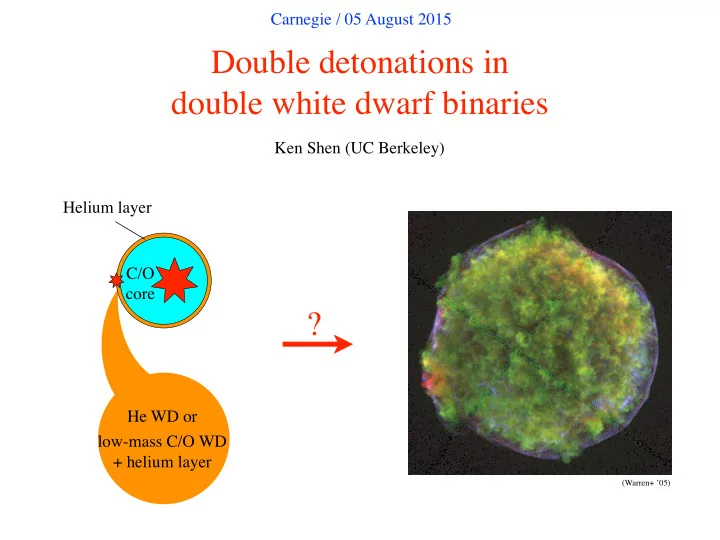

Carnegie / 05 August 2015 Double detonations in double white dwarf binaries Ken Shen (UC Berkeley) Helium layer C/O core ? He WD or ! low-mass C/O WD + helium layer (Warren+ ’05)
Double detonations: Overview 5 t = 0 . 40 s t = 0 . 70 s • Taam / Nomoto / Woosley+ / Livne+ in 1980s-1990s ! 4 4 ! 2 ! 3 ρ [10 7 g cm − 3 ] z [1000 km] ! C + O He 0 • MPA / Woosley & Kasen / etc. in 2000s-2010s ! 2 -2 ! 1 ! -4 ! -6 0 t = 1 . 00 s t = 1 . 09 s • Helium shell detonation → inward converging shock wave → carbon core detonation ! 4 ! 2 ! z [1000 km] ! 0 • Pure detonations of ~1.0 Msol C/O WDs: ! -2 decent match to SNe Ia (Shigeyama+ ’92, Sim+ ’10, Kromer+ ‘10) (Fink+ ’07) -4 -6 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 r [1000 km] r [1000 km] Ken Shen
Double detonations: Overview � # of papers mentioning “double detonation” and “white dwarf” # of papers mentioning “supernova” and “white dwarf” � � 0.08 � � � � 0.06 � � � � 0.04 � � � � 0.02 � � � (Google scholar) 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Ken Shen
He detonations via stable accretion and convection (~10 6 yr)… • 1980s-1990s (Nomoto / Woosley / et al.): stable H-burning or He MS donor (sdB/sdO) ! • Late 2000s (Bildsten, Shen, et al.): low-mass He WD donor (low mass ratio, pre-AM CVn) ! • For “large enough” He shell, convective transport is inefficient → strong turbulent fluctuations Convective He envelope C/O core He-burning layer Ken Shen
…Or He detonations via dynamical accretion (~100 s) • 2010s (Guillochon / Dan / Raskin / Pakmor): ! Dynamical processes during He + C/O or C/O + C/O WD merger ! • Especially if all double WD binaries merge (Shen ’15a) Helium WD or low-mass C/O WD + helium layer (Guillochon+ ’10) Ken Shen
Ken Shen First detonation: Does the helium ignite? Likely yes • Spontaneous initiation via Zel’dovich gradient mechanism → minimum r hotspot • Shen & Moore ’14: Small CNO pollution + complete nuclear network → Minimum r hotspot < 10-100 km, helium detonation easy to ignite r hotspot • Hotspot expectations: T ~ 10 9 K, ρ = 10 5 - 10 6 g/cm 3 hot fuel ρ , T cold fuel C/O core
Does the helium detonation propagate? Yes, even for small shells Burnt helium 1 ashes M WD = 1 . 0 M � 10 � 1 28 Si Post-shock radial 40 Ca 10 � 2 expansion X i C/O 44 Ti core 48 Cr 10 � 3 52 Fe 56 Ni Unburnt 10 � 4 helium shell (Shen & Moore ’14) 10 � 3 10 � 2 10 � 1 M env ( M � ) • Helium detonation propagates for M env > 0.004 Msol ! - 0.7 Msol C/O WD donor has ~0.01 Msol He layer ! • Smallest (first) helium detonations → 28 Si + 40 Ca + unburnt 4 He ! - No IGE ! - High velocity features? Asymmetry (accretion stream, point explosion, etc.)? Ken Shen
Second detonation: Does the C/O ignite? Likely yes 10 1.60 s • Impossible to resolve ignition in full-star 2D sim ρ 7 (burning lengthscale ~ 0.1-1 cm ; R WD ~ 10 8-9 cm) ! ! 2.6 ! 5 ! 2.2 • Shen & Bildsten ’14: zoom in on the inner 10 3 − 10 5 cm around focal point in 1D spherical symmetry ! z [1000 km] 1.9 - C/O easy to ignite via converging shocks ! 0 - O/Ne very difficult (high primary mass cutoff) ! 1.5 - Lower densities difficult (low primary mass cutoff) ! ! 1.1 ! -5 0.7 ! • Also the possibility of “edge-lit” detonation ! 0.4 - Not well-studied yet 0.0 -10 0 2 4 6 8 0 r [1000 km] (Fink+ ’10) Ken Shen
