥ ) s = if s x = 0 s, ( F 2 ⊥ ) s = F ( F ⊥ ) s ( ( F ⊥ ) s ′ , if s x � = 0 = if s x = 0 s, 8 if s x � = 0 and s ′ x � = 0 undef , > > < if s x � = 0 and s ′ x = 0 = s ′ , > > if s x = 0 s, : 8 if s x � = 0 and s x � = 1 undef , > > < = s ′ , if s x = 1 > > if s x = 0 s, : ( undef , if s x � = 0 and s x � = 1 = s [ y �→ ( s y + s x )][ x �→ 0] , if 0 ≤ s x ≤ 1 2
Example: Summation program (constructive fixed point computation (2)) ( g ( s [ y �→ ( s y + s x )][ x �→ ( s x − 1)]) , if s x � = 0 ( F g ) s = if s x = 0 s, ( F 0 ⊥ ) s = undef ( if s x � = 0 undef , ( F 1 ⊥ ) s = if s x = 0 s, ( undef , if s x � = 0 and s x � = 1 ( F 2 ⊥ ) s = s [ y �→ ( s y + s x )][ x �→ 0] , if 0 ≤ s x ≤ 1 . . . 8 if s x < 0 or s x > n − 1 undef , > > < ( F n ⊥ ) s = s [ y �→ ( s y + s x + ( s x − 1)+ > > . . . + 1][ x �→ 0] , if 0 ≤ s x ≤ n − 1 : ( if s x < 0 undef , ( FIX F ) s = s [ y �→ ( s y + P m k =1 k )][ x �→ 0] , if m = s x ≥ 0 3
Example: Summation program (denotational semantics: final result) S ds [ [ P ] ] s = S ds [ [ y := 0 ; while ¬ ( x = 0) do ( y := y + x ; x := x − 1)] ] s = ( FIX F )( s [ y �→ 0]), where 8 g ( s [ y �→ ( s y + s x )][ x �→ ( s x − 1)]) , if s x � = 0 < ( F g ) s = if s x = 0 s, : Morever: 8 if s x < 0 undef , < ( FIX F ) s = s [ y �→ ( s y + P m k =1 k )][ x �→ 0] , if m = s x ≥ 0 : Hence: 8 if s x < 0 undef , < S ds [ [ P ] ] s = ( FIX F )( s [ y �→ 0]) = s [ y �→ P s x k =1 k )][ x �→ 0] , if s x ≥ 0 : 4
Recommend
More recommend