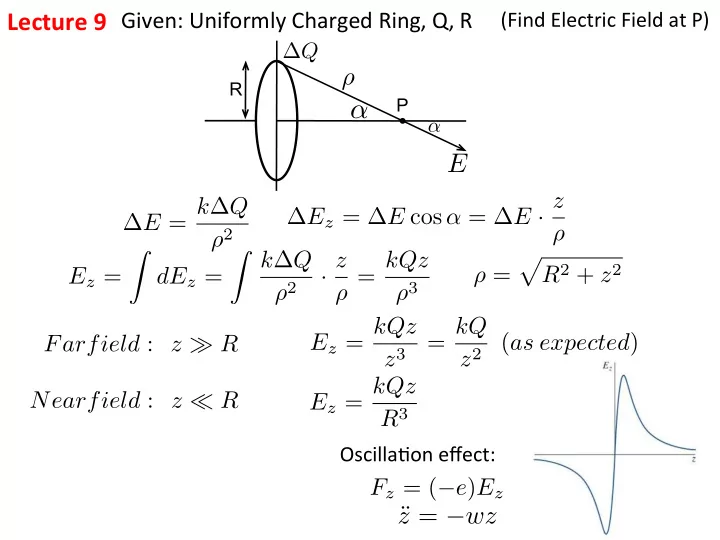

Lecture ¡9 ¡ Given: ¡Uniformly ¡Charged ¡Ring, ¡Q, ¡R ¡ (Find ¡Electric ¡Field ¡at ¡P) ¡ ∆ Q ρ R P α α E ∆ E z = ∆ E cos α = ∆ E · z ∆ E = k ∆ Q ρ 2 ρ Z k ∆ Q Z · z ρ = kQz p R 2 + z 2 E z = dE z = ρ = ρ 2 ρ 3 E z = kQz = kQ ( as expected ) Farfield : z � R z 3 z 2 E z = kQz Nearfield : z ⌧ R R 3 Oscilla@on ¡effect: ¡ F z = ( − e ) E z z = − wz ¨
Clicker ¡Ques/on ¡9-‑1 ¡ For ¡a ¡posi@vely ¡charged ¡ring, ¡determine ¡the ¡sign ¡of ¡the ¡test ¡ charge ¡placed ¡near ¡z ¡= ¡0, ¡which ¡will ¡lead ¡to ¡small ¡z ¡oscilla@ons ¡ about ¡z=0. ¡ Sign ¡of ¡Test ¡Charge ¡ 1 ¡ Posi@ve ¡charge ¡ 2 ¡ Nega@ve ¡charge ¡
Uniformly ¡Charged ¡Disk ¡ X Q disk = ∆ Q disk concentric ¡rings ¡ E ring = kQ ring z ∆ Q disk = σ 2 π r ∆ r, ρ 3 Q disk = ∆ Q disk = X X σ (2 π r ∆ r ) X k ∆ Q disk z X k σ 2 π r ∆ rz E disk = = ρ 3 ρ 3 ( k σ 2 π z ) r ∆ r X = ρ 3 Z rdr = ( k σ 2 π z ) ρ 3
Uniformly ¡charged ¡disk ¡con3nued... ¡ Z d ρ Z r Z ρ d ρ √ z 2 + R 2 � rdr ρ 2 = − 1 � I = ρ 3 = ρ 3 − − − − − − − − − − → � change of int var ρ � 0 z ρ 2 = z 2 + R 2 2 ρ d ρ = 2 rdr 1 1 � E disk = ( k � 2 ⇡ z ) z − √ z 2 + R 2 where ✏ = R 2 � 1 = ( k � 2 ⇡ ) 1 − z 2 (1 + ✏ ) 1 / 2
IQ: ¡Clicker ¡Ques@on ¡9.2 ¡ Lecture 9 Field due to uniformly charged disk Lec9-1 Evaluate E of uniformly charged disk of radius R when z >> R For a uniformly charged circular disk in the xy -plane with total charge Q , area A = ⇡ R 2 , and centered on the origin, E ( z ) = Q / A � z 1 � . ( R 2 + z 2 ) 1 / 2 2 ✏ 0 (1+ ✏ ) 1 / 2 , where ✏ = R 2 1 When z � R , [...] = 1 � z 2 . What is the term in [ · ] equal to in the small ✏ approximation? Choice 1 2 3 4 h i 1 1 � in small ✏ approximation � ✏ / 2 ✏ / 2 � ✏ ✏ (1+ ✏ ) 1 / 2
Uniformly ¡charged ¡disk ¡con3nued... ¡ 1 � E disk = ( k � 2 ⇡ ) 1 − (1 + ✏ ) 1 / 2 Far ¡Field: ¡ Near ¡Field: ¡ z ⌧ R E disk = ( k � 2 ⇡ ) h ⇣ ⌘i 1 − ✏ 1 − 2 1 z � 1 R ⇡ 1 h ✏ i = ( k � 2 ⇡ ) z 2 ✓ R 2 ◆ 1 � 1 E disk = ( k � 2 ⇡ z ) = k � 2 ⇡ 2 z 2 √ z − z 2 + R 2 = k �⇡ R 2 = k � 2 ⇡ z 2 = � = kQ 2 ✏ 0 z 2
IQ: ¡Clicker ¡Ques@on ¡9.3 ¡ Lec9-2 The field of parallel plate capacitor For z ⌧ R , E ( z ) for a charged disk of radius R in the xy -plane reduces to E ( z ) = E 1 = ( Q / A ) / (2 ✏ 0 ); close to the disk and far from its edges, the field is uniform on either side of the disk, as shown on the left in fig. 9.2. Use this fact to analyze the parallel-plate capacitor shown on the right in the figure. A. Field within the gap (region II) Choice 1 2 3 E in region II ( Q / A ) / ( ✏ 0 ) ( Q / A ) / (2 ✏ 0 ) 0 B. Field outside the gap (region I) Choice 1 2 3 E in region II ( Q / A ) / ( ✏ 0 ) ( Q / A ) / (2 ✏ 0 ) 0
Capacitor ¡field ¡within ¡the ¡gap ¡ I II III + Q − Q − � + � + � E left 2 ✏ 0 2 ✏ 0 2 ✏ 0 I II III + � + � − � E right 2 ✏ 0 2 ✏ 0 2 ✏ 0 � E resultant 0 0 ✏ 0 + Q − Q
Recommend
More recommend