How does a surviving companion influence the remnant? • If it survives, RLOF companion (non-degenerate or WD) casts shadow Density Temperature (Shen ‘15b) Ken Shen
SNR forward shock is usually spherical (more or less) SN 1006, H α Tycho, 24 µ m LMC 0509, H α (Winkler+ ’14) (Williams+ ’13) (Warren & Hughes ’04) Kepler, H α RCW 86, H α 1997AJ....114.2664S (Blair+ ’91) (Smith ’97) • Almost certainly dominated by ISM inhomogeneities, but could mask ejecta asymmetry Ken Shen
Reverse-shocked ejecta less spherical Tycho, Fe K α Kepler, Fe K α LMC 0509, Fe L (Warren+ ’05) (Cassam-Chenaï+ ’04) (Warren & Hughes ’04) Ken Shen
Emission maps v forward shock = 5000 km/s v forward shock = 3000 km/s Density 2 integrated along line of sight, viewed at 30° Reverse-shocked γ = 1.2 SN ejecta Forward-shocked ISM γ = 5/3 (Shen ‘15b) Ken Shen
How does the ejecta influence a surviving companion WD? • If WD companion survives, will be shock heated and polluted with 56 Ni Density Temperature (Shen ‘15c) Ken Shen
How does the ejecta influence a surviving companion WD? • Hydro simulation with FLASH, spherically average and map to MESA for stellar evolution (e.g. Pan+, Shappee+) ! • q 56 = 10 17 erg/g ~ q binding ~ 10 17 erg/g (for cold 0.6 Msol WD) 10 5 Luminosity [ L � ] and T e ff [K] 0 . 6 M � , 10 4 max κ 10 3 0 . 2 M � 10 2 M V ∼ 3 . 1 0 . 6 M � , most Ni 10 removed SN 2011fe SN 1006 Kepler Tycho 1 1 10 10 2 10 3 (Shen ‘15c) Time [yr] Ken Shen
Summary • Merging double WD systems with primary WD mass > 0.9 Msol likely lead to detonation ! • Companion WD < 0.7 Msol: helium triggers double detonation ! • Companion WD > 0.7 Msol: direct carbon ignition (“violent merger”) can occur ! ! • Helium WD companion not detonated by the SN ejecta if at the proper binary separation ! ! • Supernova remnant consistent with observed SNRs ! - Forward-shocked ISM spherical ! - Reverse-shocked ejecta roughly spherical ! ! • Appearance of surviving WD companion ! - Likely bright and blue, very high proper motion ! - Probably not seen in Tycho or Kepler ! - Suggests WD companion nearly or completely disrupted prior to ignition Ken Shen
Summary He WD or H MS C/O C/O C/O C/O + + + or giant WD WD WD WD C/O WD Long-lived double Detonation during double Single degenerate degenerate merger degenerate merger Explode No shock Depending on timescale interaction No H seen Nothing seen pre-explosion Ex-companion not seen post-Ia Rates Circumstellar Okay for some, ! Depending on timescale Depending on clumping absorption but not for all SN remnant IGE production Ken Shen
Questions • Can IGE production problem be avoided with sub-Chandrasekhar detonations? ! ! ! ! ! ! • If WD companion disrupted prior to ignition, is there an observable signature (polarization, SNR appearance, early-time excess)? If WD companion survives, why don’t we see it? Ken Shen
Recommend
More recommend